Difference between revisions of "Civilisation/World Geography - South America"
(Added map of South America) |
(Brought up to date) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
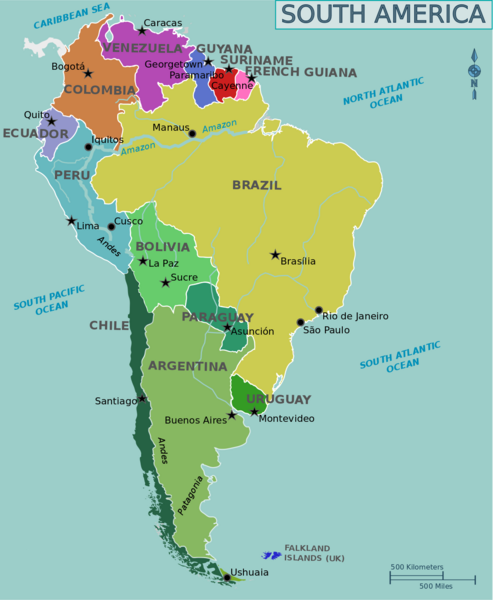
| − | [[File:Map of South America.png|none|thumb]] | + | [[File:Map of South America.png|none|thumb|alt=|487x487px]] |
== Argentina == | == Argentina == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|Aconcagua | |Aconcagua | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Argentina is the eighth-largest country in the world, the second-largest in Latin America, and the largest Spanish-speaking one. The country has its roots in Spanish | + | Argentina is the eighth-largest country in the world, the second-largest country in Latin America, and the largest Spanish-speaking one. The country has its roots in Spanish colonisation of the region beginning in 1512. Argentina rose as the successor state of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, a Spanish overseas colony founded in 1776 |
Buenos Aires is served by Ministro Pistarini International Airport | Buenos Aires is served by Ministro Pistarini International Airport | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Buenos Aires was originally named City of the Holy Trinity and Port of Saint Mary of the Fair Winds | Buenos Aires was originally named City of the Holy Trinity and Port of Saint Mary of the Fair Winds | ||
| + | |||
| + | La Boca is a district of Buenos Aires | ||
| + | |||
| + | Teatro Colon is an opera house in Buenos Aries | ||
| + | |||
| + | July 9 Avenue in Buenos Aires honours Argentina's Independence Day, 9 July 1816 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Inhabitants of Buenos Aires are known as portenos | ||
| + | |||
| + | Plaza de Mayo is a city square in Buenos Aires | ||
| + | |||
| + | Buenos Aires is served by Ministro Pistarini International Airport | ||
| + | |||
| + | MALBA is the Latin American Art Museum of Buenos Aires | ||
Ushuaia in Tierra del Fuego is the most southerly city in the world | Ushuaia in Tierra del Fuego is the most southerly city in the world | ||
| − | Perito Moreno is a glacier in Patagonia | + | Perito Moreno is a glacier in Patagonia. Named after the explorer Francisco Moreno |
Aconcagua is the highest mountain (22,800’) outside of the Himalayas, in the province of Mendoza | Aconcagua is the highest mountain (22,800’) outside of the Himalayas, in the province of Mendoza | ||
Mendoza produces 70% of the wine from Argentina | Mendoza produces 70% of the wine from Argentina | ||
| + | |||
| + | Monte Pissis is an extinct volcano | ||
| + | |||
| + | A villa miseria is a type of shanty town or slum found in Argentina | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cueva de las Manos (Spanish for ‘Cave of Hands’) is a cave and complex of rock art sites in the province of Santa Cruz | ||
Laguna del Carbon (Spanish: Coal Lagoon) is an endorheic salt lake in Argentina. At 105 metres (344 ft) below sea level, it is the lowest point of both the Western and Southern hemispheres | Laguna del Carbon (Spanish: Coal Lagoon) is an endorheic salt lake in Argentina. At 105 metres (344 ft) below sea level, it is the lowest point of both the Western and Southern hemispheres | ||
| − | Straits of Magellan | + | Straits of Magellan lie between Argentina and Tierra del Fuego |
== Bolivia == | == Bolivia == | ||
| Line 54: | Line 74: | ||
Note: La Paz is the seat of government. Sucre is the constitutional capital | Note: La Paz is the seat of government. Sucre is the constitutional capital | ||
| − | + | Bolivia is named after Simon Bolívar | |
| − | + | In 2009, a new constitution changed the country's official name to ‘Plurinational State of Bolivia’ | |
| + | |||
| + | Bolivia became a landlocked country after Chile seized the province of Litoral in the War of the Pacific in 1884. Bolivia is the largest landlocked country in the Southern Hemisphere | ||
In the late 19th century, an increase in the world price of silver brought Bolivia relative prosperity and political stability. During the early 20th century, tin replaced silver as the country's most important source of wealth | In the late 19th century, an increase in the world price of silver brought Bolivia relative prosperity and political stability. During the early 20th century, tin replaced silver as the country's most important source of wealth | ||
| − | Potosi was the major | + | La Paz is, ''de facto'', the world's highest administrative capital. Towered over by Mount Illimani |
| + | |||
| + | El Alto International Airport in La Paz is the highest international airport in the world. Until 1999, El Alto was known as John F. Kennedy | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mi Teleferico is an aerial cable car urban transit system serving the La Paz–El Alto metropolitan area | ||
| + | |||
| + | Potosi was the major supplier of silver for Spain during the period of the New World Spanish Empire | ||
The US Geological Service estimates that Bolivia has 5.4 million cubic tonnes of lithium which represents 50% – 70% of world reserves | The US Geological Service estimates that Bolivia has 5.4 million cubic tonnes of lithium which represents 50% – 70% of world reserves | ||
| Line 67: | Line 95: | ||
Tiwanaku is an important Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia. Tiwanaku is recognized by Andean scholars as one of the most important precursors to the Inca Empire | Tiwanaku is an important Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia. Tiwanaku is recognized by Andean scholars as one of the most important precursors to the Inca Empire | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Poopo is a dried-up saline lake | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sajama Lines are a network of thousands of geoglyphs | ||
| + | |||
| + | Yungas Road is a cycle route which links the city of La Paz and the Yungas region. Nicknamed the "Road of Death" | ||
== Brazil == | == Brazil == | ||
| Line 76: | Line 110: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Largest cities | |Largest cities | ||
| − | |Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Salvador, | + | |Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Brasilia, Salvador, Fortaleza |
|- | |- | ||
|Currency | |Currency | ||
| Line 84: | Line 118: | ||
|Pico da Neblina | |Pico da Neblina | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Brazil is the world's fifth largest country | + | Brazil is the world's fifth largest country by area and the seventh largest by population. It is the largest Portuguese-speaking country in the world. It borders all other South American countries except Ecuador and Chile and occupies 47% of the continent of South America. The country's economy is the seventh largest by GDP. Brazil has been the world's largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years |
The name of Brazil is shortened from Terra do Brasil "land of brazilwood" | The name of Brazil is shortened from Terra do Brasil "land of brazilwood" | ||
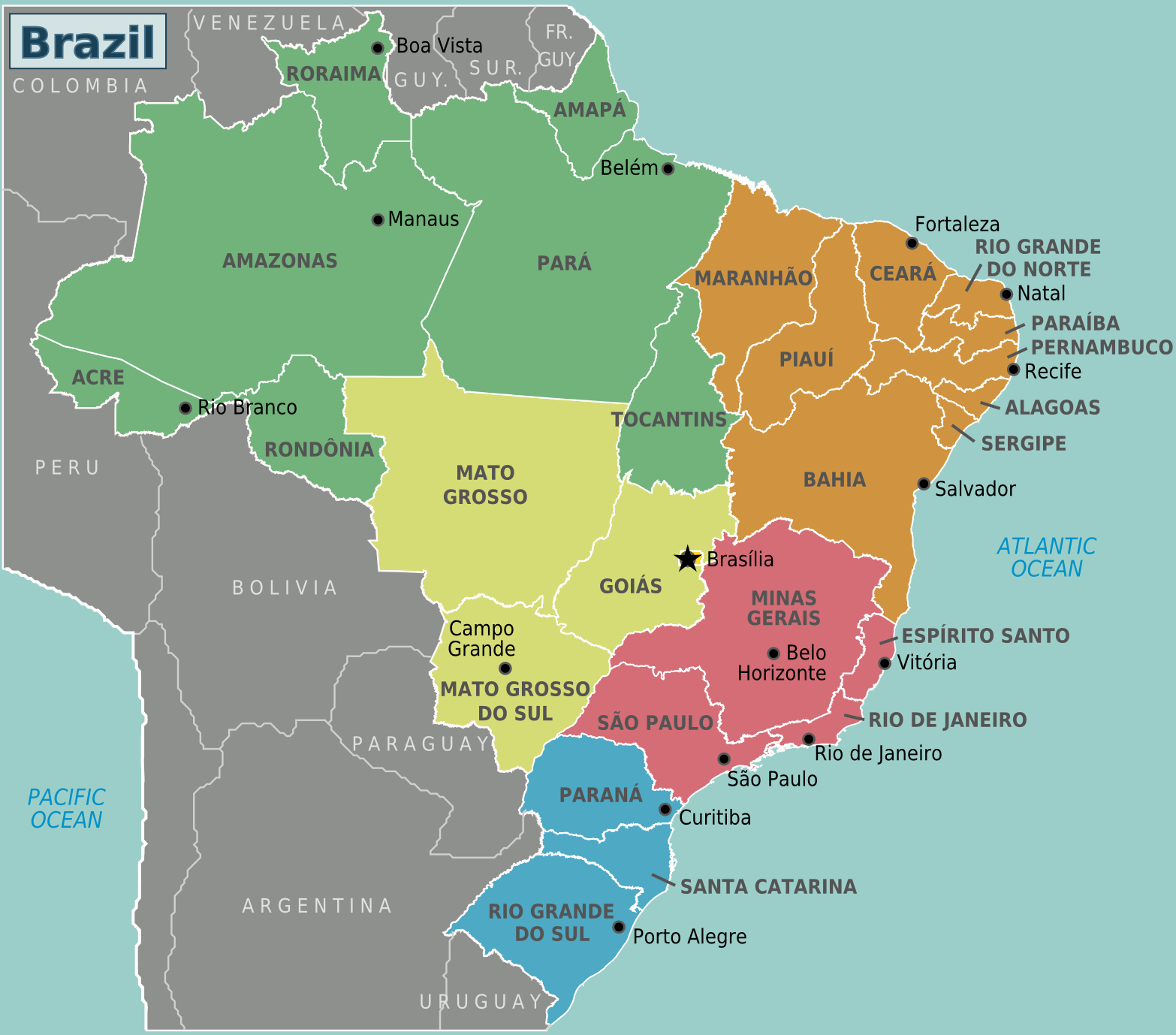
| + | [[File:Brazil regions.png|center|thumb|600x600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Largest states by area – Amazonas, Para, Mato Grosso | ||
| + | |||
| + | Largest states by population – Sao Paulo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro | ||
Rio de Janeiro was the capital of Portugal in the 19th century | Rio de Janeiro was the capital of Portugal in the 19th century | ||
| Line 101: | Line 140: | ||
Petropolis was the official capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro between 1894 and 1903 | Petropolis was the official capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro between 1894 and 1903 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carioca is a demonym used to refer to anything related to the City of Rio de Janeiro | ||
Tijuca Forest is a mountainous hand-planted rainforest in the city of Rio de Janeiro. It is the world's largest urban forest | Tijuca Forest is a mountainous hand-planted rainforest in the city of Rio de Janeiro. It is the world's largest urban forest | ||
| + | |||
| + | Petropolis was the official capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro between 1894 and 1903 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fluminense is a demonym for people indigenous to the state of Rio de Janeiro | ||
President Kubitschek ordered the construction of Brasilia, enacting a long-forgotten article of the country's republican constitutions stating that the capital should be relocated from Rio de Janeiro. Its main urban planner was Lucio Costa. Oscar Niemeyer was the chief architect of most of the public buildings and Roberto Burle Marx was the landscape designer. The city plan was based on the ideas of Le Corbusier. Brasília was built in 41 months, from 1956 to 1960, when it was officially inaugurated | President Kubitschek ordered the construction of Brasilia, enacting a long-forgotten article of the country's republican constitutions stating that the capital should be relocated from Rio de Janeiro. Its main urban planner was Lucio Costa. Oscar Niemeyer was the chief architect of most of the public buildings and Roberto Burle Marx was the landscape designer. The city plan was based on the ideas of Le Corbusier. Brasília was built in 41 months, from 1956 to 1960, when it was officially inaugurated | ||
| Line 108: | Line 153: | ||
Brasilia is laid out in the form of an airplane | Brasilia is laid out in the form of an airplane | ||
| − | The Cathedral of | + | The Cathedral of Brasilia is an expression of the architect Oscar Niemeyer. This concrete-framed hyperboloid structure, seems with its glass roof to be reaching up, open, to heaven |
| − | The Juscelino Kubitschek Bridge, also known as the JK Bridge, crosses Lake | + | The Juscelino Kubitschek Bridge, also known as the JK Bridge, crosses Lake Paranoa in Brasília. It is named for Juscelino Kubitschek de Oliveira, former president of Brazil. It was designed by architect Alexandre Chan |
| − | Sao Paulo is the largest city in | + | Sao Paulo is the largest city in the southern hemisphere and in Latin America. The name of the city honours Saint Paul of Tarsus |
Salvador is the capital of the state of Bahia. Until 1763, Salvador was the capital of Brazil | Salvador is the capital of the state of Bahia. Until 1763, Salvador was the capital of Brazil | ||
| − | + | Belo Horizonte was the second planned city in Brazil, after Teresina | |
| − | Santos is a coffee-exporting port | + | Santos is a coffee-exporting port and is the busiest container port in Latin America |
| − | Manaus is the largest city along the Amazon River | + | Manaus is the largest city along the Amazon River. It is the capital of the state of Amazonas |
Opera house in Manaus was built in 1896 | Opera house in Manaus was built in 1896 | ||
| Line 135: | Line 180: | ||
Curitiba is the capital and largest city of Parana | Curitiba is the capital and largest city of Parana | ||
| + | |||
| + | Oscar Niemeyer Museum is located in Curitiba | ||
| + | |||
| + | Belem was founded in 1616 by the Kingdom of Portugal and was the first European colony on the Amazon | ||
Brazil has largest Japanese population outside of Japan | Brazil has largest Japanese population outside of Japan | ||
Pantanal is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul | Pantanal is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cerrado is a tropical savanna ecosystem | ||
Sao Francisco is the longest river entirely in Brazil | Sao Francisco is the longest river entirely in Brazil | ||
| + | |||
| + | Brazil has the largest population of Japanese ancestry outside of Japan | ||
Brazil has the largest Arabic diaspora | Brazil has the largest Arabic diaspora | ||
| Line 165: | Line 218: | ||
Santiago was founded by conquistadors in 1541 | Santiago was founded by conquistadors in 1541 | ||
| − | Gran Torre Santiago is a 64-story tall skyscraper in Santiago. It is the tallest building in Latin America | + | Gran Torre Santiago is a 64-story tall skyscraper in Santiago. It is the tallest building in Latin America and the second tallest building in Latin America (behind Mexico's T.Op Torre 1) |
| + | |||
| + | Puente Alto is located at the south of the Great Santiago conurbation and is the most populous commune in Chile | ||
Chilean territory includes the Pacific islands of Juan Fernandez, Salas y Gomez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania | Chilean territory includes the Pacific islands of Juan Fernandez, Salas y Gomez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania | ||
| − | + | Mapocho River flows from the Andes Mountains and divides Santiago in two | |
Chile is world’s largest exporter of copper | Chile is world’s largest exporter of copper | ||
| − | + | 33 miners were rescued from the San Jose copper–gold mine north of Copiaco in 2010 | |
| + | |||
| + | Loa is the longest river in Chile and the main watercourse in the Atacama Desert | ||
| + | |||
| + | Punta Arenas (English: ‘Sandy Point’) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena | ||
| + | |||
| + | Antofagasta is a port city in northern Chile. It was part of Bolivia but was captured by Chile in 1879, triggering the War of the Pacific | ||
| + | |||
| + | Puyehue and Cordon Caulle are two coalesced volcanic edifices that form a major mountain massif in Puyehue National Park in the Andes of Ranco Province. Erupted in 2011 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nevado Ojos del Salado is a massive stratovolcano in the Andes on the Argentina-Chile border and the highest volcano in the world at 6893 metres. It is also the second highest mountain in the Western Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere and the highest in Chile | ||
| + | |||
| + | Calbuco volcano erupted in 2015 | ||
| − | + | Torres del Paine National Park is in Patagonia | |
| − | + | Cape Froward is the southernmost point in mainland South America | |
| − | + | Diego Ramirez Islands are a small group of subantarctic islands. Most southerly point of South America | |
| − | + | Juan Fernandez Islands are composed of three main volcanic islands: Robinson Crusoe, Alejandro Selkirk and Santa Clara. The islands are named after Juan Fernandez, the explorer who discovered them in the 1570s | |
| − | + | Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego is an island near the southern tip of South America from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan. The western portion of the island is in Chile, while the eastern portion is in Argentina | |
| − | Cape Horn is named after the city of Hoorn in the Netherlands | + | Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. It is named after the city of Hoorn in the Netherlands |
== Colombia == | == Colombia == | ||
| Line 194: | Line 261: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Largest cities | |Largest cities | ||
| − | |Bogota, Cali, Medellin | + | |Bogota, Cali, Medellin, Barranquilla |
|- | |- | ||
|Currency | |Currency | ||
| Line 204: | Line 271: | ||
Note: Pico Simon Bolivar has almost the same elevation as Pico Cristobal Colon | Note: Pico Simon Bolivar has almost the same elevation as Pico Cristobal Colon | ||
| − | Colombia | + | Colombia derives its name from the last name of Christopher Columbus |
| − | Bogota has been called | + | Bogota has been called the ‘Athens of South America’ |
| + | |||
| + | El Dorado International Airport serves Bogota | ||
Gold Museum (Spanish: El Museo del Oro) in Bogota displays the largest pre-Hispanic gold work collection in the world | Gold Museum (Spanish: El Museo del Oro) in Bogota displays the largest pre-Hispanic gold work collection in the world | ||
| − | + | Cartagena is a major port. It is named after the city of Cartagena in Spain | |
| − | + | Punta Gallinas is the northernmost point in mainland South America | |
| − | + | Nevado del Ruiz is a stratovolcano. Eruptions often cause massive lahars | |
| − | + | Galeras is considered the most active volcano in Colombia | |
Pico Cristobal Colon is named after Christopher Columbus | Pico Cristobal Colon is named after Christopher Columbus | ||
| + | |||
| + | Magdalena river is the principal river of Colombia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chiribiquete National Natural Park is the largest natural park and the largest tropical rainforest national park in the world | ||
== Ecuador == | == Ecuador == | ||
[[File:Flag-of-Ecuador.png|none|thumb]] | [[File:Flag-of-Ecuador.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| − | |||
Coat of arms on the flag of Ecuador features a condor over Chimborazo | Coat of arms on the flag of Ecuador features a condor over Chimborazo | ||
| Line 238: | Line 310: | ||
|Chimborazo | |Chimborazo | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Ecuador takes its name from Spanish for ‘equator’ | + | Ecuador takes its name from the Spanish for ‘equator’ |
At an elevation of 2,800 meters above sea level, Quito is the highest official capital city in the world | At an elevation of 2,800 meters above sea level, Quito is the highest official capital city in the world | ||
| − | + | Quito is located on the slopes of Pichincha volcano | |
| + | |||
| + | Guayaquil is the main port of Ecuador | ||
| + | |||
| + | Guayas River is the most important river in South America that does not flow into the Atlantic Ocean or any of its marginal seas | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cotopaxi is the world’s highest active volcano | ||
Chimborazo is a currently inactive stratovolcano located in the Andes. With a peak elevation of 6268 m, Chimborazo is the highest mountain in Ecuador. It is the highest peak in close proximity to the equator. While Chimborazo is not the highest mountain by elevation above sea level, its location along the equatorial bulge makes its summit the farthest point on the Earth's surface from the Earth's centre | Chimborazo is a currently inactive stratovolcano located in the Andes. With a peak elevation of 6268 m, Chimborazo is the highest mountain in Ecuador. It is the highest peak in close proximity to the equator. While Chimborazo is not the highest mountain by elevation above sea level, its location along the equatorial bulge makes its summit the farthest point on the Earth's surface from the Earth's centre | ||
| − | Galapagos | + | Cayambe is a volcano with permanent snow cover |
| + | [[File:Galapagos Island Names.svg|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | Galapagos | + | Galapagos Islands were discovered by the Bishop of Panama. Charles Darwin reached the islands in 1835 in HMS ''Beagle'' |
| + | |||
| + | Galapagos Islands were formerly known as the Columbus Archipelago | ||
Fernandina Island (formerly known in English as Narborough Island) is the third largest, and youngest, island of the Galapagos Islands. The island is an active shield volcano that last erupted in 2005 | Fernandina Island (formerly known in English as Narborough Island) is the third largest, and youngest, island of the Galapagos Islands. The island is an active shield volcano that last erupted in 2005 | ||
| − | Isabela Island is the largest island of the Galapagos, nearly four times larger than Santa Cruz, the next largest of the islands. | + | Isabela Island is the largest island of the Galapagos, nearly four times larger than Santa Cruz, the next largest of the islands. The island was named in honour of Queen Isabella of Spain who sponsored the voyage of Columbus. The former English name was Albemarle Island. The island is shaped like a seahorse |
| + | |||
| + | Wolf Volcano is the highest peak in the Galapagos Islands, and is situated on Isabela Island | ||
| + | |||
| + | Puerto Baquerizo Moreno is the capital of Galapagos Province. It is located on the island of San Cristobal | ||
== Guyana == | == Guyana == | ||
| Line 277: | Line 364: | ||
Georgetown was named after George III in 1812 | Georgetown was named after George III in 1812 | ||
| − | Kaieteur Falls is a waterfall on the Potaro River in Kaieteur National Park | + | Kaieteur Falls is a waterfall on the Potaro River in Kaieteur National Park and is the world's largest single drop waterfall |
Demerara River is a river in eastern Guyana | Demerara River is a river in eastern Guyana | ||
| + | |||
| + | Essequibo is the largest river in Guyana, and the largest river between the Orinoco and Amazon | ||
== Paraguay == | == Paraguay == | ||
| Line 300: | Line 389: | ||
Paraguay's indigenous language and culture, Guaraní, remains highly influential | Paraguay's indigenous language and culture, Guaraní, remains highly influential | ||
| + | |||
| + | Paraguay has ports on the Paraguay and Parana rivers that give exit to the Atlantic Ocean | ||
| + | |||
| + | The majority of Paraguay's 7 million people are mestizo | ||
Asuncion is home to nearly a third of Paraguay's population | Asuncion is home to nearly a third of Paraguay's population | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Peru == | == Peru == | ||
| Line 324: | Line 415: | ||
Lima airport named after Jorge Chavez, the first person to fly across the Alps | Lima airport named after Jorge Chavez, the first person to fly across the Alps | ||
| − | Cuzco is a city in southeastern Peru, near the Urubamba Valley (Sacred Valley) of the Andes. Cuzco was the capital of Inca Empire | + | Cuzco is a city in southeastern Peru, near the Urubamba Valley (Sacred Valley) of the Andes. Cuzco was the capital of the Inca Empire, and is said to have been originally designed in the shape of a puma |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Machu Picchu is situated on a mountain ridge above the Sacred Valley which is 80 km northwest of Cuzco and through which the Urubamba River flows. Most archaeologists believe that Machu Picchu was built as an estate for the Inca emperor Pachacuti (1438–1472). Often mistakenly referred to as the "Lost City of the Incas” | + | Machu Picchu is situated on a mountain ridge above the Sacred Valley which is 80 km northwest of Cuzco and through which the Urubamba River flows. Most archaeologists believe that Machu Picchu was built as an estate for the Inca emperor Pachacuti (1438–1472). Often mistakenly referred to as the "Lost City of the Incas”. Hiram Bingham made public the existence of the Inca citadel of Machu Picchu in 1911 with the guidance of local indigenous farmers |
Arequipa is known as the “white city”. It is the second most industrialized and commercial city of Peru | Arequipa is known as the “white city”. It is the second most industrialized and commercial city of Peru | ||
| − | Moray is a town in Peru approximately 50 km northwest of Cuzco that is noted for a large complex of unusual Inca ruins. These include | + | Moray is a town in Peru approximately 50 km northwest of Cuzco that is noted for a large complex of unusual Inca ruins. These include several enormous terraced circular depressions that were used to study the effects of different climatic conditions on crops |
Punta Parinas in Peru is the westernmost point in mainland South America | Punta Parinas in Peru is the westernmost point in mainland South America | ||
| Line 338: | Line 427: | ||
Yumbilla Falls is considered the world's fifth tallest waterfall | Yumbilla Falls is considered the world's fifth tallest waterfall | ||
| − | + | Huaynaputina is a volcano that erupted in Peru in 1600, which is the largest eruption ever recorded in South America | |
Callao is the chief seaport of Peru | Callao is the chief seaport of Peru | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chan Chan was the largest city of the pre-Columbian era in South America. It was the capital of the historical empire of the Chimor from 900 to 1470, when they were defeated and incorporated into the Inca Empire | ||
== Suriname == | == Suriname == | ||
| Line 357: | Line 448: | ||
|Julianatop | |Julianatop | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Suriname is the smallest sovereign state in South America | + | Suriname is the smallest sovereign state in South America. French Guiana, while less extensive and populous, is an overseas department of France |
In 1667 Suriname was captured by the Dutch, who governed Suriname as Dutch Guiana until 1954. Gained independence in 1975, but Dutch is still the official language | In 1667 Suriname was captured by the Dutch, who governed Suriname as Dutch Guiana until 1954. Gained independence in 1975, but Dutch is still the official language | ||
Most of the population lives on the country's north coast, in and around Paramaribo | Most of the population lives on the country's north coast, in and around Paramaribo | ||
| + | |||
| + | The forest cover is 90%, the highest of any nation in the world | ||
== Uruguay == | == Uruguay == | ||
| Line 381: | Line 474: | ||
Uruguay is officially the Eastern Republic of Uruguay. It is ranked first in Latin America in democracy, peace, lack of corruption, and quality of living | Uruguay is officially the Eastern Republic of Uruguay. It is ranked first in Latin America in democracy, peace, lack of corruption, and quality of living | ||
| − | Uruguay is geographically the second-smallest nation in South America after Suriname | + | Uruguay is geographically the second-smallest nation in South America, after Suriname |
| − | Uruguay is home to 3. | + | Uruguay is home to 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the metropolitan area of Montevideo |
Montevideo was first found by Juan Diaz De Solis in 1516 | Montevideo was first found by Juan Diaz De Solis in 1516 | ||
Montevideo is served by Carrasco International Airport | Montevideo is served by Carrasco International Airport | ||
| + | |||
| + | Punta del Este is a city and seaside resort. Known as ‘the Monaco of the South’ | ||
== Venezuela == | == Venezuela == | ||
| Line 405: | Line 500: | ||
|Pico Bolivar | |Pico Bolivar | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | Official name is Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela | ||
| + | |||
Venezuela has the world's largest oil reserves | Venezuela has the world's largest oil reserves | ||
In 1499, an expedition led by Alonso de Ojeda visited the Venezuelan coast. The stilt houses in the area of Lake Maracaibo reminded the navigator, Amerigo Vespucci, of the city of Venice, so he named the region "Veneziola" | In 1499, an expedition led by Alonso de Ojeda visited the Venezuelan coast. The stilt houses in the area of Lake Maracaibo reminded the navigator, Amerigo Vespucci, of the city of Venice, so he named the region "Veneziola" | ||
| − | + | Lake Maracaibo is the largest lake in South America. Catatumbo lightning (named after the Catatumbo River) regularly produces more lightning than any other place on the planet | |
| − | |||
| − | Lake Maracaibo is the largest lake in South America | ||
Margarita Island is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated in the Caribbean Sea | Margarita Island is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated in the Caribbean Sea | ||
Pico Humboldt is the second highest peak in Venezuela | Pico Humboldt is the second highest peak in Venezuela | ||
| + | |||
| + | Angel Falls is the world's tallest uninterrupted waterfall, with a height of 979 metres. The waterfall drops over the edge of the Auyan-tepui mountain in the Canaima National Park. Named after Jimmie Angel, an American aviator, who was the first person to fly over the falls | ||
== Overseas territories == | == Overseas territories == | ||
=== French Guiana === | === French Guiana === | ||
| − | + | French Guiana (French: Guyane) is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America | |
| + | |||
| + | A large part of the department's economy derives from the presence of the Guiana Space Centre, now the European Space Agency's primary launch site near the equator, at Kourou | ||
Devil’s Island is the smallest and northernmost island of the three Iles du Salut located off the coast of French Guiana | Devil’s Island is the smallest and northernmost island of the three Iles du Salut located off the coast of French Guiana | ||
Cayenne is the capital city | Cayenne is the capital city | ||
| + | |||
| + | 98.9% of the land territory of French Guiana is covered by forests | ||
=== Falkland Islands === | === Falkland Islands === | ||
| + | The principal islands are about 300 mi (480 km) east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 mi (1,210 km) from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula | ||
| + | |||
The islands took their English name from Falkland Sound, the channel between the two main islands, which was in turn named after Anthony Cary, 5th Viscount Falkland by Captain John Strong, who landed on the islands in 1690 | The islands took their English name from Falkland Sound, the channel between the two main islands, which was in turn named after Anthony Cary, 5th Viscount Falkland by Captain John Strong, who landed on the islands in 1690 | ||
| − | + | The archipelago consists of two main islands, West Falkland and East Falkland, and 776 smaller islands | |
| + | |||
| + | Stanley, or Port Stanley, is the capital of the Falkland Islands. It is located on the island of East Falkland. It was renamed Puerto Argentino, briefly, during the Falklands War of 1982 | ||
| − | + | In May 2022, it was announced that, as part of the Platinum Jubilee Civic Honours, Stanley would receive city status | |
| − | + | Mount Usborne is the highest point on the Falkland Islands | |
| − | Mount | + | RAF Mount Pleasant airport serves as the islands' main international airport |
| + | |||
| + | Pebble Island is situated north of West Falkland | ||
=== South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands === | === South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands === | ||
| − | British overseas territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean | + | British overseas territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean. South Georgia is by far the largest island in the territory. The South Sandwich Islands lie about 700 km southeast of South Georgia and are uninhabited |
| − | Grytviken is the principal settlement of South Georgia | + | Grytviken is the principal settlement of South Georgia and is the site of a disused whaling station |
| − | King Edward Point is the capital | + | King Edward Point is the capital and has a population of 22 |
Mount Paget on South Georgia is the highest peak in any territory under the sovereignty of the United Kingdom | Mount Paget on South Georgia is the highest peak in any territory under the sovereignty of the United Kingdom | ||
| − | Mount Asphyxia forms the summit of Zavodovski Island, northernmost of the South Sandwich Islands | + | Mount Asphyxia is a volcanic cone and forms the summit of Zavodovski Island, the northernmost of the South Sandwich Islands |
| + | |||
| + | == Physical Geography == | ||
| + | <u>Regions</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gran Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semi-arid lowland region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, Paraguay, northern Argentina and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region | ||
| + | |||
| + | Llanos is a tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela | ||
| + | |||
| + | Atlantic Forest extends along the Atlantic coast of Brazil and inland as far as Paraguay and Argentina. It was the first environment that the Portuguese colonists encountered over 500 years ago | ||
| + | |||
| + | Southern Cone is a geographic region composed of the southernmost areas of South America, south of and around the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile and Uruguay | ||
| + | |||
| + | Triple Frontier is a tri-border area along the junction of Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay, where the Iguazu and Parana rivers converge | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tres Fronteras is the Spanish name for an area of the Amazon Rainforest in the Upper Amazon region. It includes, and is named for, the tripoint where the borders of Brazil, Peru, and Colombia meet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Altiplano plateau is the world’s second-highest following the Tibetan plateau. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Mountains</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Highest mountains in South America – Aconcagua, Ojos del Salado, Monte Pissis | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Andes is the longest continental mountain range in the world, stretching for 4,300 miles through Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. The Altiplano plateau is the world’s second-highest following the Tibetan plateau | ||
| + | |||
| + | Parinacota, a composite volcano, is located on the Chilean / Bolivian frontier and is one of two volcanoes that make up the Nevados Payachata range. The other older volcano, Pomerape, is located to the northeast of Parinacota and makes up the northern part of this volcanic range | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mount Roraima includes the triple border point of Venezuela, Brazil and Guyana | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Deserts</u> |
| − | + | The Atacama Desert is located on the Pacific coast of South America (Argentina and Chile). Stretching over a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land west of the Andes Mountains, it covers an area of 105,000 km2 (41,000 sq mi) It is the driest nonpolar desert in the world | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Rivers</u> | |
| − | + | Longest rivers in South America – Amazon, Parana, Madeira, Purus, Sao Francisco | |
| − | + | Amazon River is the largest river by discharge of water in the world. The Amazon basin is the largest drainage basin in the world. Flows for 6,500 km (4,000 miles) through Brazil, Colombia and Peru | |
| − | + | The Nile has traditionally been considered longer than the Amazon, but this is disputed | |
| − | + | Pororoca is a tidal bore on the Amazon | |
Javary River is a tributary of the Amazon that forms the boundary between Brazil and Peru for more than 500 miles | Javary River is a tributary of the Amazon that forms the boundary between Brazil and Peru for more than 500 miles | ||
| Line 468: | Line 602: | ||
In its upper stretches, above the confluence of the Rio Negro, the Amazon is called Solimoes in Brazil | In its upper stretches, above the confluence of the Rio Negro, the Amazon is called Solimoes in Brazil | ||
| − | Madeira River is | + | Parana River runs through Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina |
| + | |||
| + | Madeira River is the biggest tributary of the Amazon | ||
| + | |||
| + | Orinoco River flows through Venezuela and Colombia. it is the fourth largest river in the world by discharge volume of water | ||
| + | |||
| + | Itaipu is the third largest hydroelectric dam in the world, and lies on the border of Brazil and Paraguay, on the Parana. It is a gravity dam, and was completed in 1982 | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Lakes</u> | |
| − | + | Lake Titicaca is the highest commercially navigable lake in the world, at 3,812 m above sea level. Located in the Altiplano high in the Andes on the border of Peru and Bolivia, Titicaca has a maximum depth of 281 m | |
| − | + | Uros, Amantani, and Taquile are islands in Lake Titicaca | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Seas</u> | |
Drake Passage is the body of water between the southern tip of South America at Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica | Drake Passage is the body of water between the southern tip of South America at Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica | ||
| − | Beagle Channel is a strait separating islands of the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago. The Beagle Channel, the Straits of Magellan to the north, and the open ocean Drake Passage to the south are the three navigable passages around South America between the Pacific and the Atlantic oceans. Most commercial shipping is through the Drake Passage | + | Beagle Channel is a strait separating the islands of the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago. The Beagle Channel, the Straits of Magellan to the north, and the open ocean Drake Passage to the south are the three navigable passages around South America between the Pacific and the Atlantic oceans. Most commercial shipping is through the Drake Passage |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Waterfalls</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Angel Falls in Venezuela is the world's tallest uninterrupted waterfall | ||
| + | |||
| + | Iguazu Falls are located on the border of the Brazilian state of Parana and the Argentine province of Misiones. The falls divide the river into the upper and lower Iguazu. The waterfall system consists of 275 falls, including The Devil’s Throat | ||
Latest revision as of 12:27, 14 July 2023
Argentina
Flag of Argentina was created by Manuel Belgrano in 1812. Features the Sun of May that is a national emblem of Argentina and Uruguay
| Capital | Buenos Aires |
| Largest cities | Buenos Aires, Cordoba, Rosario |
| Currency | Peso |
| Highest point | Aconcagua |
Argentina is the eighth-largest country in the world, the second-largest country in Latin America, and the largest Spanish-speaking one. The country has its roots in Spanish colonisation of the region beginning in 1512. Argentina rose as the successor state of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, a Spanish overseas colony founded in 1776
Buenos Aires is served by Ministro Pistarini International Airport
Buenos Aires is known as “Paris of the South”. Spanish seaman Juan Diaz de Solís was the first European to reach the Río de la Plata, in 1516, but his expedition was cut short by an attack in which he was killed by the native Charrúa or Guaraní tribe. The city was first founded as the 'city of Good Air' (old Spanish for 'Fair Winds’) in 1536 by a Spanish gold-seeking expedition under Pedro de Mendoza
Buenos Aires was originally named City of the Holy Trinity and Port of Saint Mary of the Fair Winds
La Boca is a district of Buenos Aires
Teatro Colon is an opera house in Buenos Aries
July 9 Avenue in Buenos Aires honours Argentina's Independence Day, 9 July 1816
Inhabitants of Buenos Aires are known as portenos
Plaza de Mayo is a city square in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires is served by Ministro Pistarini International Airport
MALBA is the Latin American Art Museum of Buenos Aires
Ushuaia in Tierra del Fuego is the most southerly city in the world
Perito Moreno is a glacier in Patagonia. Named after the explorer Francisco Moreno
Aconcagua is the highest mountain (22,800’) outside of the Himalayas, in the province of Mendoza
Mendoza produces 70% of the wine from Argentina
Monte Pissis is an extinct volcano
A villa miseria is a type of shanty town or slum found in Argentina
Cueva de las Manos (Spanish for ‘Cave of Hands’) is a cave and complex of rock art sites in the province of Santa Cruz
Laguna del Carbon (Spanish: Coal Lagoon) is an endorheic salt lake in Argentina. At 105 metres (344 ft) below sea level, it is the lowest point of both the Western and Southern hemispheres
Straits of Magellan lie between Argentina and Tierra del Fuego
Bolivia
| Capital | La Paz (see note below) |
| Largest cities | Santa Cruz, El Alto, La Paz |
| Currency | Boliviano |
| Highest point | Nevado Sajama |
Note: La Paz is the seat of government. Sucre is the constitutional capital
Bolivia is named after Simon Bolívar
In 2009, a new constitution changed the country's official name to ‘Plurinational State of Bolivia’
Bolivia became a landlocked country after Chile seized the province of Litoral in the War of the Pacific in 1884. Bolivia is the largest landlocked country in the Southern Hemisphere
In the late 19th century, an increase in the world price of silver brought Bolivia relative prosperity and political stability. During the early 20th century, tin replaced silver as the country's most important source of wealth
La Paz is, de facto, the world's highest administrative capital. Towered over by Mount Illimani
El Alto International Airport in La Paz is the highest international airport in the world. Until 1999, El Alto was known as John F. Kennedy
Mi Teleferico is an aerial cable car urban transit system serving the La Paz–El Alto metropolitan area
Potosi was the major supplier of silver for Spain during the period of the New World Spanish Empire
The US Geological Service estimates that Bolivia has 5.4 million cubic tonnes of lithium which represents 50% – 70% of world reserves
Salar de Uyuni is the world's largest salt flat. It is located in southwest Bolivia
Tiwanaku is an important Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia. Tiwanaku is recognized by Andean scholars as one of the most important precursors to the Inca Empire
Lake Poopo is a dried-up saline lake
Sajama Lines are a network of thousands of geoglyphs
Yungas Road is a cycle route which links the city of La Paz and the Yungas region. Nicknamed the "Road of Death"
Brazil
Flag of Brazil features a blue disc with 27 stars and the motto "Ordem e Progresso" (‘Order and Progress’)
| Capital | Brasilia |
| Largest cities | Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Brasilia, Salvador, Fortaleza |
| Currency | Real |
| Highest point | Pico da Neblina |
Brazil is the world's fifth largest country by area and the seventh largest by population. It is the largest Portuguese-speaking country in the world. It borders all other South American countries except Ecuador and Chile and occupies 47% of the continent of South America. The country's economy is the seventh largest by GDP. Brazil has been the world's largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years
The name of Brazil is shortened from Terra do Brasil "land of brazilwood"
Largest states by area – Amazonas, Para, Mato Grosso
Largest states by population – Sao Paulo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro was the capital of Portugal in the 19th century
Corcovado, meaning ‘hunchback’ in Portuguese, is a mountain in central Rio de Janeiro. It is known worldwide for the 38-meter (125 ft) statue of Jesus atop its peak, entitled ‘Christ the Redeemer’
Sugarloaf Mountain (in Portuguese, Pao de Acucar), is a peak situated in Rio de Janeiro, at the mouth of Guanabara Bay
Ipanema is a district of Rio de Janeiro
Rocinha is the largest favela in Rio and in Brazil
Rio de Janeiro International Airport is named after songwriter Tom Jobim
Petropolis was the official capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro between 1894 and 1903
Carioca is a demonym used to refer to anything related to the City of Rio de Janeiro
Tijuca Forest is a mountainous hand-planted rainforest in the city of Rio de Janeiro. It is the world's largest urban forest
Petropolis was the official capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro between 1894 and 1903
Fluminense is a demonym for people indigenous to the state of Rio de Janeiro
President Kubitschek ordered the construction of Brasilia, enacting a long-forgotten article of the country's republican constitutions stating that the capital should be relocated from Rio de Janeiro. Its main urban planner was Lucio Costa. Oscar Niemeyer was the chief architect of most of the public buildings and Roberto Burle Marx was the landscape designer. The city plan was based on the ideas of Le Corbusier. Brasília was built in 41 months, from 1956 to 1960, when it was officially inaugurated
Brasilia is laid out in the form of an airplane
The Cathedral of Brasilia is an expression of the architect Oscar Niemeyer. This concrete-framed hyperboloid structure, seems with its glass roof to be reaching up, open, to heaven
The Juscelino Kubitschek Bridge, also known as the JK Bridge, crosses Lake Paranoa in Brasília. It is named for Juscelino Kubitschek de Oliveira, former president of Brazil. It was designed by architect Alexandre Chan
Sao Paulo is the largest city in the southern hemisphere and in Latin America. The name of the city honours Saint Paul of Tarsus
Salvador is the capital of the state of Bahia. Until 1763, Salvador was the capital of Brazil
Belo Horizonte was the second planned city in Brazil, after Teresina
Santos is a coffee-exporting port and is the busiest container port in Latin America
Manaus is the largest city along the Amazon River. It is the capital of the state of Amazonas
Opera house in Manaus was built in 1896
Londrina is a city in Parana state
Natal is the capital city of Rio Grande do Norte, a northeastern state in Brazil. It was founded on 25 December 1599
Recife is a major port on the Atlantic Ocean. The name Recife means ‘reef’ in Portuguese
Marajo is an island located at the mouth of the Amazon River. It is the largest island to be completely surrounded by freshwater in the world
Fordlandia is a now-abandoned, prefabricated industrial town established in the Amazon Rainforest in 1928 by American industrialist Henry Ford for the purpose of securing a source of cultivated rubber for the automobile manufacturing operations of the Ford Motor Company
Curitiba is the capital and largest city of Parana
Oscar Niemeyer Museum is located in Curitiba
Belem was founded in 1616 by the Kingdom of Portugal and was the first European colony on the Amazon
Brazil has largest Japanese population outside of Japan
Pantanal is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul
Cerrado is a tropical savanna ecosystem
Sao Francisco is the longest river entirely in Brazil
Brazil has the largest population of Japanese ancestry outside of Japan
Brazil has the largest Arabic diaspora
Brazil is the only country on the Tropic of Capricorn and the Equator
Chile
| Capital | Santiago |
| Largest cities | Santiago, Valparaiso, Concepcion |
| Currency | Peso |
| Highest point | Ojos del Salado |
Chile declared its independence from Spain in 1818
Santiago was founded by conquistadors in 1541
Gran Torre Santiago is a 64-story tall skyscraper in Santiago. It is the tallest building in Latin America and the second tallest building in Latin America (behind Mexico's T.Op Torre 1)
Puente Alto is located at the south of the Great Santiago conurbation and is the most populous commune in Chile
Chilean territory includes the Pacific islands of Juan Fernandez, Salas y Gomez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania
Mapocho River flows from the Andes Mountains and divides Santiago in two
Chile is world’s largest exporter of copper
33 miners were rescued from the San Jose copper–gold mine north of Copiaco in 2010
Loa is the longest river in Chile and the main watercourse in the Atacama Desert
Punta Arenas (English: ‘Sandy Point’) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena
Antofagasta is a port city in northern Chile. It was part of Bolivia but was captured by Chile in 1879, triggering the War of the Pacific
Puyehue and Cordon Caulle are two coalesced volcanic edifices that form a major mountain massif in Puyehue National Park in the Andes of Ranco Province. Erupted in 2011
Nevado Ojos del Salado is a massive stratovolcano in the Andes on the Argentina-Chile border and the highest volcano in the world at 6893 metres. It is also the second highest mountain in the Western Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere and the highest in Chile
Calbuco volcano erupted in 2015
Torres del Paine National Park is in Patagonia
Cape Froward is the southernmost point in mainland South America
Diego Ramirez Islands are a small group of subantarctic islands. Most southerly point of South America
Juan Fernandez Islands are composed of three main volcanic islands: Robinson Crusoe, Alejandro Selkirk and Santa Clara. The islands are named after Juan Fernandez, the explorer who discovered them in the 1570s
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego is an island near the southern tip of South America from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan. The western portion of the island is in Chile, while the eastern portion is in Argentina
Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. It is named after the city of Hoorn in the Netherlands
Colombia
| Capital | Bogota |
| Largest cities | Bogota, Cali, Medellin, Barranquilla |
| Currency | US dollar |
| Highest point | Pico Cristobal Colon (see note below) |
Note: Pico Simon Bolivar has almost the same elevation as Pico Cristobal Colon
Colombia derives its name from the last name of Christopher Columbus
Bogota has been called the ‘Athens of South America’
El Dorado International Airport serves Bogota
Gold Museum (Spanish: El Museo del Oro) in Bogota displays the largest pre-Hispanic gold work collection in the world
Cartagena is a major port. It is named after the city of Cartagena in Spain
Punta Gallinas is the northernmost point in mainland South America
Nevado del Ruiz is a stratovolcano. Eruptions often cause massive lahars
Galeras is considered the most active volcano in Colombia
Pico Cristobal Colon is named after Christopher Columbus
Magdalena river is the principal river of Colombia
Chiribiquete National Natural Park is the largest natural park and the largest tropical rainforest national park in the world
Ecuador
Coat of arms on the flag of Ecuador features a condor over Chimborazo
| Capital | Quito |
| Largest cities | Guayaquil, Quito |
| Currency | US dollar |
| Highest point | Chimborazo |
Ecuador takes its name from the Spanish for ‘equator’
At an elevation of 2,800 meters above sea level, Quito is the highest official capital city in the world
Quito is located on the slopes of Pichincha volcano
Guayaquil is the main port of Ecuador
Guayas River is the most important river in South America that does not flow into the Atlantic Ocean or any of its marginal seas
Cotopaxi is the world’s highest active volcano
Chimborazo is a currently inactive stratovolcano located in the Andes. With a peak elevation of 6268 m, Chimborazo is the highest mountain in Ecuador. It is the highest peak in close proximity to the equator. While Chimborazo is not the highest mountain by elevation above sea level, its location along the equatorial bulge makes its summit the farthest point on the Earth's surface from the Earth's centre
Cayambe is a volcano with permanent snow cover
Galapagos Islands were discovered by the Bishop of Panama. Charles Darwin reached the islands in 1835 in HMS Beagle
Galapagos Islands were formerly known as the Columbus Archipelago
Fernandina Island (formerly known in English as Narborough Island) is the third largest, and youngest, island of the Galapagos Islands. The island is an active shield volcano that last erupted in 2005
Isabela Island is the largest island of the Galapagos, nearly four times larger than Santa Cruz, the next largest of the islands. The island was named in honour of Queen Isabella of Spain who sponsored the voyage of Columbus. The former English name was Albemarle Island. The island is shaped like a seahorse
Wolf Volcano is the highest peak in the Galapagos Islands, and is situated on Isabela Island
Puerto Baquerizo Moreno is the capital of Galapagos Province. It is located on the island of San Cristobal
Guyana
Flag of Guyana is known as The Golden Arrowhead
| Capital | Georgetown |
| Largest cities | Georgetown |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Roraima |
Guyana was originally colonised by the Netherlands. Later, it became a British colony, known as British Guiana, and remained so for over 200 years until it achieved independence in 1966. In 1970, Guyana officially became a republic
Guyana is a member state of the Commonwealth of Nations and has the distinction of being the only South American nation in which English is the official language. The majority of the population speaks Guyanese Creole
Georgetown was named after George III in 1812
Kaieteur Falls is a waterfall on the Potaro River in Kaieteur National Park and is the world's largest single drop waterfall
Demerara River is a river in eastern Guyana
Essequibo is the largest river in Guyana, and the largest river between the Orinoco and Amazon
Paraguay
Flag of Paraguay differs on its obverse and reverse sides: the obverse shows the national coat of arms, and the reverse shows the seal of the treasury
| Capital | Asuncion |
| Largest cities | Asuncion, Ciudad del Este |
| Currency | Guarani |
| Highest point | Cerro Pero |
Paraguay is sometimes to as the “Heart of America”
Paraguay's indigenous language and culture, Guaraní, remains highly influential
Paraguay has ports on the Paraguay and Parana rivers that give exit to the Atlantic Ocean
The majority of Paraguay's 7 million people are mestizo
Asuncion is home to nearly a third of Paraguay's population
Peru
| Capital | Lima |
| Largest cities | Lima, Arequipa, Trujillo |
| Currency | Sol |
| Highest point | Huascaran |
Peru was home to the Inca Empire, the largest state in Pre-Columbian America. The main spoken language is Spanish, although a significant number of Peruvians speak Quechua
Lima airport named after Jorge Chavez, the first person to fly across the Alps
Cuzco is a city in southeastern Peru, near the Urubamba Valley (Sacred Valley) of the Andes. Cuzco was the capital of the Inca Empire, and is said to have been originally designed in the shape of a puma
Machu Picchu is situated on a mountain ridge above the Sacred Valley which is 80 km northwest of Cuzco and through which the Urubamba River flows. Most archaeologists believe that Machu Picchu was built as an estate for the Inca emperor Pachacuti (1438–1472). Often mistakenly referred to as the "Lost City of the Incas”. Hiram Bingham made public the existence of the Inca citadel of Machu Picchu in 1911 with the guidance of local indigenous farmers
Arequipa is known as the “white city”. It is the second most industrialized and commercial city of Peru
Moray is a town in Peru approximately 50 km northwest of Cuzco that is noted for a large complex of unusual Inca ruins. These include several enormous terraced circular depressions that were used to study the effects of different climatic conditions on crops
Punta Parinas in Peru is the westernmost point in mainland South America
Yumbilla Falls is considered the world's fifth tallest waterfall
Huaynaputina is a volcano that erupted in Peru in 1600, which is the largest eruption ever recorded in South America
Callao is the chief seaport of Peru
Chan Chan was the largest city of the pre-Columbian era in South America. It was the capital of the historical empire of the Chimor from 900 to 1470, when they were defeated and incorporated into the Inca Empire
Suriname
| Capital | Paramaribo |
| Largest cities | Paramaribo |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Julianatop |
Suriname is the smallest sovereign state in South America. French Guiana, while less extensive and populous, is an overseas department of France
In 1667 Suriname was captured by the Dutch, who governed Suriname as Dutch Guiana until 1954. Gained independence in 1975, but Dutch is still the official language
Most of the population lives on the country's north coast, in and around Paramaribo
The forest cover is 90%, the highest of any nation in the world
Uruguay
Flag of Uruguay features the Sun of May
| Capital | Montevideo |
| Largest cities | Montevideo, Salto |
| Currency | Peso |
| Highest point | Cerro Catedral |
Uruguay is officially the Eastern Republic of Uruguay. It is ranked first in Latin America in democracy, peace, lack of corruption, and quality of living
Uruguay is geographically the second-smallest nation in South America, after Suriname
Uruguay is home to 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the metropolitan area of Montevideo
Montevideo was first found by Juan Diaz De Solis in 1516
Montevideo is served by Carrasco International Airport
Punta del Este is a city and seaside resort. Known as ‘the Monaco of the South’
Venezuela
An eighth star was added to the flag of Venezuela in 2006
| Capital | Caracas |
| Largest cities | Caracas, Maracaibo, Valencia |
| Currency | Bolivar |
| Highest point | Pico Bolivar |
Official name is Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
Venezuela has the world's largest oil reserves
In 1499, an expedition led by Alonso de Ojeda visited the Venezuelan coast. The stilt houses in the area of Lake Maracaibo reminded the navigator, Amerigo Vespucci, of the city of Venice, so he named the region "Veneziola"
Lake Maracaibo is the largest lake in South America. Catatumbo lightning (named after the Catatumbo River) regularly produces more lightning than any other place on the planet
Margarita Island is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated in the Caribbean Sea
Pico Humboldt is the second highest peak in Venezuela
Angel Falls is the world's tallest uninterrupted waterfall, with a height of 979 metres. The waterfall drops over the edge of the Auyan-tepui mountain in the Canaima National Park. Named after Jimmie Angel, an American aviator, who was the first person to fly over the falls
Overseas territories
French Guiana
French Guiana (French: Guyane) is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America
A large part of the department's economy derives from the presence of the Guiana Space Centre, now the European Space Agency's primary launch site near the equator, at Kourou
Devil’s Island is the smallest and northernmost island of the three Iles du Salut located off the coast of French Guiana
Cayenne is the capital city
98.9% of the land territory of French Guiana is covered by forests
Falkland Islands
The principal islands are about 300 mi (480 km) east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 mi (1,210 km) from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula
The islands took their English name from Falkland Sound, the channel between the two main islands, which was in turn named after Anthony Cary, 5th Viscount Falkland by Captain John Strong, who landed on the islands in 1690
The archipelago consists of two main islands, West Falkland and East Falkland, and 776 smaller islands
Stanley, or Port Stanley, is the capital of the Falkland Islands. It is located on the island of East Falkland. It was renamed Puerto Argentino, briefly, during the Falklands War of 1982
In May 2022, it was announced that, as part of the Platinum Jubilee Civic Honours, Stanley would receive city status
Mount Usborne is the highest point on the Falkland Islands
RAF Mount Pleasant airport serves as the islands' main international airport
Pebble Island is situated north of West Falkland
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
British overseas territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean. South Georgia is by far the largest island in the territory. The South Sandwich Islands lie about 700 km southeast of South Georgia and are uninhabited
Grytviken is the principal settlement of South Georgia and is the site of a disused whaling station
King Edward Point is the capital and has a population of 22
Mount Paget on South Georgia is the highest peak in any territory under the sovereignty of the United Kingdom
Mount Asphyxia is a volcanic cone and forms the summit of Zavodovski Island, the northernmost of the South Sandwich Islands
Physical Geography
Regions
Gran Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semi-arid lowland region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, Paraguay, northern Argentina and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region
Llanos is a tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela
Atlantic Forest extends along the Atlantic coast of Brazil and inland as far as Paraguay and Argentina. It was the first environment that the Portuguese colonists encountered over 500 years ago
Southern Cone is a geographic region composed of the southernmost areas of South America, south of and around the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile and Uruguay
Triple Frontier is a tri-border area along the junction of Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay, where the Iguazu and Parana rivers converge
Tres Fronteras is the Spanish name for an area of the Amazon Rainforest in the Upper Amazon region. It includes, and is named for, the tripoint where the borders of Brazil, Peru, and Colombia meet.
The Altiplano plateau is the world’s second-highest following the Tibetan plateau. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia
Mountains
Highest mountains in South America – Aconcagua, Ojos del Salado, Monte Pissis
The Andes is the longest continental mountain range in the world, stretching for 4,300 miles through Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. The Altiplano plateau is the world’s second-highest following the Tibetan plateau
Parinacota, a composite volcano, is located on the Chilean / Bolivian frontier and is one of two volcanoes that make up the Nevados Payachata range. The other older volcano, Pomerape, is located to the northeast of Parinacota and makes up the northern part of this volcanic range
Mount Roraima includes the triple border point of Venezuela, Brazil and Guyana
Deserts
The Atacama Desert is located on the Pacific coast of South America (Argentina and Chile). Stretching over a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land west of the Andes Mountains, it covers an area of 105,000 km2 (41,000 sq mi) It is the driest nonpolar desert in the world
Rivers
Longest rivers in South America – Amazon, Parana, Madeira, Purus, Sao Francisco
Amazon River is the largest river by discharge of water in the world. The Amazon basin is the largest drainage basin in the world. Flows for 6,500 km (4,000 miles) through Brazil, Colombia and Peru
The Nile has traditionally been considered longer than the Amazon, but this is disputed
Pororoca is a tidal bore on the Amazon
Javary River is a tributary of the Amazon that forms the boundary between Brazil and Peru for more than 500 miles
In its upper stretches, above the confluence of the Rio Negro, the Amazon is called Solimoes in Brazil
Parana River runs through Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina
Madeira River is the biggest tributary of the Amazon
Orinoco River flows through Venezuela and Colombia. it is the fourth largest river in the world by discharge volume of water
Itaipu is the third largest hydroelectric dam in the world, and lies on the border of Brazil and Paraguay, on the Parana. It is a gravity dam, and was completed in 1982
Lakes
Lake Titicaca is the highest commercially navigable lake in the world, at 3,812 m above sea level. Located in the Altiplano high in the Andes on the border of Peru and Bolivia, Titicaca has a maximum depth of 281 m
Uros, Amantani, and Taquile are islands in Lake Titicaca
Seas
Drake Passage is the body of water between the southern tip of South America at Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica
Beagle Channel is a strait separating the islands of the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago. The Beagle Channel, the Straits of Magellan to the north, and the open ocean Drake Passage to the south are the three navigable passages around South America between the Pacific and the Atlantic oceans. Most commercial shipping is through the Drake Passage
Waterfalls
Angel Falls in Venezuela is the world's tallest uninterrupted waterfall
Iguazu Falls are located on the border of the Brazilian state of Parana and the Argentine province of Misiones. The falls divide the river into the upper and lower Iguazu. The waterfall system consists of 275 falls, including The Devil’s Throat