Difference between revisions of "Civilisation/World Geography - Europe"
(Added flags and information tables) |
(Brought up to date - finally) |
||
| (79 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
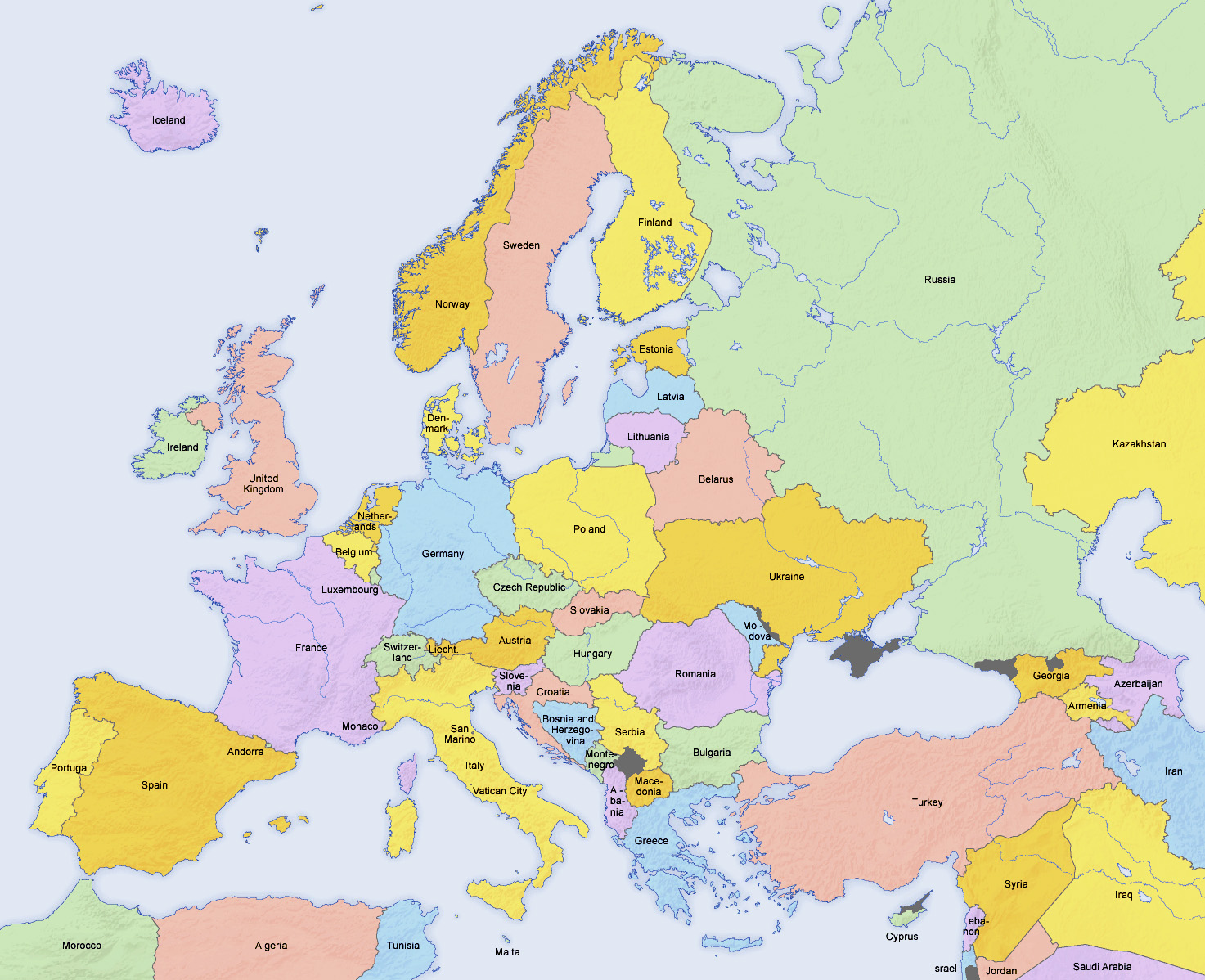
| + | [[File:Europe countries map en 3.jpg|center|thumb|700x700px|link=Special:FilePath/Europe_countries_map_en_3.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
== Albania == | == Albania == | ||
[[File:Flag-of-Albania.png|thumb|alt=|none]] | [[File:Flag-of-Albania.png|thumb|alt=|none]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
|Mount Korab | |Mount Korab | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | Albania is officially the Republic of Albania (Albanian: Republika e Shqipërisë) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tirana was founded as a city in 1614 by the Ottoman Albanian general Sylejman Pasha Bargjini | ||
| + | |||
Durres is the main port of Albania | Durres is the main port of Albania | ||
Vlore is the old capital of Albania. It is the city where the Albanian Declaration of Independence was proclaimed in 1912 | Vlore is the old capital of Albania. It is the city where the Albanian Declaration of Independence was proclaimed in 1912 | ||
| − | Albania is only European country with a 20th century Muslim monarch | + | Karaburun peninsula is located along the Albanian Ionian Sea Coast |
| + | |||
| + | Albania is the only European country with a 20th century Muslim monarch | ||
In 1967 Enver Hoxha proclaimed Albania the world's first 'atheist state' | In 1967 Enver Hoxha proclaimed Albania the world's first 'atheist state' | ||
| Line 46: | Line 54: | ||
Andorra is divided into seven parishes | Andorra is divided into seven parishes | ||
| + | |||
| + | Andorra is the largest country in the world which does not have an airport | ||
== Armenia == | == Armenia == | ||
| Line 65: | Line 75: | ||
In August 1990, Armenia declared independence, becoming the first non-Baltic republic to secede from the Soviet Union | In August 1990, Armenia declared independence, becoming the first non-Baltic republic to secede from the Soviet Union | ||
| − | Armenia supports the de facto independent | + | Armenia supports the de facto independent Artsakh |
Armenia was the first country to adopt Christianity as its state religion | Armenia was the first country to adopt Christianity as its state religion | ||
| + | |||
| + | Armenia is the smallest ex-Soviet republic | ||
== Austria == | == Austria == | ||
| Line 87: | Line 99: | ||
Austria is a federal republic made up of nine states, known in German as Länder | Austria is a federal republic made up of nine states, known in German as Länder | ||
| − | + | Vindobona was the Roman name for Vienna | |
Ringstrasse is a circular road surrounding the Innere Stadt district of Vienna | Ringstrasse is a circular road surrounding the Innere Stadt district of Vienna | ||
| − | + | Graben is one of the most famous streets in Vienna's first district, the city centre | |
| + | |||
| + | Prater is a large public park in Vienna. Oldest amusement park in the world | ||
| − | + | Zentralfriedhof (German for "Central Cemetery") is one of the largest cemeteries in the world, largest by number of interred in Europe and most famous cemetery among Vienna's nearly 50 cemeteries. Beethoven is interred in this cemetery | |
| − | + | Vienna Zoo (Tiergarten Schonbrunn) was founded as an imperial menagerie in 1752 and is the oldest continuously operating zoo in the world | |
| − | + | Graz is the capital of Styria | |
| − | + | Lower Austria is the largest state in Austria | |
| − | + | Linz is the capital of Upper Austria. It lies on the River Danube. In 2009, it was a European Capital of Culture | |
| − | + | Salzburg (Geman: ‘salt castle’) lies on the site of the Roman settlement of Iuvavum. Salzburg's historic centre is renowned for its Baroque architecture | |
| − | + | Innsbruck is the capital of Tyrol. It lies on the River Inn | |
Semmering is a mountain pass in the Eastern Northern Limestone Alps connecting Lower Austria and Styria, between which it forms a natural border | Semmering is a mountain pass in the Eastern Northern Limestone Alps connecting Lower Austria and Styria, between which it forms a natural border | ||
| − | Brenner Pass | + | Brenner Pass is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria |
== Azerbaijan == | == Azerbaijan == | ||
| Line 127: | Line 141: | ||
|Mount Bazardudu | |Mount Bazardudu | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
Baku is the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region | Baku is the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region | ||
| Line 140: | Line 155: | ||
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers 5,500 km<sup>2</sup> and borders Armenia, Iran and Turkey | Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers 5,500 km<sup>2</sup> and borders Armenia, Iran and Turkey | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lachin corridor is a mountain pass within de-jure borders of Azerbaijan, It is the shortest route which connects Armenia with Nagorno-Karabakh Republic | ||
== Belarus == | == Belarus == | ||
| Line 165: | Line 182: | ||
Belarus is the last country in Europe to still retain and use the death penalty | Belarus is the last country in Europe to still retain and use the death penalty | ||
| + | |||
| + | Belarus is the only newly-independent country to keep the Ruble as its currency after 1993 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Homyel is also known as Gomel | ||
== Belgium == | == Belgium == | ||
| Line 189: | Line 210: | ||
NATO Headquarters are in Brussels | NATO Headquarters are in Brussels | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Brussels is on River Zenne/Senne, a tributary of the Scheldt | Brussels is on River Zenne/Senne, a tributary of the Scheldt | ||
| − | Grand Place or Grote Markt is the central square of Brussels | + | Grand Place or Grote Markt is the central square of Brussels. It is surrounded by Baroque guildhalls of the former Guilds of Brussels and two larger edifices; the city's Flamboyant Town Hall, and the neo-Gothic King's House or Bread House building, containing the Brussels City Museum |
| − | + | In the centre of Brussels, the River Zenne was completely covered up and major boulevards were built over top in the 19th and early 20th centuries | |
| − | + | Menin Gate is at Ypres | |
| − | + | Tyne Cot is a Commonwealth War Graves Commission burial ground for the dead of the First World War in the Ypres Salient | |
Zeebrugee is also known as Bruges-sur-mer | Zeebrugee is also known as Bruges-sur-mer | ||
| Line 207: | Line 226: | ||
Rubenshuis is the former home and studio of Peter Paul Rubens in Antwerp. It is now a museum | Rubenshuis is the former home and studio of Peter Paul Rubens in Antwerp. It is now a museum | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ghent is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province | ||
Belgium was known as “The Cockpit of Europe”, due to the number of battles fought there | Belgium was known as “The Cockpit of Europe”, due to the number of battles fought there | ||
| Line 222: | Line 243: | ||
Baarle-Hertog is a Flemish municipality of Belgium, much of which consists of a number of small Belgian exclaves in the Netherlands. Baarle-Hertog is noted for its complicated borders with Baarle-Nassau, Netherlands | Baarle-Hertog is a Flemish municipality of Belgium, much of which consists of a number of small Belgian exclaves in the Netherlands. Baarle-Hertog is noted for its complicated borders with Baarle-Nassau, Netherlands | ||
| + | == Bosnia and Herzegovina == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Bosnia-Herzegovina.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | The white stars on a blue background on the flag of Bosnia and Herzegovina represent links with the EU | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Sarajevo | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Sarajevo, Banja Luka | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Mark | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Maglic | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Republika Srpska is one of the two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located in the north and east of the country. Its largest city and administrative centre is Banja Luka | ||
| + | Mostar Bridge (Stari Most, ‘old bridge’) is a 16th century Ottoman bridge that crosses the River Neretva in Bosnia and Herzegovina and connects two parts of the city. The Old Bridge stood for 427 years, until it was destroyed in 1993 during the Croat-Bosniak War. Subsequently, a project was set in motion to reconstruct it, and the rebuilt bridge opened in 2004 | ||
| − | + | Miljacka River passes through Sarajevo | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for 20 km of coastline on the Adriatic Sea surrounding the city of Neum | Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for 20 km of coastline on the Adriatic Sea surrounding the city of Neum | ||
| + | Brcko District is a self-governing administrative unit in Bosnia and Herzegovina | ||
| − | + | == Bulgaria == | |
| − | + | [[File:Flag-of-Bulgaria.png|none|thumb]] | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Sofia | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Sofia, Plovdiv, Varna | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Lev | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Musala | ||
| + | |} | ||
Sofia was originally a Thracian settlement | Sofia was originally a Thracian settlement | ||
| Line 241: | Line 290: | ||
National Palace of Culture and Vitosha Boulevard are in Sofia | National Palace of Culture and Vitosha Boulevard are in Sofia | ||
| − | Plovdiv | + | Plovdiv was the European Capital of Culture in 2019 |
| − | Varna is the | + | Varna is the largest city and seaside resort on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. It was named Stalin between 1949 and 1956 |
| + | The three national parks in Bulgaria are Pirin National Park, Rila National Park and Central Balkan National Park | ||
| − | + | Musala is the highest point in the Rila Mountains, in the Balkan Peninsula | |
| + | == Croatia == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Croatia.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Zagreb | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Zagreb, Split, Rijeka | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Kuna | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Dinara | ||
| + | |} | ||
Zagreb lies on the Sava river | Zagreb lies on the Sava river | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zagreb Airport is named after Franjo Tudman, the first President of Croatia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Split is the largest city in the region of Dalmatia. Diocletian’s Palace is a World Heritage Site | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rijeka is the largest port in Croatia. because of its strategic position and its excellent deep-water port, the city was fiercely contested, especially between the Holy Roman Empire, Hungary (serving as the Kingdom of Hungary's largest and most important port, known as Fiume), Italy and Croatia | ||
Trogir is a historic town and harbour on the Adriatic coast. The centre of Trogir is a World Heritage Site | Trogir is a historic town and harbour on the Adriatic coast. The centre of Trogir is a World Heritage Site | ||
| − | Byron called Dubrovnik the “pearl of the Adriatic” | + | Lord Byron called Dubrovnik the “pearl of the Adriatic” |
Dubrovnik was known as Ragusa until 1909 | Dubrovnik was known as Ragusa until 1909 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zadar is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatian city | ||
| + | |||
| + | Slavonia, Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria are the four historical regions of Croatia | ||
Cres and Krk are the largest Croatian islands | Cres and Krk are the largest Croatian islands | ||
| + | |||
| + | Korkula is the second most populous Adriatic island after Krk | ||
Plitvice Lakes National Park is the oldest national park in Southeast Europe and the largest national park in Croatia | Plitvice Lakes National Park is the oldest national park in Southeast Europe and the largest national park in Croatia | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The Danube runs through the city of Vukovar in the extreme east and forms part of the border with Serbia | The Danube runs through the city of Vukovar in the extreme east and forms part of the border with Serbia | ||
| Line 266: | Line 341: | ||
Karst topography makes up about half of Croatia and is especially prominent in the Dinaric Alps | Karst topography makes up about half of Croatia and is especially prominent in the Dinaric Alps | ||
| − | + | == Cyprus == | |
| − | + | [[File:Flag-of-Cyprus.png|none|thumb]] | |
| − | + | The outline of the island on the flag of Cyprus is a copper-orange colour, symbolising the large deposits of copper ore on the island | |
| − | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Nicosia | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Nicosia, Limassol | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mount Olympus | ||
| + | |} | ||
Cyprus is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean | Cyprus is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean | ||
| Line 279: | Line 366: | ||
United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus is a demilitarised zone that was established in 1974 following the Turkish invasion of Cyprus. The zone runs for more than 180 km along what is colloquially known as the Green Line. Turkish forces built a barrier on the zone's northern side – this line is also referred to as the Attila Line | United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus is a demilitarised zone that was established in 1974 following the Turkish invasion of Cyprus. The zone runs for more than 180 km along what is colloquially known as the Green Line. Turkish forces built a barrier on the zone's northern side – this line is also referred to as the Attila Line | ||
| − | + | Ledra Street is a major shopping thoroughfare in central Nicosia. It is the site of the former Ledra Street barricade, across the United Nations buffer zone | |
| + | Limassol, on the southern coast, was built between two ancient Greek cities, Amathus and Kourion, and during Byzantine rule it was known as Neapolis | ||
| − | + | Karpas Peninsula is the long peninsula of northeast Cyprus | |
| − | + | Akrotiri and Dhekelia is a British Overseas Territory on Cyprus | |
| − | + | == Czech Republic (Czechia) == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Czech-Republic.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Prague | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Prague, Brno, Ostrava | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Koruna | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Sněžka | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Czechia is the official short name of Czech Republic | ||
| − | + | Kraj is the highest-level administrative unit in the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic | |
| − | + | Prague is known as the ‘City of a Hundred Spires’ | |
| − | Prague | + | Charles Square in Prague is one of the largest squares in the world and was the largest town square of the medieval Europe |
| − | + | Charles Bridge is a medieval stone arch bridge that crosses the Vltava river in Prague. Its construction started in 1357 | |
| − | + | Wenceslas Square is one of the main city squares and the centre of the business and cultural communities in the New Town of Prague | |
| − | + | Prague astronomical clock, or Prague orloj was first installed in 1410, making it the oldest astronomical clock in the world still working | |
| − | + | Karlovy Vary, known in English as Carlsbad, is a spa city situated in Bohemia, the western part of the Czech Republic, on the confluence of the rivers Ohře and Teplá. Part of the Spa Triangle, along with Marinnske Lazne and Frantiskovy Lizne. Carlsbad is named after Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV, who founded the city in 1370. Moser is a luxury, high-quality glass manufacturer based in Carlsbad | |
Moravia occupies most of the eastern third of the Czech Republic | Moravia occupies most of the eastern third of the Czech Republic | ||
Czech Silesia is one of the three Czech lands and a section of the Silesian historical region. It is located in the north-east of the Czech Republic | Czech Silesia is one of the three Czech lands and a section of the Silesian historical region. It is located in the north-east of the Czech Republic | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Vltava is the longest river in the Czech Republic, running north from its source near the German Border, through Prague, merging with the Elbe at Melník | Vltava is the longest river in the Czech Republic, running north from its source near the German Border, through Prague, merging with the Elbe at Melník | ||
| + | == Denmark == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Denmark.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | The flag of Denmark, the Dannebrog, holds the world record of being the oldest continuously used national flag. Adopted in 1219 | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Copenhagen | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Copenhagen, Aarhus, Odense | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Krone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mollehoj | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Denmark consists of the peninsula of Jutland and an archipelago of 443 named islands | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tivoli, also known as Tivoli Gardens, is an amusement park and pleasure garden in Copenhagen. The park opened in 1843 | ||
| − | + | Bakken is an amusement park near Copenhagen. It opened in 1583 and is the world's oldest operating amusement park | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Copenhagen is located partly on the islands of Zealand and Amager | |
Kastrup Airport serves Copenhagen | Kastrup Airport serves Copenhagen | ||
| − | Aarhus is the | + | Aarhus is located on the eastern shore of Jutland in the Kattegat sea |
| + | |||
| + | The island of Bornholm is part of Denmark | ||
| + | |||
| + | Odense is the largest city on the island of Funen | ||
| − | + | Billund is a town in Jutland that is home to the Lego Group head office and the Legoland theme park | |
Roskilde Cathedral is the burial site for Danish monarchs | Roskilde Cathedral is the burial site for Danish monarchs | ||
| Line 331: | Line 449: | ||
Viking Ship Museum in Roskilde is the Danish national museum for ships. Around 1070, five Viking ships were deliberately sunk at Skuldelev in Roskilde Fjord in order to block the most important fairway and to protect Roskilde from enemy attack from the sea | Viking Ship Museum in Roskilde is the Danish national museum for ships. Around 1070, five Viking ships were deliberately sunk at Skuldelev in Roskilde Fjord in order to block the most important fairway and to protect Roskilde from enemy attack from the sea | ||
| + | The Vikingemuseet Ladby in Denmark is the only place in the world where a Viking burial ship may be seen in its original position inside a burial mount | ||
| − | + | Kronborg is a castle in the town of Helsingor. Immortalized as Elsinore in ''Hamlet'' | |
| − | + | Capital Region of Denmark is the easternmost administrative region of Denmark | |
| − | + | Denmark generates 40% of its electricity from wind power | |
| + | Samso is a carbon-neutral island in the Kattegat. All of its electricity comes from wind power and biomass | ||
| − | + | Great Belt Fixed Link is a multi-element fixed link crossing the Great Belt strait between the Danish islands of Zealand and Funen (Fyn). It consists of a road suspension bridge and a railway tunnel between Zealand and the small island Sprogø in the middle of the Great Belt, and a box-girder bridge for both road and rail traffic between Sprogø and Funen | |
| − | + | Limfjord is a shallow part of the sea that has been regarded as a fjord ever since Viking times | |
| − | + | === Faroe Islands === | |
| + | [[File:Flag of the Faroe Islands.svg.png|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | Faroe Islands have been a self-governing country within the Danish Realm since 1948 | ||
| − | + | Streymoy and Esturoy are the largest of the Faroe Islands | |
| − | + | Torshavn is the capital of the Faroe Islands and is situated on the island of Streymoy | |
| − | + | == Estonia == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Estonia.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Tallinn | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Tallinn, Tartu | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Suur Munamagi | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known as Reval, its historical Danish name | ||
| − | + | Soomaa (‘land of bogs’) National Park is a Ramsar site of protected wetlands | |
| + | Suur Munamagi is the highest point in the Baltic states | ||
| − | + | Saaremaa and Hiiumaa are the two largest islands of Estonia | |
| − | + | Peipus is the largest lake in Estonia, and the fifth largest lake in Europe | |
| − | + | == Finland == | |
| − | + | [[File:Flag-of-Finland.png|none|thumb]] | |
| − | Espoo | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | + | |Capital | |
| − | + | |Helsinki | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Helsinki, Espoo, Tampere | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Halti | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Uusimaa is the region of Finland that contains Helsinki | |
| − | + | Helsinki was founded by Gustav I of Sweden | |
| + | Helsinki is known as Helsingfors in Sweden | ||
| − | ' | + | Helsinki Metro has bright orange trains and is is the world's northernmost subway |
| − | + | Turku was the capital of Finland until 1812 | |
| − | + | Rovaniemi is the capital of Lapland. It is home to the Santa Claus Village at the Arctic Circle and SantaPark Arctic World | |
| − | + | Finland is the most sparsely populated country in the European Union | |
| − | + | Finland has about 168,000 lakes and 179,000 islands. Its largest lake, Saimaa, is the fourth largest in Europe | |
| − | + | Kemijoki is the longest river in Finland | |
| − | + | Archipelago Sea is a part of the Baltic Sea between the Gulf of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland and the Sea of Aland, within Finnish territorial waters. By some definitions it contains the largest archipelago (island group) in the world by the number of islands | |
| − | + | Aland Islands form an archipelago in the Baltic Sea. They are situated at the entrance to the Gulf of Bothnia and form an autonomous Swedish-speaking region of Finland. Mariehamm is the capital | |
| − | + | == France == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-France.png|none|thumb]]Flag of France has a variant with lighter shades | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Paris | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Paris, Marseille, Lyon, Toulouse, Nice | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mont Blanc | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | France is the largest country in the EU | ||
| + | Due to its shape, France is often referred to as l'Hexagone (‘The Hexagon’) | ||
| − | + | There are 18 regions, of which 13 are in continental metropolitan France | |
| − | + | In 2016 the number of metropolitan regions was reduced from 22 to 13 | |
| − | + | Gascony is currently divided between the Aquitaine region and the Midi-Pyrenees region[[File:Regions France 2016.svg|none|thumb|alt=|400x400px]] | |
| + | '''Auvergne-Rhone-Alpes''' | ||
| − | + | Former regions – Auvergne (capital – Clermont Ferrand) and Rhone-Alpes (capital – Lyon) | |
| − | Capital – | + | Capital – Lyon |
| − | + | Auvergne is part of the Massif Central | |
| − | + | Vichy is a spa town, famous for thermal baths. Connects the Garonne to the Mediterranean | |
| + | Lyon is at the confluence of the Rhone and Saone | ||
| − | + | Lyon was historically known as an important area for the production and weaving of silk | |
| − | + | Roman name for Lyon was Lugdunum | |
| − | + | Chauvet Cave in the Ardeche department of southern France became famous in 1994 after speleologists found that its walls were richly decorated with Paleolithic artwork, that it contained the fossilized remains of many animals, including those that are now extinct | |
| − | + | Val Thorens is Europe’s highest skiing resort | |
| + | |||
| + | Isere rises in the Alps and flows through Grenoble | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bourgogne-Franche-Comte''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Former regions – Burgundy (capital – Dijon) and Franche-Comte (capital – Besancon) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capital – Dijon | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dijon holds an International and Gastronomic Fair every year | ||
| + | |||
| + | Beaune is the wine capital of Burgundy in the Cote d'Or department | ||
| + | Franche-Comte was part of the Kingdom of Burgundy | ||
| − | Brittany | + | '''Brittany''' |
Capital – Rennes | Capital – Rennes | ||
| Line 431: | Line 609: | ||
Carnac is famous as the site of more than 3000 prehistoric standing stones. The stones were hewn from local rock and erected by the pre-Celtic people of Brittany | Carnac is famous as the site of more than 3000 prehistoric standing stones. The stones were hewn from local rock and erected by the pre-Celtic people of Brittany | ||
| + | Rance tidal power station was opened in 1966 and was the largest tidal power station in the world by installed capacity until the South Korean Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Station surpassed it in 2011 | ||
| − | + | Ushant is an island in the English Channel which marks the north-westernmost point of metropolitan France | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Centre-Val de Loire | + | '''Centre-Val de Loire''' |
Capital – Orleans | Capital – Orleans | ||
| Line 449: | Line 623: | ||
Fontevraud Abbey, near Chinon, was the site of the graves of King Henry II of England, his wife Eleanor of Aquitaine, their son King Richard I of England, their daughter Joan, their grandson Raymond VII of Toulouse, and Isabella of Angouleme, wife of Henry and Eleanor's son King John | Fontevraud Abbey, near Chinon, was the site of the graves of King Henry II of England, his wife Eleanor of Aquitaine, their son King Richard I of England, their daughter Joan, their grandson Raymond VII of Toulouse, and Isabella of Angouleme, wife of Henry and Eleanor's son King John | ||
| + | Canal de Briare is one of the oldest canals in France. It connects the Loire and Seine valleys | ||
| − | + | '''Corsica''' | |
| − | Capital – | + | Capital – Ajaccio |
| − | + | Corsica is known as ‘The Scented Isle’ | |
| + | Corsica is the fourth largest island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily, Sardinia and Cyprus | ||
| − | + | Bastia was the capital of Corsica until 1791. It is the second largest city of Corsica | |
| − | + | Corsica is divided in two departments: Corse-du-Sud and Haute-Corse | |
| − | + | Napoleon Bonaparte Airport is the main airport serving Ajaccio | |
| + | Porto-Vecchio is a commune in Corsica | ||
| − | + | Monte Cinto is the highest mountain on Corsica | |
| − | + | '''Grand Est''' | |
| − | + | Former regions – Alsace (capital – Strasbourg), Champagne-Ardenne (capital – Chalons-en-Champagne) and Lorraine (capital – Metz) | |
| − | + | Capital – Strasbourg | |
| − | + | Strasbourg is principal city of the Alsace region and is the official seat of the European Parliament. It is the capital of the Bas-Rhin department | |
| − | + | EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg is located in France, on the administrative territory of the commune of Saint-Louis near the Swiss and German borders. The airport has a Swiss customs area connected to Basel | |
| − | + | Reims played a prominent ceremonial role in French monarchical history as the traditional site of the crowning of the kings of France | |
| − | + | Sedan is known for its castle that is claimed to be the largest fortified medieval castle in Europe | |
| − | + | Metz is the first regional outpost of the Pompidou Centre, opened in 2010 | |
| − | + | Metz is the capital of Lorraine, on the River Moselle | |
| − | + | The last working coalfield in France was in Lorraine | |
| − | + | Nancy was formerly the capital of the Duchy of Lorraine | |
| − | + | Mulhouse is the second largest city in Alsace | |
| − | + | Verdun Memorial is situated on the battlefield, close to the destroyed village of Fleury-devant-Douaumont in the department of Meuse | |
| − | + | Clairvaux Abbey is a Cistercian monastery founded in 1115 | |
| − | + | '''Hauts-de-France''' | |
| − | + | Former regions – Nord-Pas-de-Calais (capital – Lille) and Picardy (capital – Amiens) | |
| − | + | Capital – Lille | |
| − | + | Pas-de-Calais is a department in northern France. Its name is the French equivalent of the Strait of Dover, which it borders | |
| − | + | Arras is the capital of the Pas-de-Calais department | |
| − | + | Nord is the most populous French department | |
| − | + | Canadian National Vimy Memorial is a memorial site dedicated to the memory of Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War | |
| − | + | Amiens Cathedral is the tallest Gothic cathedral in France | |
| − | + | Aisne, Oise, and Somme are departments of Picardy | |
| − | + | Thiepval Memorial to the Missing of the Somme is a major war memorial to 72,191 missing British and South African men who died in the Battles of the Somme with no known grave. Designed by Edwin Lutyens | |
| − | + | Musee Conde is an art gallery located inside the Chateau de Chantilly | |
| − | + | During the Hundred Years' War, Ponthieu, now part of Picardy, changed hands a number of times | |
| − | + | '''Ile-de-France''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Paris | |
| − | + | Ile-de-France is the wealthiest and most populated of the 27 administrative regions of France. It consists mostly of the Paris metropolitan area | |
| − | + | Paris is known the ‘City of Light’ | |
| − | + | Distances from Paris are measured from Notre Dame Cathedral | |
| − | + | Gare du Nord is the busiest railway station in Europe | |
| − | + | Gare de Lyon is the second-busiest railway station in France | |
| − | Paris | + | Gare St Lazare opened in 1837. First station in Paris |
| − | + | Charles de Gaulle-Etoile is a Paris Metro station | |
| − | + | Place de la Concorde is the largest Place in Paris. During the French Revolution the statue of Louis XV of Franc was torn down and the area renamed ‘Place de la Revolution’. Marie Antoinette was executed there | |
| − | + | Place Charles de Gaulle, historically known as the Place de l'Etoile, is a large road junction in Paris, the meeting point of twelve straight avenues (hence its historic name, which translates as ‘Place of the Star’) including the Champs-Elysees which continues to the east. In the centre is the Arc de Triomphe | |
| − | + | Pere Lachaise takes its name from Pere François de la Chaise, the confessor of Louis XIV, who lived in the Jesuit house rebuilt in 1682 on the site of the chapel. The cemetery was established by Napoleon in 1804 | |
| − | + | Flooding in Paris is measured by the height of the water against the Zouave statue on Pont de l'Alma | |
| − | + | Champs-Elysees was designed by Andre Le Notre | |
| − | + | Monparnasse Cemetery is the second largest cemetery in Paris. Interments include Jean Paul Sartre, Simone de Beauvoir, Charles Baudelaire, and Camille Saint-Seans | |
| + | Montmartre Ceremony is the final resting place of many famous artists. Interments include Vaslav Nijinsky, Hector Berlioz, and Edgar Degas | ||
| − | + | Reseau Express Regional (RER) is a hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit system serving Paris and its suburbs | |
| − | + | Shakespeare and Company is an English-language bookstore located on the Left Bank | |
| − | + | Prix d'Amerique is a harness race held at the Hippodrome de Vincennes in Paris. It is widely considered the most prestigious harness race in the world | |
| − | + | Place Vendome was begun in 1698. The original Vendome Column at the centre of the square was erected by Napoleon I to commemorate the Battle of Austerlitz | |
| + | Ponf Neuf is the oldest standing bridge across the river Seine | ||
| − | + | The Bastille was a castle built in the 14th century in response to a threat to Paris during the Hundred Years' War. The Place de la Bastille is a square where the Bastille prison once stood until the storming of the Bastille in 1789 and its subsequent destruction | |
| − | + | Bois de Vincennes is the largest public park in Paris | |
| − | + | Bois de Boulognes is the second largest public park in Paris | |
| − | + | Place de la Concorde was known as Place Louis XV until 1795 | |
| + | Latin Quarter is an area in the 5th and the 6th arrondissements of Paris. It is situated on the left bank of the Seine, around the Sorbonne | ||
| − | + | Palace of Fontainbleau is one of the largest French royal chateaux. The medieval castle and subsequent palace served as a residence for the French monarchs from Louis VII to Napoleon III | |
| − | + | '''Normandy''' | |
| − | + | Former regions – Upper Normandy (capital – Rouen) and Lower Normandy (capital – Caen) | |
| − | + | Capital – Rouen | |
| − | + | Rouen Cathedral is a Roman Catholic Gothic cathedral. Claude Monet produced a series of paintings of the cathedral | |
| − | + | Etretat is a resort in Normandy frequently painted by impressionist artists | |
| − | + | Mont-Saint-Michel is a tidal island and mainland commune. The island lies approximately one kilometre off France's north-western coast. It is visited by more than three million people each year | |
| + | During the Hundred Years' War, the English made repeated assaults on the island of Mont-Saint-Michel, but were unable to seize it due to the abbey's improved fortifications | ||
| − | + | Bayeux is a commune in the Calvados department | |
| − | + | Thierville is the only village in all of France with no men lost from World War I | |
| − | + | Le Havre is situated on the estuary of the Seine. The city and port were founded by King Francis I in 1517 | |
| + | River Seine is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen | ||
| − | + | Honfleur is located on the southern bank of the estuary of the Seine across from Le Havre and very close to the exit of the Pont de Normandie | |
| − | + | '''Nouvelle-Aquitaine''' | |
| − | + | Former regions – Aquitaine (capital – Bordeaux), Limousin (capital – Limoges) and Poitou-Charantes (capital – Poitiers) | |
| − | + | Capital – Bordeaux | |
| − | + | Nouvelle-Aquitaine is the largest French region | |
| + | Bordeaux is on River Garonne. It is the prefecture of the Gironde department | ||
| − | + | Cite du Vin is a wine theme park in Bordeaux | |
| − | + | Lascaux is the setting of a complex of caves in southwestern France famous for its cave paintings. The original caves are located near the village of Montignac, in the department of Dordogne. They contain some of the best-known Upper Paleolithic art. Since 1998 the cave has been beset with a fungus | |
| − | + | Medoc is well known as a wine growing region on the left bank of the Gironde estuary, north of Bordeaux | |
| − | + | Limoges is famous for porcelain | |
| − | + | Limousin is situated largely in the Massif Central | |
| + | |||
| + | The port of La Rochelle is in Poitou-Charantes | ||
| + | |||
| + | Futuroscope is a French theme park based upon multimedia, cinematographic and audio-visual techniques. It is located 10 km north of Poitiers | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gironde estuary is formed from the meeting of the rivers Dordogne and Garonne just downstream of Bordeaux | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ile d’Oleron is an island west of Rochefort. It is the second largest island of Metropolitan France, after Corsica | ||
| + | '''Occitanie''' | ||
| − | + | Former regions – Midi-Pyrenees (capital – Toulouse) and Languedoc-Roussillon (capital – Montpellier) | |
| − | Capital – | + | Capital – Toulouse |
| − | + | Musee Fabre is an art and sculpture museum in Montpellier | |
| + | Pont du Gard is an aqueduct constructed by the Roman Empire, and located near Remoulins, in the Gard department, close to Nimes | ||
| − | + | Odeillo solar furnace is the world largest solar furnace | |
| − | + | Toulouse lies on the River Garonne | |
| − | + | Millau Viaduct is 270 m high and is the largest cable-stayed bridge in the world. Largest pylon is 343 m high. A75 road over the River Tarn. Designed by Norman Foster and Michel Virlogeux | |
| − | + | Pech Merle, a hillside opening in the Lot department of Midi-Pyrenees region, is the site of one of the prehistoric cave paintings remaining in France | |
| − | + | Cathedral Basilica of Saint Cecilia, also known as Albi Cathedral, was constructed from 1282 to 1480, built in the wake of the Albigensian heresy of the Cathars and the brutal crusade brought against it. This crusade, led by Simon de Montfort, involved the burning of 400 Cathars. It is claimed to be the largest brick building in the world | |
| − | + | Cevennes range of mountains is on the southeast edge of the Massif Central | |
| − | + | '''Pays-de-la-Loire''' | |
| + | Capital – Nantes | ||
| − | + | Nantes is on the banks of the River Loire | |
| − | + | Angers is a city in the Maine-et-Loire department and is the historical capital of Anjou | |
| − | + | Chantiers de l'Atlantique, one of the largest shipyards in the world, is located in Saint-Nazaire | |
| + | Sarthe is a department, named after the river Sarthe. Le Mans is a city in Sarthe | ||
| − | Provence-Alpes-Cote d’Azur | + | '''Provence-Alpes-Cote d’Azur''' |
Capital – Marseille | Capital – Marseille | ||
| Line 646: | Line 841: | ||
Nice is the capital of the Alpes-Maritimes department | Nice is the capital of the Alpes-Maritimes department | ||
| − | + | The largest Orthodox cathedral in Western Europe is in Nice | |
Promenada des Anglais is in Nice | Promenada des Anglais is in Nice | ||
| + | |||
| + | Marc Chagall National Museum and Musee Matisse are in Nice | ||
Alpes-Maritimes was created by Octavian as a Roman military district in 14 BC | Alpes-Maritimes was created by Octavian as a Roman military district in 14 BC | ||
| Line 656: | Line 853: | ||
Marseille is Europe’s largest Muslim city | Marseille is Europe’s largest Muslim city | ||
| − | Miramar restaurant is in | + | Miramar restaurant is in Marseille |
| − | La Ciotat, near | + | La Ciotat, near Marseille, was the setting of one the very first projected motion pictures, ''L'Arrivée d'un train en gare de La Ciotat'' filmed by the Lumiere brothers in 1895 |
L'Estaque is a fishing village just west of Marseille. Many artists of the Impressionist and Post-Impressionist periods visited or resided there or in the surrounding area | L'Estaque is a fishing village just west of Marseille. Many artists of the Impressionist and Post-Impressionist periods visited or resided there or in the surrounding area | ||
| Line 666: | Line 863: | ||
Pont Saint-Benezet, also known as the Pont d'Avignon, is a famous medieval bridge in the town of Avignon, in southern France. The bridge originally spanned the Rhone River between Avignon and Villeneuve-les-Avignon on the left bank. It was built between 1171 and 1185 | Pont Saint-Benezet, also known as the Pont d'Avignon, is a famous medieval bridge in the town of Avignon, in southern France. The bridge originally spanned the Rhone River between Avignon and Villeneuve-les-Avignon on the left bank. It was built between 1171 and 1185 | ||
| − | The first museum in the world to be dedicated to Picasso is in Antibes | + | The first museum in the world to be dedicated to Pablo Picasso is in Antibes |
The military port of Toulon is the major naval centre on France's Mediterranean coast | The military port of Toulon is the major naval centre on France's Mediterranean coast | ||
| Line 674: | Line 871: | ||
Mont Ventoux is a mountain in Provence. Mistral wind speeds can reach 200 mph. Mont Ventoux has become legendary as the scene of one of the most grueling climbs in the Tour de France | Mont Ventoux is a mountain in Provence. Mistral wind speeds can reach 200 mph. Mont Ventoux has become legendary as the scene of one of the most grueling climbs in the Tour de France | ||
| + | The river Rhone forks into two branches just upstream of Arles, forming the Camargue delta. Because the Camargue is for a large part administratively part of Arles, the commune is the largest commune in Metropolitan France in terms of territory | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | River Loire is the longest river entirely in France. It rises in the Massif Central in the Cevennes range; it flows north through Nevers to Orléans, then west through Tours and Nantes until it reaches the Bay of Biscay at Saint-Nazaire | |
| − | + | River Seine is the second longest river entirely in France. It rises northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre | |
| − | + | Tarn and Lot are tributaries of the Garonne | |
| − | + | River Dordogne rises in Massif Central and unites with the Garonne to form the Gironde estuary | |
| + | Bay of Biscay is known in France as the Gulf of Gascony | ||
| − | + | Canal du Midi runs from the city of Toulouse down to the Mediterranean port of Sete | |
| − | + | Malpas tunnel was excavated in 1679, allowing the passage of the Canal du Midi. It was Europe's first navigable canal tunnel | |
| − | + | Mer de Glace ("Sea of Ice") is a valley glacier located on the northern slopes of the Mont Blanc massif, in the French Alps. It is the second longest in the Alps after the Aletsch Glacier | |
| − | + | === Overseas regions === | |
| + | The five overseas regions of France are Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion | ||
| + | The overseas collectivities are first-order administrative divisions of France. The five collectivities are Saint Barthelemy, Saint Martin, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Wallis and Futuna, and French Polynesia | ||
| + | New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France | ||
| − | + | The term overseas territory is an administrative division of France and is currently only applied to the French Southern and Antarctic Lands. Includes Kerguelen Islands and Amsterdam Island | |
| − | + | == Georgia == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Georgia.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | Flag of Georgia, known as the Five Cross Flag, was adopted in 2004 | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Tbilisi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Tbilisi, Batumi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Lari | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Shkhara | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Georgia contains two ''de facto'' independent regions, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, which gained limited international recognition after the 2008 Russo-Georgian War | ||
| − | + | Georgia is known as Sakartvelo in Georgia | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Tbilisi is on the River Kura | |
| − | + | Tbilisi was also capital of the Democratic Republic of Georgia from 1918 to 1921, the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic from 1921 to 1991, and the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic from 1922 to 1936 | |
| − | + | Veryovkina Cave and Krubera Cave are the deepest-known caves on Earth. They are located in Abkhazia | |
| + | == Germany == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Germany.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Berlin | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, Cologne, Frankfurt | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Zugspitze | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Germany is a Federal Republic made up of 16 States, known as Lander. The term Bundeslander (‘states of the federation’) is commonly used as it is more specific. Three cities (Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg) are states in their own right, termed Stadtstaaten (‘city states’). The remaining 13 states are termed Flachenlander (‘area states’) | ||
| − | The | + | Nine countries share a land border with Germany. The longest land border is with Austria |
| + | [[File:States of Germany.svg|none|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | <u>City states</u> | |
| + | '''Berlin''' | ||
| − | + | Unter den Linden (‘under the lime trees’) is an area east of Brandenburg Gate | |
| − | + | Brandenburg Gate is located on the Pariser Platz. It consists of 12 Doric columns, and above the gate is the Quadriga consisting of the goddess of peace driving a four-horse chariot, a design based on the Propylea (the gateway to the Acropolis). Designed by Carl Langhans | |
| + | Kaufhaus des Westens, or KaDeWe, is the second largest department store in Europe after Harrods | ||
| − | + | Tiergarten is an inner-city park in Berlin | |
| − | + | Kulturforum is a collection of cultural buildings in Berlin | |
| − | + | Oberhaum Bridge is a double-deck bridge crossing the Spree river | |
| − | + | Berlin Central Station (Berlin Hauptbahnhof) began full operation in 2006. It is located on the site of the historic Lehrter Bahnhof | |
| + | Tempelhof was designated as an airport in 1923. Tempelhof was one of Europe's three iconic pre-World War II airports, the others being London’s Croydon Airport and the old Paris–Le Bourget Airport | ||
| − | + | Tegel airport was built in 1948 for the Berlin airlift. Tegel Airport is named after Otto Lilienthal, the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful gliding flights | |
| − | + | Berlin Brandenburg Airport is named after Willy Brandt. The new airport replaced Tempelhof, Schonefeld, and Tegel airports, and opened in 2020 | |
| − | + | Berlin orbital motorway (BAB 10) is 196 km long, and is the longest orbital in Europe | |
| + | '''Bremen''' | ||
| − | + | The state consists of two cities (Bremen and Bremerhaven) and is the smallest German state | |
| + | River Weser flows through Bremen and Bremerhaven | ||
| − | + | Town Musicians of Bremen is a statue depicting a donkey, a dog, a cat, and a rooster from a fairy tale by the Brothers Grimm | |
| − | + | '''Hamburg''' | |
| − | + | Hamburg is officially known as the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg | |
| − | + | The port of Hamburg, on the river Elbe, is the second largest port in Europe (after the Port of Rotterdam) | |
| − | The | + | The area of Reeperbahn in the quarter St. Pauli is Europe's largest red-light district |
| − | + | Hamburg is the largest non-capital city in the European Union | |
| − | + | Miniatur Wunderland is the world's largest model railway museum | |
| − | + | Hamburg's rivers and canals are crossed by around 2,500 bridges, making it the city with the highest number of bridges in Europe | |
| − | + | <u>Area states</u> | |
| − | + | '''Baden-Wurttemberg''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Stuttgart | |
| − | + | Restaurant Top Air in Stuttgart Airport has a Michelin star | |
| − | + | Stuttgart is on the Neckar river | |
| − | + | Ulm is primarily known for its Ulm Munster (a Lutheran cathedral and the tallest church in the world, its steeple measuring 530 ft high) and as the birthplace of Albert Einstein. It lies on the Danube | |
| − | + | Ruins of Heidelberg Castle are among the most important Renaissance structures north of the Alps | |
| + | Heidelberg is on the Neckar river | ||
| − | + | The Rhine joins the Necker at Mannheim | |
| − | |||
| − | The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Hockenheimring race track was built in 1932 | |
| − | + | Busingen is a German exclave surrounded by Switzerland | |
| + | Europa-Park is located in Rust. It is the second most popular theme park in Europe, after Disneyland Paris | ||
| − | Bavaria | + | '''Bavaria''' |
Capital – Munich | Capital – Munich | ||
| Line 819: | Line 1,030: | ||
Olympic Stadium in Munich was designed by the German architect Günther Behnisch and the engineer Frei Otto. Design included large sweeping canopies of acrylic glass stabilized by steel cables that were used for the first time in a large scale | Olympic Stadium in Munich was designed by the German architect Günther Behnisch and the engineer Frei Otto. Design included large sweeping canopies of acrylic glass stabilized by steel cables that were used for the first time in a large scale | ||
| + | |||
| + | Munich is on the River Isar | ||
Pilgrimage Church of Wies is an oval rococo church in Bavaria, designed in the 1740s by Dominikus Zimmermann | Pilgrimage Church of Wies is an oval rococo church in Bavaria, designed in the 1740s by Dominikus Zimmermann | ||
| Line 825: | Line 1,038: | ||
Nuremberg is in Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia | Nuremberg is in Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Coburg was one of the capitals of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha until 1918 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Augsburg was named after Emperor Augustus | ||
Regensburg, historically also Ratisbon, is a city in Bavaria | Regensburg, historically also Ratisbon, is a city in Bavaria | ||
| Line 830: | Line 1,047: | ||
Wurzburg Residence is a palace in Wurzburg. Balthasar Neumann, architect of the court of the Bishop of Wurzburg, was the principal architect. Giovanni Tiepolo, assisted by his son, Domenico, painted frescoes in the building | Wurzburg Residence is a palace in Wurzburg. Balthasar Neumann, architect of the court of the Bishop of Wurzburg, was the principal architect. Giovanni Tiepolo, assisted by his son, Domenico, painted frescoes in the building | ||
| + | Rhine–Main–Danube Canal connects the North Sea and Atlantic Ocean to the Black Sea | ||
| − | Brandenburg | + | '''Brandenburg''' |
Capital – Potsdam | Capital – Potsdam | ||
| − | Sanssouci is the former summer palace of Frederick the Great, King of Prussia, in Potsdam | + | Sanssouci is the former summer palace of Frederick the Great, King of Prussia, in Potsdam. Sanssouci means ‘without worries’ |
| + | |||
| + | Cecilienhof Palace is built in the layout of an English Tudor manor house. It was the location of the Potsdam Conference in 1945 | ||
| + | Glienicke Bridge across the Havel River connects the Wannsee district of Berlin with Potsdam. Known as the “Bridge of Spies” during the Cold War | ||
| − | Hesse | + | '''Hesse''' |
Capital – Wiesbaden | Capital – Wiesbaden | ||
| Line 844: | Line 1,065: | ||
Wiesbaden is one of the oldest spa towns in Europe. Its name literally means ‘meadow baths’ | Wiesbaden is one of the oldest spa towns in Europe. Its name literally means ‘meadow baths’ | ||
| − | Frankfurt is the largest city in Hesse | + | Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main, is the largest city in Hesse |
Frankfurt is home to the European Central Bank and the German Federal Bank | Frankfurt is home to the European Central Bank and the German Federal Bank | ||
Frankfurt Stock Exchange is the largest in Germany | Frankfurt Stock Exchange is the largest in Germany | ||
| + | |||
| + | Frankfurt is known as “Mainhattan” due to the large number of skyscrapers | ||
| + | |||
| + | Commerzbank Tower is the tallest building in Germany. It was designed by Norman Foster | ||
Messel Pit is a disused quarry near the village of Messel, close to Frankfurt. Bituminous shale was mined there. Because of its abundance of fossils, it has significant geological and scientific importance | Messel Pit is a disused quarry near the village of Messel, close to Frankfurt. Bituminous shale was mined there. Because of its abundance of fossils, it has significant geological and scientific importance | ||
| + | '''Lower Saxony''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capital – Hanover | ||
| − | Lower Saxony | + | Hanover is the largest city in Lower Saxony |
| − | + | Hanover is on the River Leine | |
The northwestern area of Lower Saxony, which lies on the coast of the North Sea, is called East Frisia | The northwestern area of Lower Saxony, which lies on the coast of the North Sea, is called East Frisia | ||
| − | + | '''Mecklenburg-Vorpommern''' | |
| − | Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | ||
State is also known as Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania in English | State is also known as Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania in English | ||
| Line 866: | Line 1,093: | ||
Capital – Schwerin | Capital – Schwerin | ||
| − | Mecklenburg | + | Mecklenburg is the region between Berlin and Hamburg |
| − | Rostock | + | Rostock is the largest city and the principal overseas port of the former GDR |
Mecklenburg Lake District is sometimes called "the land of a thousand lakes" | Mecklenburg Lake District is sometimes called "the land of a thousand lakes" | ||
| Line 876: | Line 1,103: | ||
Prora is a beach resort on the island of Rugen, known especially for its colossal Nazi-planned touristic structures. The massive building complex was built between 1936 and 1939 | Prora is a beach resort on the island of Rugen, known especially for its colossal Nazi-planned touristic structures. The massive building complex was built between 1936 and 1939 | ||
| − | + | '''North-Rhine Westphalia''' | |
| − | North-Rhine Westphalia | ||
Capital – Dusseldorf | Capital – Dusseldorf | ||
| Line 883: | Line 1,109: | ||
North-Rhine Westphalia is the most populous lander | North-Rhine Westphalia is the most populous lander | ||
| − | Cologne | + | Cologne became acknowledged as a city by the Romans in 50 AD |
| + | |||
| + | Cologne Bonn Airport is named after Konrad Adenauer | ||
| + | |||
| + | Museum Lugwig is a modern art museum in Cologne | ||
| − | + | Bonn is the second official seat and second official residence of the President of Germany, the Chancellor of Germany, the Bundesrat, and the first official seat and first official residence of six German federal ministries | |
| − | + | Bonn was the capital of West Germany from 1949 to 1990 | |
| − | + | Duisburg lies on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers and is the largest inland port in Europe | |
| − | + | Charlemagne is buried in Aachen Cathedral, the oldest cathedral in northern Europe | |
| − | + | Bielefeld is well known for the Bielefeld conspiracy, which satirises conspiracy theories by claiming that Bielefeld does not exist | |
| − | + | Wuppertal Schwebebahn is a suspension railway (a form of elevated monorail) that started operations in 1901 | |
| + | Neuss is primarily known for its historic Roman sites. Neuss and Trier share the title of "Germany's oldest city" | ||
| − | Rhineland-Palatinate | + | '''Rhineland-Palatinate''' |
Capital – Mainz | Capital – Mainz | ||
| + | |||
| + | To celebrate the 400th anniversary of his death, the Gutenberg Museum was founded in 1900 in Johannes Gutenberg’s hometown of Mainz | ||
| + | |||
| + | Trier lies on the banks of the Moselle. It was founded by the Celts in the 4th century BC as Treuorum and conquered 300 years later by the Romans | ||
Porta Nigra (Latin for ‘black gate’) is a large Roman city gate in Trier. It is today the largest Roman city gate north of the Alps and has been designated a World Heritage Site | Porta Nigra (Latin for ‘black gate’) is a large Roman city gate in Trier. It is today the largest Roman city gate north of the Alps and has been designated a World Heritage Site | ||
| Line 912: | Line 1,147: | ||
The wine festival called Wurstmarkt in Bad Durkheim is the largest wine festival in the world | The wine festival called Wurstmarkt in Bad Durkheim is the largest wine festival in the world | ||
| − | + | '''Saarland''' | |
| − | Saarland | ||
Capital – Saarbrucken | Capital – Saarbrucken | ||
| − | Apart from the city states, it is Germany's smallest federal state | + | Apart from the city states, it is Germany's smallest federal state. It has borders with France and Luxembourg |
| − | |||
| − | Saxony | + | '''Saxony''' |
Capital – Dresden | Capital – Dresden | ||
| − | + | Dresden is known as the ‘Florence of the Elbe’ and the ‘Florence of the North’ | |
| − | + | Frauenkirche (Church of Our Lady) is a Lutheran church in Dresden. It was destroyed in the bombing of Dresden during World War II, and the ruins were left for 50 years as a war memorial. The church was rebuilt after the reunification of Germany | |
| − | Dresden | + | Zwinger is a palace in Dresden and a major landmark of German baroque architecture |
Leipzig is the largest city in Saxony | Leipzig is the largest city in Saxony | ||
| Line 936: | Line 1,169: | ||
Chemnitz was known as Karl-Marx-Stadt between 1953 and 1990 | Chemnitz was known as Karl-Marx-Stadt between 1953 and 1990 | ||
| + | In 2009, UNESCO voted to remove the status of World Heritage Site from the Dresden Elbe Valley on the basis of the Waldschlosschen Bridge that was under construction and would bisect the valley. The bridge opened in 2013 | ||
| − | Saxony-Anhalt | + | '''Saxony-Anhalt''' |
Capital – Magdeburg | Capital – Magdeburg | ||
| Line 945: | Line 1,179: | ||
Brocken – the highest peak of the Harz mountain range and also the highest peak of Northern Germany | Brocken – the highest peak of the Harz mountain range and also the highest peak of Northern Germany | ||
| − | + | '''Schleswig-Holstein''' | |
| − | Schleswig-Holstein | ||
Capital – Kiel | Capital – Kiel | ||
| − | + | Kiel is known for a variety of international sailing events, including the annual Kiel Week, which is the biggest sailing event in the world. It is a major high-tech shipbuilding centre | |
| − | + | Lubeck was the largest and most powerful member of the Hanseatic League | |
| + | Lubeck is the second-largest German Baltic port after the port of Rostock | ||
| − | + | St. Mary's Church in Lubeck was built in Gothic architecture style using north German brick. It has the tallest brick vault in the world | |
| − | + | Holsten Gate is a city gate marking off the western boundary of the old centre of Lubeck. It is known for its two-round towers and arched entrance | |
| − | + | Heligoland – German island in the North Sea. Matches the description of Azkaban in the Harry Potter books | |
| + | Kiel Canal links the North Sea with the Baltic Sea. It is the world’s busiest artificial waterway | ||
| − | + | Sylt is the northernmost island of Germany and is known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It is one of the North Frisian Islands in the Wadden Sea | |
| − | + | '''Thuringia''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Erfurt | |
| − | + | Weimar was a focal point of the German Enlightenment. The Bauhaus movement was founded in Weimar in 1919 | |
| − | + | Jena is the second largest city in Thuringia, after Erfurt | |
| − | + | Wartburg Castle is in Eisanach | |
| − | + | The Bachhaus in Eisanach was the first museum worldwide to be dedicated to the life and work of Johann Sebastian Bach, who was born there | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Danube river originates in the Black Forest in Germany as two smaller rivers: the Brigach and the Breg rivers | |
| − | + | Meissen, Pardubice, Wittenberg, Dessau, Magdeburg and Cuxhaven are on the Elbe river | |
| − | + | Swabia is normally thought of as comprising the former German state of Wurttemberg (with the Prussian Hohenzollern Province) and the administrative region of Bavarian Swabia | |
| − | + | Harz National Park is a nature reserve in the federal states of Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt. It comprises large portions of the western Harz mountain range | |
| − | + | Reichenau Island lies in Lake Constance. It was declared a World Heritage Site in 2000 because of its monastery, the Abbey of Reichenau | |
| − | North | + | Teutoburg forest – range of low forested mountains in Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Fulda Gap is an area between the Hesse-Thuringian border and Frankfurt. During the Cold War, the Fulda Gap offered a route for a hypothetical Soviet tank attack on West Germany | ||
| + | == Greece == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Greece.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Athens | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Athens, Thessaloniki | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mount Olympus | ||
| + | |} | ||
Parthenon is a temple of the Greek goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their protector. Its construction began in 447 BC and was completed in 438 BC on the Athenian Acropolis, although decorations of the Parthenon continued until 431 BC. It is the most important surviving building of Classical Greece, generally considered to be the culmination of the development of the Doric order | Parthenon is a temple of the Greek goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their protector. Its construction began in 447 BC and was completed in 438 BC on the Athenian Acropolis, although decorations of the Parthenon continued until 431 BC. It is the most important surviving building of Classical Greece, generally considered to be the culmination of the development of the Doric order | ||
| Line 1,001: | Line 1,248: | ||
Athens is known as the “violet crowned city” | Athens is known as the “violet crowned city” | ||
| + | |||
| + | Panathenaic Stadium in Athens is the only stadium made entirely of marble | ||
The Philippeion in the Altis of Olympia was an Ionic circular memorial of ivory and gold, which contained statues of Philip's family and Alexander the Great. It was made by the Athenian sculptor Leochares in celebration of Philip's victory at the battle of Chaeronea (338 BC) | The Philippeion in the Altis of Olympia was an Ionic circular memorial of ivory and gold, which contained statues of Philip's family and Alexander the Great. It was made by the Athenian sculptor Leochares in celebration of Philip's victory at the battle of Chaeronea (338 BC) | ||
| − | + | Thessaloniki or Salonica is Greece’s second-largest city and the capital of Macedonia, the largest region of Greece | |
| − | + | Great Thessaloniki Fire of 1917 destroyed two thirds of the city | |
| − | + | The region of Argos, in Greece is called the Argolid. The inhabitants of Argos were called Argives | |
| − | + | Cape Matapan is the southernmost point of Greek mainland | |
| − | + | Piraeus is the largest port in Europe (and third largest in the world) in terms of passenger transportation, servicing 19 million passengers annually | |
| − | + | Gulf of Corinth is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece. In medieval times, the gulf was known as the Gulf of Lepanto | |
| − | + | Corinth Canal connects the Gulf of Corinth with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea. It cuts through the narrow Isthmus of Corinth and separates the Peloponnesian peninsula from the Greek mainland. Completed in 1893. The canal has been closed since the beginning of 2021 after a landslide | |
| − | + | Corinth was founded as New Corinth in 1858 after an earthquake destroyed the existing settlement of Corinth | |
| − | + | Rion-Antirion Bridge is one of the world's longest multi-span cable-stayed bridge. It crosses the Gulf of Corinth near Patras, linking the town of Rion on the Peloponnese to Antirion on mainland Greece | |
| − | + | Cadmea was the citadel of ancient Thebes, named after Cadmus | |
| − | + | Apidima cave is located on the Mani Peninsula. Neanderthal and Homo sapiens fossils have been found at the cave | |
| − | + | Meteora is a rock formation in Greece that is host to six Eastern Orthodox monasteries | |
| − | + | Mount Athos in Macedonia is a self-governed state in the Hellenic Republic. Referred to in Greek as the ‘Holy Mountain’ | |
| − | + | Athos is an important centre of Eastern Orthodox monasticism | |
| − | + | Arcadia is a region of Greece in the Peloponnese. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas | |
| − | + | Mycanae, in the Peloponnese, was Agamemnon’s capital, and is the site of the Lion Gate, the main entrance of the Mycanae citadel | |
| − | + | The city of Pavlopetri, underwater off the coast of southern Laconia in Peloponnese, is about 5000 years old, and is the oldest submerged archeological town site. It is unique in having an almost complete town plan | |
| − | + | Delphi is both an archaeological site and a modern town in Greece on Mount Parnassus | |
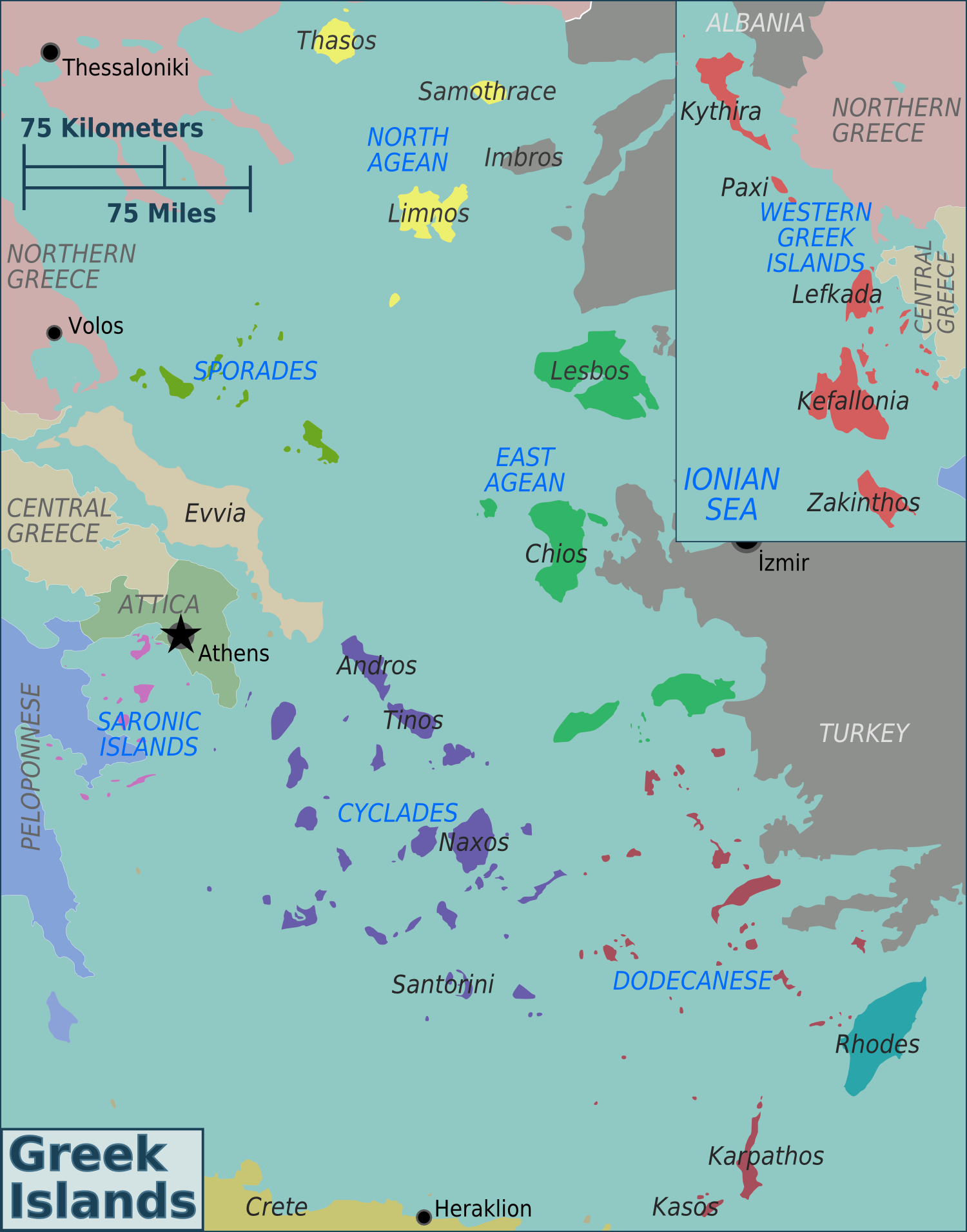
| − | + | <u>Greek Islands</u> | |
| + | [[File:Greek Islands regions map.png|center|thumb|573x573px]] | ||
| − | Rhodes | + | Largest islands – Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes, Chios |
| − | + | Crete is the most populous of the Greek islands | |
| − | + | Palace of Knossos is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and probably the ceremonial and political centre of the Minoan civilization and culture | |
| − | + | Heraklion is the capital of Crete | |
| − | + | Mount Ida is the highest point in Crete | |
| − | + | Chania is an old city and port on Crete | |
| − | + | The island of Gavdos is located to the south of Crete. it is the southernmost point of Europe | |
| − | + | Euboea, also known as Evia, is the second largest of the Aegean Islands, after Crete. The chief town is Chalcis, that was known as Negroponte In the Late Middle Ages | |
| − | + | Lesbos is located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. Capital city is Mytilene. Home of the ancient Greek poet Sappho | |
| − | + | Chios is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mastic gum. It was the site of the Chios massacre during the Greek War of Independence in 1822 | |
| + | |||
| + | Lemnos is an island in the northern part of the Aegean Sea. The principal town is Myrina | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Ionian Islands''' are in the Ionian Sea, west of Mainland Greece. They are known as the Hepanese (‘seven islands’) but the group includes many smaller islands | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kefalonia is the largest of the Ionian Islands | ||
| + | |||
| + | Argostoli is the capital of Kefalonia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Corfu or Kerkyra is the second largest island. The northeastern edge of Corfu lies off the coast of Sarande, Albania | ||
| + | |||
| + | The other major islands are Cythera, Ithaca, Lefkas, Paxos, and Zante | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Cyclades''' are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece | ||
| + | |||
| + | Naxos is the largest of the Cyclades. The island is famous as a source of emery | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syros is the most populous island. Ermoupoli, the capital of the Cyclades, is on the island | ||
| + | |||
| + | Andros is the northernmost island of the Cyclades, 10 km southeast of Euboea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Santorini is the southernmost island of the Cyclades. The island was the site of the Minoan eruption, that was one of the largest volcanic eruptions in recorded history | ||
| + | |||
| + | Akrotiri is an ancient city buried, and preserved by, the volcanic ash on the island of Santorini | ||
| + | |||
| + | Milos and Mykanos are islands in the Cyclades | ||
| − | + | '''Dodecanese''' (‘twelve islands’) are a group of islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia | |
| − | + | Rhodes is the largest of the Dodecanese Islands. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Rhodes. Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem ruled the island from 1310 to 1522 | |
| − | + | Colossus of Rhodes was a statue of the Greek sun-god Helios, erected by Chares of Lindos in 280 BC. One of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World | |
| − | + | Faliraki is the primary seaside resort village on Rhodes | |
| − | + | Acropolis of Lindos on Rhodes is a natural citadel | |
| − | + | Kos is the third largest of the Dodecanese by area, after Rhodes and Karpathos, and the second largest by population | |
| − | + | Patmos is famous as the location where John of Patmos received the visions found in the Book of Revelation of the New Testament, and where the book was written | |
| − | + | Monastery of Saint John the Theologian is a Greek Orthodox monastery founded in 1088 on the island of Patmos | |
| − | + | '''Sporades''' are a group of 24 islands northeast of Euboea. There are four permanently inhabited islands – Alonnisos, Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros | |
| + | Rupert Brooke is buried on Skyros | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Saronic Islands''' are named after the Saronic Gulf in which they are located. The main inhabited islands of this group are Salamis, Aegina, Agistri, and Poros |
| + | == Hungary == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Hungary.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Budapest | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Budapest, Debrecen, Szeged | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Forint | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Kekes | ||
| + | |} | ||
Budapest is the combination of the city names Buda and Pest, which were (together with Obuda) united into a single city in 1873 | Budapest is the combination of the city names Buda and Pest, which were (together with Obuda) united into a single city in 1873 | ||
| Line 1,097: | Line 1,389: | ||
The ancient city of Aquincum was situated on the North-Eastern borders of the Pannonia province within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found today in Budapest | The ancient city of Aquincum was situated on the North-Eastern borders of the Pannonia province within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found today in Budapest | ||
| − | + | Shoes on the Danube Bank is a memorial to honour the Jews who were massacred by fascist Hungarian militia in Budapest during the Second World War | |
| − | + | Szeged is known as the home of paprika | |
| + | Pecs was a 2010 European Capital of Culture | ||
| − | + | Kelenfold Power Station was the largest electrical generation plant in the world after its construction in 1912 | |
| − | Mount Hekla is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes | + | Lake Balaton is the largest lake in Central Europe |
| + | |||
| + | == Iceland == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Iceland.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Reykjavik | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Reykjavik, Kopavogur | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Krona | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Hvannadalshnjukur | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Iceland observes Greenwich Mean Time all year round | ||
| + | |||
| + | Keflavik International is the largest airport in Iceland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reykjavik is the most northerly capital in the world | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mount Hekla is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes | ||
Vatnajokull (meaning ‘Glacier of Rivers’), also known as the Vatna Glacier, is the largest and most voluminous Icelandic glacier | Vatnajokull (meaning ‘Glacier of Rivers’), also known as the Vatna Glacier, is the largest and most voluminous Icelandic glacier | ||
| Line 1,110: | Line 1,426: | ||
Eyjafjallajokull lies 25 km west of another subglacial volcano, Katla, which is much more active and known for its powerful subglacial eruptions and its large magma chamber. Each of the eruptions of Eyjafjallajokull in 920, 1612, and 1821–1823 has preceded an eruption of Katla | Eyjafjallajokull lies 25 km west of another subglacial volcano, Katla, which is much more active and known for its powerful subglacial eruptions and its large magma chamber. Each of the eruptions of Eyjafjallajokull in 920, 1612, and 1821–1823 has preceded an eruption of Katla | ||
| − | Eyjafjallajokull erupted in 2010 | + | Eyjafjallajokull erupted in 2010, causing enormous disruption to air travel across northern and western Europe for a week |
Katla last erupted in 1918 | Katla last erupted in 1918 | ||
| Line 1,121: | Line 1,437: | ||
In 1973 a volcanic eruption of the mountain Eldfell began on Heimaey. Townspeople constantly sprayed the lava with cold seawater, causing some of it to solidify and much to be diverted, thus saving the harbour from destruction | In 1973 a volcanic eruption of the mountain Eldfell began on Heimaey. Townspeople constantly sprayed the lava with cold seawater, causing some of it to solidify and much to be diverted, thus saving the harbour from destruction | ||
| + | |||
| + | Silfra is a rift formed in the divergent tectonic boundary between the North American and Eurasian plates. It is popular with scuba divers | ||
Karahnjukar is Europe’s biggest dam and is part of a hydroelectricity plant | Karahnjukar is Europe’s biggest dam and is part of a hydroelectricity plant | ||
| Line 1,126: | Line 1,444: | ||
Surtsey, one of the youngest islands in the world, is part of Iceland. It rose above the ocean in a series of volcanic eruptions between 1963 and 1968 | Surtsey, one of the youngest islands in the world, is part of Iceland. It rose above the ocean in a series of volcanic eruptions between 1963 and 1968 | ||
| + | Dettifoss is a waterfall in Vatnajokull National Park, and is reputed to be the most powerful waterfall in Europe | ||
| − | ' | + | Blue Lagoon is a geothermal spa supplied by water used in the nearby Svartsengi geothermal power station. The water's milky blue shade is due to its high silica content |
| − | + | Gullfoss and Skogafoss are waterfalls in Iceland | |
| − | + | == Ireland == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Ireland.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Dublin | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Dublin, Cork, Limerick, Galway, Waterford | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Carrauntoohil | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Ireland has historically been divided into four provinces: Connacht, Leinster, Munster and Ulster. There were once five; the fifth province, Meath, was incorporated into Leinster, with parts going to Ulster | ||
| + | Ireland is divided into 32 ‘traditional counties’ | ||
| − | + | '''Connacht''' is in the west of Ireland, and is the smallest province in terms of area and population. The province is divided into five traditional counties – Galway, Leitrim, Mayo, Roscommon and Sligo | |
| − | + | Galway has an International Oyster Festival every September | |
| − | + | The Claddagh is a beach area in the western part of Galway. People have been gathering seafood and fishing from the area for millennia. Historically, its existence has been recorded since the arrival of Christianity in the 5th century. Claddagh ring is a traditional Irish ring | |
| − | + | The Twelve Bens or Twelve Pins is a mountain range in Connemara | |
| + | Benbulben is a large rock formation in County Sligo | ||
| − | + | Aran Islands are a group of three islands located at the mouth of Galway Bay. The islands are Inishmore, Inishmaan and Inisheer | |
| − | + | Knock Shrine is a pilgrimage site in County Mayo, where it is claimed there was an apparition of the Blessed Virgin Mary, Saint Joseph, John the Evangelist, angels and Jesus Christ in 1879 | |
| − | + | Croagh Patrick '(Saint) Patrick's stack') is a mountain and an important site of pilgrimage in County Mayo | |
| + | Achill Island is the largest of the Irish isles and lies off the coast of County Mayo | ||
| − | + | '''Leinster''' is in the east of Ireland, and is the largest province in terms of population. The province is divided into 12 traditional counties – Carlow, Dublin, Kildare, Kilkenny, Laois, Longford, Louth, Meath, Offaly, Westmeath, Wexford and Wicklow | |
| − | + | Dublin means ‘dark pool’. Baile Atha Cliath is the Irish name for Dublin | |
| − | + | Abbey Theatre was founded by Lady Gregory, Edward Martyn and W.B. Yeats in 1899 and opened in 1904 | |
| − | + | Olympia Theatre in Dublin was opened as ‘The Star of Erin’ music hall in 1879 | |
| − | + | Halfpenny Bridge is a pedestrian bridge across the River Liffey in Dublin. It is so called because this was the toll for pedestrians. The official name is Wellington Bridge | |
| − | + | The Custom House is a neoclassical 18th century building in Dublin which houses the Department of the Environment, Heritage and Local Government | |
| − | + | Temple Bar is promoted as ‘Dublin's cultural quarter’ | |
| − | + | O’Connell Street was known as Sackville Street until 1924 | |
| − | + | Spire of Dublin is a 121 m stainless steel monument on O’Connell Street, also known as ‘Bertie’s Pole’. Designed by Ian Ritchie Architects. It is a replacement for Nelson’s Pillar, which was destroyed by the IRA in 1966 | |
| − | + | Book of Kells is an illuminated manuscript, containing the four Gospels. The manuscript takes its name from the Abbey of Kells. It is on permanent display at Trinity College Library | |
| + | St. James's Gate Brewery was founded in 1759 by Arthur Guinness | ||
| − | + | Mountjoy prison has the largest prison population in Ireland | |
| − | + | The Chester Beatty Library was established in Dublin in 1950, to house the collections of mining magnate, Sir Alfred Chester Beatty | |
| − | + | Heuston and Connolly stations are the two main railway termini in Dublin | |
| − | + | Donnybrook Fair was held annually from 1204 to 1855. It ceased due to disorderly behaviour | |
| − | + | Anna Livia is a bronze monument in Dublin known as ‘the Floozie in the Jacuzzi’. The monument is a personification of the River Liffey. Moved from O’Connell Street to Croppies Memorial Park in 2006. Named after a character in ''Finnegan’s Wake'' | |
| + | Molly Malone is commemorated in a statue designed by Jeanne Rynhart, erected to celebrate the city's first millennium in 1988. Originally placed at the bottom of Grafton Street, the statue is known as ‘The Tart with the Cart’ | ||
| − | + | Newgrange is a passage tomb in County Meath. Newgrange was built in such a way that at dawn on the shortest day of the year, the winter solstice, a narrow beam of sunlight for a very short time illuminates the floor of the chamber at the end of the long passageway. Newgrange is the main monument in the Brú na Bóinne complex, a World Heritage Site | |
| − | + | Hill of Tara, located near the River Boyne, is an archaeological complex in County Meath. It contains a number of ancient monuments and, according to tradition, was the seat of the High King of Ireland | |
| − | + | Louth is the smallest county in Ireland | |
| − | + | '''Munster''' is in the southwest of Ireland and is the largest province in terms of area. The province is divided into six traditional counties – Clare, Cork, Kerry, Limerick, Tipperary and Waterford | |
| − | + | Cork is the largest county in Ireland | |
| − | + | Cork is the second largest city in Ireland. The city is built on the River Lee | |
| − | + | In 2005, Cork was selected as the European Capital of Culture | |
| − | + | Cork is home to the Heineken Brewery that brews Murphy’s Irish Stout | |
| − | + | Brow Head in County Cork is the most southerly point of mainland Ireland | |
| − | + | Cobh was first called Cove (‘The Cove of Cork’) in 1750. It was renamed Queenstown in 1850 to commemorate a visit by Queen Victoria. This remained the town's name until 1922 when it was renamed Cobh with the foundation of the Irish Free State. Queenstown was the final port of call for the RMS ''Titanic'' | |
| − | + | Bantry Bay is located in County Cork | |
| − | + | Blarney Stone is a block of limestone built into the battlements of Blarney Castle, about five miles from Cork. According to legend, kissing the stone endows the kisser with ‘the gift of gab’. The stone was set into a tower of the castle in 1446 | |
| − | + | Limerick lies on the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King’s Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and the Abbey River | |
| − | + | Tipperary was divided into North (capital – Nenagh) and South (capital – Clonmel) Ridings in 1838 | |
| − | + | Rock of Cashel in County Tipperary was the traditional seat of the kings of Munster for several hundred years prior to the Norman invasion | |
| − | + | Carrantuohill is the highest peak in Ireland. Located in County Kerry, it is 1,038 metres (3,406 ft) tall and is the central peak of the Macgillycuddy's Reeks range | |
| − | + | Dingle Peninsula is in County Kerry | |
| − | + | Burren is a karst limestone region of approximately 300 sq km which lies in the northwest corner of County Clare | |
| − | + | Cliffs of Moher are sea cliffs located at the southwestern edge of the Burren region | |
| − | + | Skellig Michael is an island off the coast of Kerry and is a World Heritage Site | |
| − | + | Gap of Dunloe is a mountain pass in County Kerry | |
| − | + | Tralee Bay is located off the coast of County Kerry | |
| + | In 1947, the ‘Customs Free Airport Act’ established Shannon as the world's first duty-free airport. Shannon Airport is in County Clare | ||
| − | + | '''Ulster''' is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three (Cavan, Donegal, and Monaghan) are in the Republic of Ireland | |
| − | + | Malin Head in Donegal is the northernmost point in Ireland | |
| − | |||
| − | + | River Shannon is 360 km in length and is the longest river in Ireland and the British Isles. It rises in County Cavan and empties into the Atlantic Ocean near Limerick. Athlone is located on the Shannon | |
| + | River Barrow is one of The Three Sisters; the other two being the River Suir and the River Nore. The Barrow is the longest of the three rivers. At 192 km, it is the second-longest river in Ireland | ||
| − | + | River Boyne flows through Leinster. Drogheda is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea | |
| − | + | M1 – Dublin to Dundalk | |
| − | + | M50 – Dublin ring road | |
| − | + | Fastnet Rock is the most southerly point of Ireland. Due to its location, Fastnet was known as ‘Ireland's Teardrop’, because it was the last part of Ireland that 19th century Irish emigrants saw as they sailed to North America | |
| − | + | Celtic Sea is the area of the Atlantic Ocean off the south coast of Ireland bounded to the east by Saint George's Channel; other limits include the Bristol Channel, the English Channel, and the Bay of Biscay | |
| − | + | == Italy == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Italy.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Rome | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Rome, Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mont Blanc | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Italy is subdivided into 20 regions | ||
| + | [[File:Regions of Italy with en-wiki names.png|none|thumb|link=Special:FilePath/Regions_of_Italy_with_en-wiki_names.png|alt=|400x400px]] | ||
| + | '''Abruzzo''' | ||
| − | + | Capital – L’Aquila | |
| − | + | Located on the Adriatic coast, Pescara is the most populated city in Abruzzo | |
| + | '''Aosta Valley''' | ||
| − | + | Capital – Aosta | |
| − | + | Aosta Valley is a mountainous semi-autonomous region in northwestern Italy. It is the smallest, least populous, and least densely populated region of Italy | |
| − | + | '''Apulia''' | |
| + | Capital – Bari | ||
| − | + | Apulia (Italian: Puglia) is a region in southeastern Italy bordering the Adriatic Sea in the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Otranto and Gulf of Taranto in the south. Its southern portion known as Salento, a peninsula, forms a high heel on the ‘boot’ of Italy | |
| − | + | Taranto is a coastal city in Apulia and is the main Italian naval base | |
| − | + | '''Basilicata''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Potenza | |
| + | Sassi settlements in Matera are known for their ancient cave dwellings inhabited since the Paleolithic period | ||
| − | + | '''Calabria''' | |
| − | Capital – | + | Capital – Catanzaro |
| − | + | Calabria is known as the ‘toe of Italy’s boot’. It is separated from Sicily by the Strait of Messina | |
| − | + | '''Campania''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Naples | |
| − | + | Capri is located in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the Sorrentine Peninsula, on the south side of the Gulf of Naples in the Campania region | |
| − | + | Villa Jovis is a Roman palace on Capri built by Roman emperor Tiberius | |
| − | + | Blue Grotto is a cave off the island of Capri | |
| − | + | Teatro di San Carlo is in Naples. It is the oldest continuously active venue for public opera in the world, opening in 1737 | |
| − | + | Sorrento overlooks the Bay of Naples as the key place of the Sorrentine Peninsula, and many viewpoints allow sight of Naples itself, Vesuvius and the Isle of Capri | |
| − | + | Museo di Capodimonte in Naples is the prime repository of Neapolitan painting and decorative art | |
| − | + | Castel dell'Ovo is the oldest standing fortification in Naples | |
| − | + | Castel Nuovo is a medieval castle located in front of Piazza Municipio and the city hall in central Naples | |
| − | + | Salerno is mostly known for its Schola Medica Salernitana, the first University of Medicine in the world | |
| − | + | Paestum was a major ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea in Magna Graecia | |
| + | Pompeii and Herculaneum were destroyed when Vesuvius erupted in 79 AD | ||
| − | + | Vesuvius last erupted in 1944 | |
| − | + | Amalfi Coast is a stretch of coastline on the southern side of the Sorrentine Peninsula of Italy (Province of Salerno), extending from Positano in the west to Vietri sul Mare in the east | |
| − | + | Lake Avernus is a volcanic crater lake. Avernus was of major importance to the Romans, who considered it to be the entrance to Hades | |
| − | + | '''Emilia-Romagna''' | |
| + | Capital – Bologna | ||
| − | + | Bologna is known as the Fat, Red, and the Learn'd City due to its rich cuisine, red Spanish tiled rooftops, left wing politics, and being home to the oldest university in the western world | |
| − | + | Towers of Bologna are a group of medieval structures. The two most prominent ones remaining, known as the Two Towers, are a landmark of the city | |
| − | + | Bologna Guglielmo Marconi Airport is an international airport serving the city of Bologna | |
| − | + | Rimini Airport is named after Federico Fellini | |
| − | + | Ravenna is known as ‘city of the mosaic’ | |
| − | + | Faience pottery was originally associated by French speakers with wares exported from Faenza in the province of Ravenna | |
| − | + | '''Friuli-Venezia Giulia''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Trieste | |
| − | + | As a prosperous seaport in the Mediterranean region, Trieste became the fourth largest city of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (after Vienna, Budapest, and Prague). Trieste was the main seaport of the Austro-Hungarian empire | |
| − | + | '''Lazio''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Rome | |
| − | + | The seven hills of Rome east of the river Tiber form the geographical heart of Rome, within the walls of the city. The seven hills are: Aventine Hill, Caelian Hill, Capitoline Hill, Esquiline Hill, Palatine Hill, Quirinal Hill, and Viminal Hill. Tradition holds that Romulus and Remus founded the original city on the Palatine Hill in 753 BC | |
| − | + | Trevi fountain was constructed in1762. Trevi means ‘three roads’. An estimated 3,000 Euros are thrown into the fountain each day. Designed by Nicola Salvi | |
| − | + | Spanish Steps is a monumental stairway of 138 steps was built with French diplomat Étienne Gueffier’s bequeathed funds of 20,000 scudi, in 1723–1725, linking the Bourbon Spanish Embassy, and the Trinita dei Monti church that was under the patronage of the Bourbon kings of France | |
| + | Fontana dei Quattro Fiumi (Fountain of the Four Rivers) is a fountain in the Piazza Navona in Rome. It was designed in 1651 by Gian Lorenzo Bernini for Pope Innocent X. River gods represent four major rivers of the four continents through which papal authority had spread: the Nile representing Africa, the Danube representing Europe, the Ganges representing Asia, and the Río de la Plata representing the Americas | ||
| − | + | Monte Mario is the highest hill in the modern city of Rome, Monte Mario is not one of the Seven Hills of Rome, being outside the boundaries of the ancient city | |
| − | + | Roma Termini is the central railway station in Rome | |
| − | + | Via Sacra was the main street of ancient Rome, leading from the top of the Capitoline Hill to the Colosseum | |
| − | + | Victor Emmanuel II Monument in Rome is known as the ‘Wedding Cake’ | |
| − | + | Tarpeian Rock was a steep cliff of the southern summit of the Capitoline Hill, overlooking the Roman Forum. It was used during the Roman Republic as an execution site | |
| − | + | Ostia was the port city of Ancient Rome | |
| − | + | Fiumicino–Leonardo da Vinci International Airport in Rome is the main hub for Alitalia | |
| − | + | At the time of the Emperor Augustus, Rome was the largest city in the world: with a population of about one million people | |
| − | + | Portus was a large artificial harbour of Ancient Rome. Sited on the north bank of the north mouth of the Tiber, it was established by Claudius and enlarged by Trajan to supplement the nearby port of Ostia | |
| + | Tivoli, the classical Tibur, is an ancient Italian town in Lazio, about 30 km east of Rome | ||
| − | + | Lake Nemi is a small circular volcanic lake. The lake is most famous for its sunken Roman ships | |
| − | + | Via Flaminia was an ancient road from Rome to Rimini | |
| − | + | Via Appia was an ancient road from Rome to Brindisi | |
| − | + | '''Liguria''' | |
| + | Capital – Genoa | ||
| − | + | Genoa is the largest commercial port in Italy | |
| − | + | Imperia is a coastal city and commune in the region of Liguria | |
| − | + | Sanremo Music Festival was first held in 1951 | |
| − | + | '''Lombardy''' | |
| − | + | Capital –Milan | |
| − | + | Biblioteca Ambrosiana is a historic library in Milan, also housing the Pinacoteca Ambrosiana art gallery. Named after Ambrose, the patron saint of Milan, it was founded by Cardinal Federico Borromeo | |
| − | + | Brera Art Gallery is the main public gallery for paintings in Milan | |
| − | + | Latin name for Milan was Mediolanum | |
| + | Milan Cathedral is the largest church in the Italian Republic. Construction began in 1386 and was completed in 1965 | ||
| − | + | La Scala opened in 1778 with a performance of Antonio Salieri's ''Europa riconosciuta'' | |
| − | + | UniCredit tower in Milan is the tallest building in Italy. Designed by Cesar Pelli | |
| − | + | Pirelli Tower in Milan was hit by a plane in 2002 | |
| − | + | Quadrilatero della moda ("fashion square"), or Via Montenapoleone fashion district, is a high-class shopping district in the centre of Milan | |
| − | + | Ducal Palace, Mantua was built between the 14th and the 17th century mainly by the noble family of Gonzaga as their royal residence in the capital of their Duchy | |
| − | + | Stone carvings of Val Camonica constitute one of the largest collections of prehistoric petroglyphs in the world. The collection was recognized by UNESCO in 1979 and was Italy's first recognized World Heritage Site. Include the world’s earliest map, known as the Bedolina Map | |
| + | Monza race track is 15 km north of Milan | ||
| − | + | '''Marche''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Ancona | |
| − | + | Palazzo Ducale (‘Ducal Palace’) in Urbino is a World Heritage site | |
| − | + | Rossini Opera Festival takes place in Pesaro, the birthplace of Rossini | |
| − | + | '''Molise''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Campobasso | |
| − | + | Until 1963, Molise formed part of the region of Abruzzi e Molise together with Abruzzo. The split, which did not become effective until 1970, makes Molise the newest region in Italy | |
| − | + | '''Piedmont''' | |
| + | Capital – Turin | ||
| − | + | Piedmont means ‘foot of the mountains’ | |
| − | + | Turin was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is mainly on the western bank of the Po River | |
| − | + | Turin was the political and intellectual centre of the Risorgimento that led to the unification of Italy | |
| − | + | Turin Shroud is kept in the royal chapel of the Cathedral of Saint John the Baptist in Turin | |
| + | Carnival of Ivrea includes a tradition of throwing of oranges between organized groups, known as the Battle of the Oranges | ||
| − | + | '''Sardinia''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Cagliari | |
| − | + | Sassari is the second-largest city of Sardinia | |
| − | + | Costa Smeralda is a resort in Sardinia. Development of the area started in 1961, and was financed by a consortium of companies led by Aga Khan | |
| − | + | Alghero is a town in Sardinia. The Catalan language is co-official in the city, unique in Italy | |
| + | Nuraghe is the main type of ancient megalithic edifice found in Sardinia, developed during the Nuragic Age between 1900 and 730 BC | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Sicily''' |
| − | + | Capital - Palermo | |
| − | + | Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean | |
| − | + | Catania is the second-largest city in Sicily | |
| − | + | Trapani is an important fishing port | |
| − | + | Marsala in Sicily is famous for the landing of Garibaldi in 1860 (the Expedition of the Thousand) and its wine | |
| + | Mount Etna is known as Mongibello (‘beautiful mountain’) in Italian | ||
| − | + | Mount Etna is an active stratovolcano lying between the cities of Messina and Catania | |
| − | + | Messina was destroyed by an earthquake and tsunami in 1908 | |
| − | + | Syracuse was founded by Ancient Greek Corinthians and became a very powerful city-state. Syracuse was allied with Sparta and Corinth, exerting influence over the entire Magna Graecia area of which it was the most important city | |
| − | + | Villa Romana del Casale is a large Roman villa. Excavations have revealed one of the richest, largest, and varied collections of Roman mosaics in the world | |
| − | + | '''Trentino-South Tyrol''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Trento | |
| − | + | Bolzano, commonly known as South Tyrol, is an autonomous province. 64% of the population is Austro-Bavarian or Tyrolean and speaks German. Less than a quarter of the population speak Italian as their first language | |
| + | Trentino is the other autonomous province of Trentino-South Tyrol | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Tuscany''' |
| − | + | Capital – Florence | |
| − | + | Ponte Vecchio (‘old bridge’) spans the River Arno in Florence | |
| − | + | Piazza della Signoria is an L-shaped square in front of the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence | |
| − | + | Florence Airport, Peretola, was formerly Amerigo Vespucci Airport | |
| − | + | Carrara is a city in Tuscany notable for the white or blue-grey marble quarried there | |
| − | + | Ducal palace of Mantua was built between the 14th and the 17th century mainly by the noble family of Gonzaga as their royal residence | |
| + | Pisa Botanical Garden was established in 1544 under Cosimo I de' Medici as the first university botanical garden in Europe | ||
| − | + | Pisa International Airport was formerly Galileo Galilei Airport | |
| − | + | Siena Cathedral, begun in the 12th century, is a masterpiece of Italian Romanesque-Gothic architecture | |
| − | + | Palio is a horse race that is held twice each year in Siena. The horses represent ten of the seventeen contrade, or city wards. The race circles the Piazza del Campo | |
| − | + | Livorno is a port on the Ligurian Sea. It is known in English as Leghorn | |
| + | Elba is the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago and the third-largest island of Italy | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Umbria''' |
| − | + | Capital – Perugia | |
| − | + | Umbria is bordered by Tuscany to the west, the Marche to the east and Lazio to the south. The main towns are Perugia and Terni | |
| − | + | Umbria is the only region not to have a coastline or a border with another country | |
| − | + | The Basilica of San Francesco d'Assisi (Saint Francis), the mother church of the Franciscan Order, is a World Heritage Site in Assisi. The foundation stone was laid by Pope Gregory IX in 1228. The church displays works by Giotto and Cimabue | |
| − | + | '''Veneto''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Venice | |
| + | Venice is built on 118 islands | ||
| − | + | Venice is known as La Serinissima and Bride of the Sea | |
| − | + | Venice is divided into six areas or sestiere and is built on 118 islands | |
| − | + | The banks of the Grand Canal are lined with more than 170 buildings. At one end the canal leads into the lagoon near Santa Lucia railway station and the other end leads into Saint Mark Basin: in between it makes a large S-shape through the central districts of Venice | |
| − | + | Rialto Bridge is one of the four bridges spanning the Grand Canal in Venice. It is the oldest bridge across the canal, and was the dividing line for the districts of San Marco and San Polo. The present stone bridge, a single span designed by Antonio da Ponte, was completed in 1591 | |
| + | Triumphal Quadriga or Horses of Saint Mark is a set of Roman or Greek bronze statues of four horses, originally part of a monument depicting a quadriga. It was originally erected in the Hippodrome of Constantinople, possibly on a triumphal arch, and is now in St Mark's Basilica in Venice | ||
| − | ' | + | Piazza San Marco, often known in English as Saint Mark's Square, is the principal public square of Venice |
| − | + | Santa Maria della Salute was one of five plague-churches built in Venice. The church is dedicated to Our Lady of Health (or of Deliverance, Italian: Salute) | |
| − | + | Museo Correr is a museum in St. Mark’s Square. It covers both the art and history of Venice | |
| − | + | Constitution Bridge is the fourth bridge over the Grand Canal. It was designed by Santiago Calatrava | |
| − | + | Marciana Library or Library of Saint Mark is one of the earliest surviving public libraries and repositories for manuscripts in Italy and holds one of the world's most significant collections of classical texts | |
| − | + | Venice Biennale was founded in 1895. It is now known as the Art Biennale | |
| − | + | San Michele is Venice’s cemetery island | |
| − | + | Venice is served by Marco Polo Airport | |
| + | MOSE project is intended to protect Venice from flooding. It is due to be completed in 2025 | ||
| − | + | Lido is a barrier island in the Venetian Lagoon | |
| − | + | Sant'Erasmo is an island in the Venetian Lagoon lying north of the Lido and north east of Venice | |
| − | + | Murano is an island just north of Venice. Murano became Europe's luxury glassmaking centre in the 15th and 16th centuries | |
| − | + | Mestre is a neighborhood of Venice on the mainland | |
| − | + | Traghetto is a large gondola used to ferry passengers across the Grand Canal | |
| − | + | Vaporetto is a public waterbus | |
| + | Padua is 40 km west of Venice | ||
| − | + | Padua Botanical Garden was founded in 1545 | |
| − | + | Prato della Valle is an elliptical square in Padua. It is the largest square in Italy | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Islands</u> | |
| − | + | Aeolian Islands are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily. The largest island is Lipari, and the entire archipelago is known as the Lipari Islands. The other islands include Vulcano and Stromboli | |
| + | Stromboli is known the ‘lighthouse of the Mediterranean’. Mount Stromboli has been in almost continuous eruption for the past 2,000–5,000 years; its last serious one occurred in 1921 | ||
| − | + | The island of Lampedusa belongs to Italy and is the largest of the Pelagie Islands, situated 205 km from Sicily and 113 km from Tunisia. Since the early 2000s, the island has become a primary European entry point for migrants, mainly coming from Libya | |
| − | + | Ponza is the largest island of the Italian Pontine Islands archipelago, located in the Tyrrhenian Sea | |
| − | + | Santo Stefano is an island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, and is part of the Pontine Islands. It is dominated by an old prison built by the Bourbons, completed in 1797 and in use until 1965 | |
| − | + | Ischia is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples | |
| − | + | Ferdinandea is a submerged volcanic island (also known as Graham Island) that forms part of the underwater volcano Empedocles 30 km south of Sicily. Currently a seamount, eruptions have raised it above sea level several times before erosion has caused it to submerge again. It last rose above sea level after erupting in 1831 | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Mountains</u> | |
| − | + | Apennines are a mountain range extending 1,200 km (750 miles) along the length of peninsular Italy | |
| − | + | Corno Grande in Abruzzo is the highest point in the Apennines | |
| − | + | Dolomites are a mountain range in northeastern Italy. They form part of the Southern Limestone Alps | |
| − | + | The Dolomites take their name from the rock dolomite which was named after French mineralogist Deodat Gratet de Dolomieu | |
| − | + | Marmolada is the highest point in the Dolomites | |
| + | Cortina d’Ampezzo is in the Dolomites | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Lakes</u> | |
| − | + | Largest lakes of Italy – Garda, Maggiore, Como | |
| − | + | Lake Garda is located in Northern Italy, about half-way between Brescia and Verona, and between Venice and Milan | |
| − | + | Lake Maggiore lies on the border of Italy and Switzerland | |
| − | + | Lake Como is a lake of glacial origin in Lombardy. At over 400 m (1320 ft) deep it is one of the deepest lakes in Europe | |
| − | + | Lake Como is shaped much like the character ‘Y’. The northern branch begins at the town of Colico, while the towns of Como and Lecco sit at the ends of the southwestern and southeastern branches respectively | |
| + | Lake Lugano is between Como and Maggiore | ||
| − | + | Lake Orta is west of Lake Maggiore. Basilica di San Giulio is a Roman Catholic church on the San Giulio Island in the centre of Lake Orta | |
| − | + | Lake Trasimeno in Umbria is the largest lake on the Italian peninsula south of the Po River | |
| − | + | Lake Avernus is a volcanic crater lake located in the Avernus crater in the Campania region | |
| + | Lake Bolsena is a crater lake in central Italy and is the largest volcanic lake in Europe | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Seas</u> | |
| + | Tyrrhenian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy | ||
| − | + | Ligurian Sea lies between Corsica and Genoa | |
| − | + | Strait of Messina is the strait between Sicily and Calabria | |
| − | + | Strait of Bonifacio is the strait between Corsica and Sardinia | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Rivers</u> | |
| − | + | Po flows 405 miles eastward across northern Italy, from Monviso (in the Cottian Alps) to the Adriatic Sea near Venice. It is the longest river in Italy, and passes through many important Italian towns, including Turin | |
| + | Adige is the second longest river in Italy. It rises in the province of South Tyrol and flows 250 miles through most of northeastern Italy to the Adriatic Sea | ||
| − | + | Tiber rises in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flows through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio to the Tyrrhenian Sea. Tiber flows through Rome | |
| − | + | Arno passes through Florence, Empoli, and Pisa | |
| − | + | == Kazakhstan == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Kazakhstan.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | Flag of Kazakhstan has a gold sun with 32 rays above a soaring golden steppe eagle, both centered on a sky blue background | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Astana | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Almaty, Astana | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Tenge | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Khan Tengri | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country by land area and the ninth largest country in the world | ||
| − | + | Kazakhstan was the last of the Soviet republics to declare independence following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 | |
| − | + | After the capital of Kazakhstan was moved from Almaty to Akmola in 1997, the city was consequently renamed Astana in 1998 | |
| − | + | Astana was renamed Nur-Sultan in honour of President Nursultan Nazarbayev in 2019, and reverted to the name Astana in 2022 | |
| − | + | Bayterek is the most famous landmark in Astana. The legend behind this tower as a symbol is that it represents a poplar tree, where the magic bird Samruk laid its egg | |
| − | + | Lake Balkhash is shrinking due to diversion and extraction of water from its feeders. The lake's western part is fresh water. The lake's eastern half is saline | |
| − | + | Kazakhstan produces 39% of the world’s uranium | |
| − | + | == Kosovo == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Kosovo.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | Flag of Kosovo uses a map of the country as a design element; the flag of Cyprus is the only other to do so | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Pristina | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Pristina, Prizren | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Velika Rudoka | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Note: Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence in 2008. Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. Kosovo has gained diplomatic recognition as a sovereign state by 114 member states of the United Nations | ||
| − | + | The city of Mitrovica is mainly Albanian, with a Serbian population in the north of the city | |
| − | + | Kosovo is the only mainland European country which does not border the European Union | |
| + | == Latvia == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Latvia.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Riga | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Riga, Daugavpils | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Gaizinkalns | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League member | ||
| − | + | Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states | |
| − | + | Riga lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Baltic Sea | |
| − | + | Riga has one of the largest collection of Art Nouveau buildings in the world | |
| − | + | Yarni is a pagan festival in Latvia | |
| − | + | Courland is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia | |
| − | + | == Liechtenstein == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Liechtenstein.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | The crown was added to the flag of Liechtenstein in 1937, after it was discovered by Liechtenstein's team at the 1936 Summer Olympics that the flag then in use was identical to the flag of Haiti | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Vaduz | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Schaan, Vaduz | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Swiss franc | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Grauspitz | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Liechtenstein is a constitutional monarchy with the rank of principality, headed by the Prince of Liechtenstein | ||
| + | Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked country bordered by Austria and Switzerland. The entire western border of Liechtenstein is formed by the Rhine | ||
| − | + | The principality of Liechtenstein is divided into 11 communes called Gemeinden. Five of them fall within the electoral district Unterland (the lower county), and the remainder within Oberland (the upper county) | |
| − | + | Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in the world with more registered companies than citizens | |
| − | + | Vaduz is the only capital city on the Rhine | |
| − | + | == Lithuania == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Lithuania.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Vilnius | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Vilnius, Kaunas | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Aukstojas Hill | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Lithuania is known as Lietuva in Lithuania | ||
| − | + | On 11 March 1990, a year before formal break-up of the Soviet Union, Lithuania became the first Soviet republic to declare itself independent | |
| − | + | The Old Town of Vilnius is one of the largest surviving medieval old towns in Northern Europe. It was declared a World Heritage Site in 1994 | |
| − | + | Vilnius was a European Capital of Culture in 2009 | |
| − | + | In 1995, the world's first bronze cast of Frank Zappa was installed in Vilnius | |
| − | + | == Luxembourg == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Luxembourg.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | Flag of Luxembourg is very similar to the flag of the Netherlands, but the light blue stripe and red stripe on the Luxembourg flag are a lighter shade | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Luxembourg City | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Luxembourg City | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Kneiff | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Luxembourg was founded by Count Siegfried I in 963 | ||
| − | + | Luxembourg comprises two principal regions: the Oesling in the north as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south | |
| − | + | As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by a grand duke, Henri, Grand Duke of Luxembourg, and is the world's only remaining grand duchy | |
| − | + | European Court of Justice is in Luxembourg | |
| − | + | Luxembourg was known as the “Gibraltar of the North” | |
| − | + | Three languages are recognized as official in Luxembourg: French, German, and Luxembourgish | |
| + | Luxembourg City lies at the confluence of the Alzette and Petrusse rivers | ||
| − | + | Luxembourg American Cemetery and Memorial is the final resting place of 5,076 American military dead, including General George S. Patton | |
| − | + | Schengen is near the tripoint where the borders of Germany, France, and Luxembourg meet. The Schengen Agreement of 1985 led to the creation of Europe's borderless Schengen Area | |
| + | == Malta == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Malta.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | A representation of the George Cross, awarded to Malta in 1942, is carried in the canton of the white stripe on the flag of Malta | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Valletta | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Birkirkara | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Ta' Dmejrek | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Malta is an archipelago 80 km south of Sicily across the Malta Channel. Only the three largest islands – Malta, Gozo and Comino – are inhabited | ||
| − | + | Malta is the closest commonwealth country to the United Kingdom | |
| − | + | Malta has two official languages: Maltese and English | |
| − | + | Valletta, at 0.8 km<sup>2</sup>, is the smallest national capital in the European Union | |
| − | + | Valletta is named after Jean Parisot de la Valette, a French nobleman and Grand Master of the Order of Malta | |
| − | + | Valletta contains buildings from the 16th century onwards, built during the rule of the Order of St. John of Jerusalem, also known as Knights Hospitaller | |
| − | + | Mdina served as the island's capital from antiquity until 1530, when the capital was moved to Birgu | |
| − | + | Megalithic Temples of Malta are the oldest free-standing structures on Earth, even older than the Pyramids | |
| − | + | The megalithic temple of Ggantija is on the island of Gozo | |
| − | + | Three Cities is a collective description of the three fortified cities of Birgu, Senglea and Cospicua | |
| − | + | Dghajsa is a traditional water taxi | |
| − | + | == Moldova == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Moldova.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | The tricolour of Moldova is identical to the flag of Romania, but on Moldova's flag the yellow stripe is charged with the coat of arms | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Chisinau | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Chisinau, Tiraspol (see note below) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Leu | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Balanesti Hill | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | Note: Tiraspol is a city in Transnistria | |
| + | The name Moldova is derived from the Moldova River | ||
| − | + | Moldova declared itself an independent state in 1991. It is the poorest country in Europe | |
| − | + | The largest part of the nation lies between two rivers, the Dniester and the Prut | |
| − | + | The English language name for Chisinau is Kishinev | |
| + | == Monaco == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Monaco.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Monaco | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Monaco | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Chemin des Revoires | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Monaco is a sovereign city-state and microstate. It is the second smallest and the most densely populated country in the world | ||
| − | + | Monaco is a principality governed under a form of constitutional monarchy, with Prince Albert II as head of state | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The traditional national language is Monegasque, now spoken by only a minority of residents | ||
| − | + | Monte Carlo officially refers to an administrative area of the Principality of Monaco; informally the name also refers to a larger district, the Monte Carlo Quarter | |
| − | + | Opera de Monte-Carlo was designed by Charles Garnier | |
| − | + | Monte Carlo Casino opened in 1863 | |
| − | + | == Montenegro == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Montenegro.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Podgorica | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Podgorica | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Zla Kolata | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Montenegro means “black mountain” | ||
| − | + | Montenegro declared itself independent of Serbia in 2006 | |
| − | + | The country has a segment of the Karst of the western Balkan Peninsula | |
| − | + | Podgorica was known as Titograd from 1946 to 1992 | |
| − | + | Podgorica means “under the small hill” | |
| + | Bay of Kotor is the southernmost part of the region of Dalmatia. The bay has been inhabited since antiquity. Its medieval towns are major tourist attractions | ||
| − | + | Cetinje is the former royal capital of Montenegro | |
| − | + | == Netherlands == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Netherlands.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Amsterdam | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht, Eindhoven | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Vaalserberg (see note below) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Note: Vaalserberg is the highest point on the Dutch mainland. The highest point of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is Mount Scenery on the island of Saba in the Caribbean Netherlands | |
| − | + | Netherlands is divided into twelve provinces and three overseas public bodies (Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba) | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Amsterdam is the largest city in North Holland province | |
| − | + | Amsterdam is colloquially referred to as the ‘Venice of the North’, for its large number of canals | |
| − | + | Amsterdam was founded at the mouth of the Amstel River that was dammed to control flooding | |
| − | + | Dam Square lies in the historical center of Amsterdam | |
| − | + | De Wallen, also known as Walletjes or Rosse Buurt, is a designated area for legalised prostitution and is Amsterdam's largest and most well-known red-light district | |
| − | + | Vondelpark has around 10 million visitors annually | |
| − | + | Natura Artis Magistra, commonly known just as Artis, is a zoo in Amsterdam. It is the oldest zoo in the Netherlands | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Rotterdam is the largest city of South Holland province | |
| − | + | The port of Rotterdam is the largest cargo port in Europe. Rotterdam is known as the “Gateway to Europe” | |
| − | + | The Erasmus Bridge is a cable stayed bridge across the Nieuwe Maas river, linking the northern and southern halves of the city of Rotterdam. It was designed by Ben van Berkel and completed in 1996. The bridge has a 139 metre-high asymmetrical pylon, earning the bridge its nickname of “The Swan” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The Hague is the capital of South Holland province | |
| − | The | + | The Hague is the seat of Dutch government |
| + | International Court of Justice is located at Peace Palace in The Hague, and was funded by Andrew Carnegie | ||
| − | + | Mauritshaus art museum in The Hague houses the Royal Cabinet of Paintings which consists of 841 objects, mostly Dutch Golden Age paintings | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Haarlem is the capital of North Holland province | |
| − | + | Maastrict is on River Maas and is the capital of Limburg province | |
| − | + | The presence of the Philips electronics company is probably the largest single contributing factor to the major growth of Eindhoven | |
| − | + | Limburg is the southernmost of the provinces of the Netherlands | |
| − | + | Vlissingen is also known as Flushing | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Aalsmeer flower auction is the largest flower auction in the world. Around 43 million flowers are sold daily | ||
| − | + | Alkmaar is known for its traditional cheese market | |
| − | + | Leeuwarden is the capital of Friesland | |
| − | + | Randstat is a conurbation consisting primarily of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague and Utrecht); their suburbs, and many towns in between, that all grew and merged into each other | |
| − | + | Efteling is a fantasy-themed amusement park in North Brabant. In 2020, it was the most visited theme park in Europe | |
| − | + | Flevoland is the 12th and youngest province of the Netherlands, established in 1986 | |
| − | + | Zeeland is the westernmost and least populous province. Large parts of Zeeland are below sea level | |
| − | + | Zuider Zee was dammed using boulder clay in 1932 | |
| − | + | Many dykes were breached in the North Sea flood of 1953 | |
| − | + | Vaalserberg is the location of the tripoint between Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands | |
| − | + | Ijsselmeer is a shallow artificial lake of 1100 km² in the central Netherlands. It is the largest lake in Western Europe | |
| − | + | == North Macedonia == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-North-Macedonia.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Skopje | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Skopje | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Denar | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mount Korab | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | North Macedonia is officially the Republic of North Macedonia. It became a member of the United Nations in 1993, but, as a result of an ongoing dispute with Greece over use of the name Macedonia, it was admitted under the provisional description of "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (FYROM). The name was changed from Macedonia to North Macedonia in 2019 | ||
| − | + | Skopje is on the River Vardar | |
| − | + | Skopje was known in the Roman period under the name Scupi | |
| − | + | In 2018 Skopje Alexander the Great Airport was renamed Skopje International Airport to improve relations with Greece | |
| − | + | == Norway == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Norway.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Oslo | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Oslo, Bergen, Trondheim, Stavanger | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Krone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Galdhopiggen | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Bygdoy in Oslo has several museums, including the Kon-Tiki Museum; the Norwegian Museum of Cultural History (Norsk Folkemuseum); the Viking Ship Museum; the Norwegian Maritime Museum and the ship ''Fram'', used by Roald Amundsen | ||
| − | + | The main attractions at the Viking Ship Museum in Oslo are the Oseberg ship, Gokstad ship and Tune ship | |
| − | + | Frogner Park is a public park in Oslo that contains the Vigeland installation, a permanent sculpture installation created by Gustav Vigeland | |
| − | + | Oseberg ship is a well-preserved Viking ship discovered in a large burial mound at the Oseberg farm in Norway. The characteristic motif of the Oseberg style of animal ornamentation is gripping beasts | |
| − | + | Kings of Norway were traditionally crowned at Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim | |
| − | + | Edvard Grieg Museum Troldhaugen is in Bergen | |
| − | + | Tromso is a city in Troms og Finnmark, the largest county by area in Norway | |
| − | + | Sarpsfossen has the greatest flow of any waterfall in Europe. It is the last waterfall in the river Glomma, which is the longest river in Norway | |
| − | + | Cape Nordkinn is the northernmost point of mainland Norway, and by extension the northernmost point of mainland Europe. It is in the county of Finnmark | |
| − | + | Laerdal Tunnel is a 15 mile long road tunnel connecting Laerdal and Aurland in Sogn. It is the longest road tunnel in the world | |
| − | + | Ryfylke Tunnel the world's longest and deepest subsea road tunnel, although it will be superceded by Rogfast that is projected to open in 2033 | |
| − | + | Lofoten is an archipelago in the county of Nordland. Though lying within the Arctic Circle, the archipelago experiences one of the world's largest elevated temperature anomalies relative to its high latitude. Target of oil and gas exploration | |
| − | + | Utsira is a municipality in Rogaland county. Utsira (under the spelling Utsire) gives its name to North Utsire and South Utsire, two of the sea areas of the Shipping Forecast | |
| − | + | Hammerfest claims to be the northernmost city in the world | |
| + | Hurtigruten (“the Express Route”) is a daily passenger and freight shipping service along Norway's western and northern coast between Bergen and Kirkenes. Sometimes referred to as the Norwegian Coastal Express | ||
| − | + | Galdhopiggen is the highest mountain in Norway, Scandinavia and Northern Europe | |
| − | + | Hornindalsvatnet is the deepest lake in Europe | |
| − | + | Vinnufossen is the highest waterfall in Europe | |
| − | + | Troll Wall, composed of gneiss, is the tallest vertical rock face in Europe | |
| − | + | Jostedal Glacier (Norwegian: Jostedalsbreen) is the largest glacier in continental Europe | |
| − | + | Saltstraumen and Moskstraumen are the sources of the strongest whirlpools in the world | |
| − | + | E6 is the main north-south road through Norway, and is 1,919 miles long | |
| − | + | North Cape is the northernmost point in Europe that can be accessed by car | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Svalbard (formerly known by its Dutch name Spitsbergen) is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. It is about midway between continental Norway and the North Pole | |
| − | + | Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century and several permanent communities were established | |
| + | Longyearbyen, in Svalbard, is the world’s northernmost town | ||
| − | + | Bear Island is the southernmost island of the Norwegian Svalbard archipelago | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Jan Mayen is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and a part of the Kingdom of Norway | |
| − | + | The Antarctic Peter I Island is a dependent territory and thus not considered part of the Kingdom. Norway also lays claim to a section of Antarctica known as Queen Maud Land | |
| + | Bouvet Island is an uninhabited subantarctic volcanic island and dependency of Norway located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is the most remote island in the world | ||
| − | + | == Poland == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Poland.png|none|frame]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Warsaw | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Warsaw, Lodz, Krakow, Wroclaw, Poznan | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Zloty | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Rysy | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Voivodeship is the highest-level administrative division in Poland | ||
| − | + | Warsaw international airport is named after Frederic Chopin | |
| − | + | Warsaw is known as the “Phoenix City” | |
| − | + | Warsaw is located on the Vistula river | |
| − | + | Palace of Culture and Science in Warsaw is the tallest building in Poland. It was a gift from the Soviet Union to the people of Poland | |
| − | + | Royal Castle was the official residence of the Polish monarchs. It is located in the Castle Square, at the entrance to the Warsaw Old Town | |
| + | Krakow's John Paul II International airport in Balice is Poland’s second busiest after Warsaw | ||
| − | '' | + | The main landmarks of Krakow include the St. Mary's Basilica and the Sukiennice Cloth Hall, the Wawel Castle, the Zygmunt Bell at the Wawel Cathedral, and the medieval St Florian's Gate with the Barbican along the Royal Coronation Route |
| − | + | Wieliczka salt mine, near Krakow, was built in the 13th century. It produced table salt continuously until 2007, as one of the world's oldest salt mines still in operation | |
| − | + | Lodz translates literally as “boat” It is an industrial city | |
| − | + | Wroclaw is the capital of Lower Silesia in southwestern Poland, situated on the Oder River | |
| − | + | Wroclaw is served by Copernicus Airport | |
| − | + | Wroclaw is known as Breslau in Germany | |
| − | + | Lublin is the largest Polish city east of the Vistula River | |
| + | Malbork Castle is a 13th century Teutonic castle and fortress. It is the largest castle in the world measured by land area | ||
| − | + | Poznan has the oldest cathedral in the country, which contains the tombs of the first Polish rulers | |
| − | + | Containing the painting known as the ''Black Madonna'', the Jasna Gora monastery in the city of Czestochowa is a centre for Catholic pilgrims | |
| − | + | Vistula river empties into the Baltic Sea near Gdansk | |
| − | + | Suwalki Gap is a sparsely populated area immediately southwest of the border between Lithuania and Poland, between Belarus and the Russian exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast. It is of great strategic and military importance | |
| − | + | Masurian Lakes in northeastern Poland contains more than 2,000 lakes | |
| + | Bledow desert is a sandy desert in Silesia | ||
| − | + | Bialowieza Forest is a World Heritage Site straddling the border between Poland and Belarus. It is one of the last and largest remaining parts of the immense primeval forest that once stretched across the European Plain | |
| − | + | == Portugal == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Portugal.png|none|frame]] | ||
| + | Flag of Portugal has a simple version of the national coat of arms (armillary sphere and Portuguese shield) | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Lisbon | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Lisbon, Porto | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Serra da Estrela (see note below) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Note: Serra da Estrela is the highest point on the Portuguese mainland. The highest point of Portugal is Mount Pico on Pico Island in the Azores | ||
| − | + | Aside from continental Portugal, the Portuguese Republic holds sovereignty over the Atlantic archipelagos of Azores and Madeira, which are autonomous regions of Portugal | |
| − | + | The country is named after its second largest city, Porto | |
| − | + | In 27 BC, Lusitania gained the status of Roman province. Later, a northern province of Lusitania was formed, known as Gallaecia, with the capital in Bracara Augusta, today's Braga | |
| − | + | Lisbon was built on seven hills | |
| − | + | Belem Tower was commissioned by King John II to be both part of a defence system at the mouth of the Tagus River and a ceremonial gateway to Lisbon. It was built in the early 16th century and is a prominent example of the Portuguese Manueline style | |
| − | + | Lisbon was known to the Romans as Felicitas Julia Olissipo | |
| − | + | Calouste Gulbenkian Museum in Lisbon houses one of the world's most important private art collections | |
| − | + | Vasco da Gama Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge that spans the Tagus River in Lisbon. It is the second longest bridge in Europe. It was built to alleviate the congestion on Lisbon's other bridge (25 of April Bridge) | |
| − | + | Lisbon is served by Humberto Delgado Airport | |
| − | + | Gare do Oriente station was opened in 1998 | |
| − | + | 25th of April Bridge is a suspension bridge connecting Lisbon to Almada on the left bank of the Tagus river. Named after the date of the Carnation Revolution in 1974 | |
| − | + | Braga Munipical Stadium was carved out of a quarry (Monte Castro) that overlooks the city of Braga | |
| + | Douro enters the Atlantic near Porto | ||
| − | + | Mondego is the longest river wholly within Portugal | |
| − | + | Serra da Estrela (English: Mountain Range of the Star) is the highest mountain range in Continental Portugal | |
| − | + | Sintra is a World Heritage Site on account of its 19th century Romantic architecture | |
| − | + | Fatima is associated with the Marian apparitions that were purportedly witnessed by three local shepherd children at the Cova da Iria in 1917 | |
| − | + | Most westerly point in mainland Europe is Cabo da Roca | |
| + | Algarve is the southernmost region of mainland Portugal. Faro is the administrative centre | ||
| − | + | Praia do Norte (North Beach) at Nazare is listed on the Guinness World Records for the biggest waves ever surfed | |
| − | + | === Autonomous regions === | |
| + | '''Azores''' | ||
| − | + | Azores is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands 1,400 km west of Lisbon | |
| + | Largest islands – Sao Miguel, Pico, Terceira | ||
| − | + | Ponta Delgada is the capital of the Azores and is on the island of Sao Miguel | |
| − | + | '''Madeira''' | |
| − | + | Madeira is an archipelago located in the north Atlantic Ocean, west and slightly south of Portugal. It includes the islands of Madeira, Porto Santo, and the Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands | |
| − | + | Madeira is famous for Madeira wine and embroidery | |
| − | + | The main harbour is in Funchal, the capital of Madeira | |
| + | Funchal is served by Cristiano Ronaldo International Airport | ||
| − | + | Monte in a town in Funchal with a toboggan run that uses large wicker baskets | |
| − | Capital | + | == Romania == |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Romania.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Bucharest | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Bucharest, Cluj, Timisoara | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Leu | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Moldoveanu Peak | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Modern Romania emerged within the territories of the ancient Roman province of Dacia, and was formed in 1859 through a personal union of the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia. The new state, officially named Romania since 1866, gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1877 | ||
| − | + | The Palace of the Parliament in Bucharest is the world's heaviest building and the world's second largest administrative building, after the Pentagon | |
| + | Carpathian Mountains dominate the centre of Romania | ||
| − | + | Transylvania was part of Hungary until 1918 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Bran Castle is a national monument and landmark in Transylvania. Commonly known outside Transylvania as Dracula's Castle | |
| − | + | Danube empties in Romania's Danube Delta | |
| + | Danube Delta has three distributaries | ||
| − | + | == Russia == | |
| − | + | [[File:Flag-of-Russia.png|none|thumb]] | |
| − | Capital | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Moscow | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Moscow, St Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Kazan | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Ruble | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mount Elbrus | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Russia is the largest country in the world, covering more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area. Russia is also the world's ninth most populous nation | ||
| − | + | Russia is a federation which, since 2008, consisted of 83 federal subjects. In 2014, Sevastopol and the Republic of Crimea became the 84th and 85th federal subjects | |
| − | + | Federal subjects are divided into 46 oblasts, 22 republics, 9 krais, 4 autonomous okrugs, 3 federal cities (Moscow, Saint Petersburg, and Sevastopol) and 1 autonomous oblast (Jewish Autonomous Oblast) | |
| + | There are 11 time zones in Russia, ranging from UTC+02:00 (Kaliningrad) to UTC+12:00 (Kamchatka) | ||
| − | + | Russia is the only country that borders the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea | |
| + | [[File:Map of Russia-en.svg|center|thumb|800x800px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Moscow was founded in 1147 | |
| − | + | Boulevard Ring is Moscow's second centremost ring road (the first is formed by the Central Squares of Moscow running along the former walls of Kitai-gorod) | |
| − | + | Sheremetyevo and Domodedovo are the international airports in Moscow | |
| − | + | Moscow Metro was opened in 1935 with one line and 13 stations. It was the first underground railway system in the Soviet Union. As of 2023, the Moscow Metro has 258 stations. The Moscow Metro is the busiest metro system in Europe | |
| − | + | The underground stations being constructed under Stalin's regime, in the style of socialist classicism, were meant as underground ‘palaces of the people’ | |
| − | + | Moscow is known as the ‘Port of the Five Seas’ | |
| + | Tverskaya Street in Moscow was named Gorky Street from 1935 to 1990 | ||
| − | + | Arbat Street in the historical centre of Moscow has existed since at least the 15th century | |
| − | + | Europe's largest shopping centre, Aviapark, is in Moscow | |
| − | + | Moskva River passes through central Moscow | |
| − | + | Dubna is a town in Moscow Oblast. It is home to the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, an international nuclear physics research centre and one of the largest scientific foundations in the country | |
| − | |||
| + | Saint Petersburg was founded by Tsar Peter the Great in 1703. It was known as Petrograd from 1914 to 1924, and Leningrad from 1924 to 1991 | ||
| − | + | Saint Petersburg is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea | |
| − | + | Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents | |
| − | + | Nevsky Prospect is a main street in Saint Petersburg | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Novosibirsk is the most populous city in Asian Russia. It lies on the Ob river | |
| − | + | Yekaterinburg is the largest city in Urals and is the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk. The city was formerly known as Sverdlovsk | |
| − | + | Kazan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan. It is the most populous city on the Volga | |
| − | + | Nizhny Novgorod was known as Gorky from 1932 to 1990 | |
| − | + | Volgograd was known as Tsaritsyn from 1598 to 1925, and Stalingrad from 1925 to 1961 | |
| − | + | The Motherland Calls is a statue in Mamayev Kurgan in Volgograd commemorating the Battle of Stalingrad. Sculpted by Vevgeny Vuchetich | |
| − | + | Astrakhan is the principal port on River Volga | |
| + | Arkhangelsk, also known as Archangel, is on the White Sea. It was the chief seaport of Russia until 1703, when it was replaced by the newly-founded Saint Petersburg | ||
| − | + | Krasnoyarsk is located on the Yenisei River. It is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk and Omsk | |
| − | + | Anadyr is a town in far northeastern Russia. It lies on the southern shore of the estuary of the Anadyr River, which empties into the Bering Sea | |
| − | + | Norilsk in Siberia is known for nickel mining | |
| + | Birobidzhan is a town and the administrative centre of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, located on the Trans-Siberian Railway | ||
| − | + | Sakha Republic, also known as Yakutia, is the largest subnational governing body by area in the world at 1,190,555 sq miles and the eighth largest territory in the world. Its capital is Yakutsk | |
| − | + | Yakutsk is the coldest city on earth | |
| − | + | Great Patriotic War Monument is a large statue in Murmansk | |
| − | + | Samara lies on the River Volga. Chosen to be the capital of the USSR should Moscow fall to the invading Germans during World War II | |
| + | Taymyr Peninsula, in the Siberian Federal District, forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Lake Taymyr and the Byrranga Mountains are located within the vast Taymyr Peninsula. Cape Chelyuskin, the northernmost point of the Eurasian continent, is located at the northern end of the Taymyr Peninsula | ||
| − | + | Samara lies on the River Volga. Chosen to be the capital of the USSR should Moscow fall to the invading Germans during World War II | |
| − | + | Mount Narodnaya is the highest peak of the Urals in Russia | |
| − | + | Kamchatka has around 30 active volcanoes | |
| − | + | Kalmykia is the only region in Europe where Buddhism is the main religion | |
| − | + | Vladikavkaz is the capital of North Ossetia-Alania | |
| − | + | Magas is the capital of Ingushetia | |
| − | + | Grozny is the capital of Chechnya | |
| − | + | Makhachkala is the capital of Dagestan | |
| + | Derbent is a city in the Republic of Dagestan. It is the southernmost city in Russia. Often identified with the legendary Gates of Alexander, Derbent claims to be the oldest city in Russia | ||
| − | + | Kaliningrad Oblast is an exclave of Russia surrounded by Poland, Lithuania and the Baltic Sea | |
| − | + | Konigsberg was renamed Kaliningrad in 1946 | |
| − | + | Museum of the World’s Ocean is in Kaliningrad | |
| − | + | Kaliningrad is situated on the Pregolya River | |
| − | + | Rostov-on-Don is a port city 30 km from the Sea of Azov | |
| − | + | Franz Josef Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It was discovered in 1873 and named in honour of the Austro-Hungarian emperor Franz Joseph I | |
| − | + | Solovki was the first Gulag. Located on the Solovetsky Islands, in the White Sea | |
| − | + | Novaya Zemlya (Russian: New Land) is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky. Novaya Zemlya consists of two major islands, separated by the narrow Matochkin Strait. The two main islands are Severny (northern) and Yuzhny (southern). Novaya Zemlya separates the Barents Sea from the Kara Sea. It was used as a nuclear test site in the Cold War. It was the site of the 1961 explosion of Tsar Bomba, the largest, most powerful nuclear weapon ever detonated | |
| − | + | Khanty-Mansiysk is an oil boom town in West Siberia | |
| − | + | Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the capital of Kamchatka | |
| − | + | Power of Siberia is a Gazprom-operated pipeline in Eastern Siberia that transports natural gas from Yakutia to China | |
| − | + | Mirny mine is an open pit diamond mine located in Mirny, Sakha Republic. The mine is more than 525 m deep | |
| − | + | Novorossiysk is a city in Krasnodar Krai. It is the largest port on the Black Sea and the largest Russian port | |
| + | Magnitogorsk is a city in the Chelyabinsk Oblast. It contains the largest iron and steel works in Russia | ||
| − | + | Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains is a site of paleoarcheological remains | |
| − | + | Kola Peninsula is part of the Murmansk Oblast. Kola Superdeep Borehole is the result of a scientific drilling project that attempted to drill as deeply as possible into the Earth’s crust. The deepest reached over 12,000 metres | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Trans-Siberian Railway is the longest railway line in the world, with a length of over 9,289 kilometres (5,772 miles), from Moscow to Vladivostok. Construction started in 1891 | |
| − | |||
| + | Kolyma Highway in Siberia is known as the Road of Bones in reference to the hundreds of thousands of forced labourers who were interred in the road after dying during its construction | ||
| − | + | Beringia is the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula | |
| − | + | Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. Woolly mammoths survived until c. 2000 BC | |
| − | + | Big Diomede or “Tomorrow Island” is the larger of the two Diomede Islands located in the middle of the Bering Strait between the Alaska mainland and Siberia. Little Diomede Island is part of the United States and is east of the International Date Line | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Rivers</u> | |
| − | + | Volga is the longest river in Europe (2,290 miles) and empties into the Caspian Sea | |
| − | + | Neva is the only river flowing from Lake Ladoga | |
| − | + | Ob, Yenisei, and Lena are the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean | |
| − | + | Ob is the westernmost of the Siberian rivers. The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary | |
| − | + | Yenisei is the largest river system flowing to the Arctic Ocean | |
| − | + | Lena is the easternmost of the three rivers. It flows into the Laptev Sea and is the longest river entirely within Russia | |
| − | + | Lena Pillars is a natural rock formation along the banks of the Lena River. The pillars are 150–300 metres high | |
| − | + | Don river rises southeast of Moscow, and flows for a distance of about 1,220 miles to the Sea of Azov | |
| − | + | Kolyma river is in northeastern Siberia and is 1,323 miles long. It is frozen for 250 days each year | |
| − | + | Angara is the only river flowing out of Lake Baikal | |
| − | + | Svir connects Lake Onega to Lake Lagoda | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <u>Lakes</u> | |
| + | Lake Baikal, in Southern Siberia is the deepest and oldest lake in the world as well as the largest (by volume) freshwater lake. It contains over 20% of the world's liquid fresh surface water and more than 90% of Russia's liquid fresh surface water. It is a World Heritage Site. Olkhon, by far the largest island in Lake Baikal, is the second largest lake-bound island in the world (the largest being Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron) | ||
| − | + | Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, not far from Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake in Europe | |
| − | + | Lake Onega is the second largest lake in Europe. Kizhi Island in Lake Onega is known for its wooden churches | |
| − | + | Lake Karachay in the Ural Mountains was used as a dumping site for radioactive waste. Today the lake is completely infilled | |
| − | + | == San Marino == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-San-Marino.png|alt=|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |San Marino | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Serraville (see note below), Borgo Maggiore, San Marino | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Monte Titano | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Note: Though it is the biggest town of the Republic, Dogana is not an autonomous castello (municipality) but belongs to the castello of Serravalle | ||
| − | + | San Marino is also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino | |
| − | + | San Marino is a microstate enclaved by Italy. It claims to be the oldest surviving sovereign state and constitutional republic in the world, as the continuation of the monastic community founded in 301, by stonecutter Marinus from the Croatian island of Rab | |
| − | + | San Marino has more vehicles than people | |
| − | + | The Captains Regent are the two heads of state of the Republic of San Marino. They are elected every six months by the Grand and General Council, the country's legislative body | |
| − | + | == Serbia == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Serbia.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Belgrade | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Belgrade, Novi Sad, Nis | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Dinar | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Velika Rudoka (see note below) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Note: Velika Rudoka is in Kosovo, but Serbia claims Kosovo as part of its own sovereign territory | |
| − | + | Serbia became landlocked after Montenegro declared independence in 2006 | |
| − | + | The province of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia in 2008. Serbia immediately condemned the declaration and continues to deny any statehood to Kosovo | |
| − | + | Air Serbia is the flag carrier and largest airline of Serbia. The airline was formerly known as Jat Airways until it was renamed in 2013. The airline has its hub at Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport | |
| − | + | Belgrade lies at the confluence of the Sava and Danube Rivers. Means “white city” | |
| − | + | House of Flowers is the mausoleum of Josip Broz Tito in Belgrade | |
| − | + | Several Roman emperors were born in Nis | |
| − | + | == Slovakia == | |
| − | + | [[File:Flag-of-Slovakia.png|none|thumb]] | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |Capital | |
| − | + | |Bratislava | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Bratislava, Kosice | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Gerlach | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Slovakia became an independent state on 1 January 1993 after the dissolution of Czechoslovakia | ||
| − | + | Bordering Austria and Hungary, Bratislava is the only national capital that borders two independent countries | |
| − | + | Bratislava was known as Pressburg until 1919 | |
| − | + | Pressburg flourished during the 18th century reign of Queen Maria Theresa, becoming the largest and most important town in “the Kingdom of Hungary” | |
| − | + | Vah is the longest river in Slovakia | |
| − | + | Gerlachov Peak, informally referred to as Gerlach, is the highest peak in the High Tatras, in Slovakia, and in the Carpathians | |
| − | + | == Slovenia == | |
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Slovenia.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | The coat of arms on the flag of Slovenia is a shield with the image of Mount Triglav, Slovenia's highest peak | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Ljubljana | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Ljubljana, Maribor | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mount Triglav | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | In 1991, Slovenia became the first country to split from Yugoslavia and become an independent country. In 2004, it entered NATO and the European Union; in 2007 it became the first former Communist country to join the Eurozone | ||
| − | + | Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport is named after the leader of the Democratic Opposition of Slovenia between 1989 and 1992 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In the Middle Ages, both the river and the town of Ljubljana were also known by the German name Laibach | |
| − | + | Piran is a town on the Adriatic Sea known for its medieval architecture | |
| − | + | Planica is an alpine valley famous for ski jumping | |
| − | + | Lake Cerknica is an intermittent lake. When full, it is the largest lake in the country | |
| − | + | Lake Bled is a tourist destination in the Julian Alps. The lake surrounds Bled Island which has several buildings, the main one being the pilgrimage church dedicated to the Assumption of Mary | |
| − | + | Mount Triglav is the highest peak of the Julian Alps and of the former Yugoslavia | |
| − | + | == Spain == | |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Spain.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Madrid | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Zaragoza | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mulhacen (see note below) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Note: Mulhacen is the highest point on the Spanish mainland. The highest point of Spain is Mount Teide on Tenerife in the Canary Islands | ||
| − | + | Spain is divided into 17 autonomous communities and two autonomous cities[[File:Autonomous-communities-of-spain-01.png|thumb|center|600x600px|link=Special:FilePath/Autonomous-communities-of-spain-01.png|alt=]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Andalusia''' | |
| + | Capital – Seville | ||
| − | + | Cordoba is known as the “Athens of the west” | |
| − | + | In the 10th century Cordoba was the most populous city in the world, and under the rule of Caliph Al Hakam II it had also become a centre for education under its Islamic rulers | |
| − | + | Cordoba has more World Heritage Sites than any other city in the world | |
| − | + | Mezquita is a mosque in Cordoba, completed in the 11th century. The building is most notable for its giant arches, with over 1,000 columns of jasper, onyx, marble, and granite | |
| − | + | Alhambra (“red castle”) is an ancient palace and fortress complex of the Moorish monarchs of Granada, in southern Spain (known as Al-Andalus when the fortress was constructed during the mid-14th century). It was the residence of the Muslim kings of Granada and their court, and is currently a museum exhibiting Islamic architecture. Court of the lions is a fountain supported by the figures of twelve lions in white marble | |
| − | + | Federico Garcia Lorca airport serves Grenada | |
| + | Seville is on the Guadalquivir river | ||
| − | + | Hispalis was the Roman name for Seville | |
| − | + | Seville Cathedral is the largest Gothic cathedral in the world. Giralda is the bell tower | |
| − | + | Almeria is a province of the Autonomous Community of Andalucia. It is bordered by the provinces of Granada and Murcia, and the Mediterranean Sea. Its capital is the city of Almeria | |
| − | + | Almeria is the driest region of Europe, with the continent's only true desert climate. A number of spaghetti westerns were shot here | |
| − | + | Tabernas Desert is in Almeria | |
| − | + | Malaga–Costa Del Sol airport has a Pablo Ruiz Picasso terminal | |
| − | + | Costa del Sol (“Sun Coast”) is a region comprising the coastal towns along the Mediterranean coastline of the Malaga province. It includes the towns of Torremolinos and Marbella | |
| − | + | The most southerly point in mainland Europe is Punta de Tarifa | |
| − | + | '''Aragon''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Zaragosa | |
| − | + | Zaragoza is on the river Ebro | |
| − | + | Zaragoza was founded by Emperor Augustus | |
| − | + | Belchite is a ghost town left as a memorial to the Spanish Civil War | |
| − | + | Pico d’Aneto is the highest point in the Pyrenees and in Aragon | |
| − | + | '''Asturias''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Oviedo | |
| − | + | Gijon is a seaport and the largest city in Asturias | |
| − | + | '''Balearic Islands''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Palma de Mallorca | |
| − | + | Palma de Mallorca is on Majorca | |
| + | The four largest islands are Majorca, Minorca, Ibiza and Formentera. There are many minor islands and islets in close proximity to the larger islands, including Cabrera, Dragonera and S'Espalmador | ||
| − | + | Miro Mallorca Foundation is a museum in Palma de Mallorca, dedicated to the work of the artist Joan Miro | |
| − | + | Pityusic Islands, or commonly but informally the Pine Islands, is the name given collectively to Ibiza, Formentera and a number of small islands | |
| − | + | Ibiza is closest to the mainland | |
| − | + | Large portions of Ibiza are registered as World Heritage Sites | |
| − | + | Privilege Ibiza is the world’s largest nightclub | |
| − | + | Mahon is the capital of Minorca | |
| − | + | '''Basque Country''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Vitoria (''de facto'') | |
| − | + | Basque Country includes the Basque provinces of Alava, Biscay and Gipuzkoa, also called Historical Territories | |
| − | + | Almost half of the inhabitants of the Basque Autonomous Community live in Greater Bilbao | |
| − | + | Guggenheim Museum Bilbao was designed by Frank Gehry and was opened in 1997 | |
| + | San Sebastian is also known as Donostia | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Canary Islands''' |
| + | [[File:Map of the Canary Islands.svg|center|thumb|800x800px|alt=]] | ||
| − | + | Capital – Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, commonly known as Las Palmas is the capital (jointly with Santa Cruz de Tenerife) and the most populous city in the Autonomous Community of the Canary Islands and the ninth largest city in Spain | |
| − | + | Santa Cruz de Tenerife is also a capital of the Canary Islands | |
| − | + | The name Islas Canarias is likely derived from the Latin name Canariae Insulae, meaning ‘Islands of the Dogs’ | |
| − | + | Tenerife is the largest and most populous island of the seven Canary Islands | |
| − | + | Playa de las Américas is a purpose-built holiday resort in Arona Municipio, in the south of Tenerife | |
| + | Mount Teide is a volcano on Tenerife. Its 3,718 m summit is the highest point in Spain | ||
| − | + | La Gomera is a mountainous island of volcanic origin on Tenerife | |
| + | Fuerteventura is the oldest island in the Canary Islands dating back 20 million years to a volcanic eruption from the Canary hotspot. It is the second largest island and the closest to Africa | ||
| − | + | El Hierro is the smallest and westernmost of the main Canary Islands | |
| + | Lanzarote is the easternmost Canary Island | ||
| − | + | Fire Mountain is on Lanzarote | |
| − | + | Arrecife is main town on Lanzarote | |
| − | + | La Palma is the most north-westerly of the Canary Islands | |
| + | Cumbre Vieja is an active volcanic ridge on the volcanic ocean island of Isla de La Palma in the Canary Islands. A future failure of the western flank of the Cumbre Vieja may cause a mega-tsunami | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Cantabria''' |
| − | + | Capital – Santander | |
| − | + | Altamira is a cave famous for its Upper Paleolithic cave paintings featuring drawings and polychrome rock paintings of wild mammals and human hands. It is located near the town of Santillana del Mar in Cantabria. The cave with its paintings has been declared a World Heritage Site | |
| + | '''Castile-La Mancha''' | ||
| − | + | Capital – Toledo | |
| + | Toledo is known as the ‘City of the Three Cultures’ for the cultural influences of Christians, Muslims, and Jews reflected in its history | ||
| − | + | Toledo is located on the banks of the River Tagus, and is known for the production of swords | |
| − | + | La Mancha is the largest continuous wine growing region in the world | |
| + | La Mancha's windmills were immortalized in the novel ''Don Quixote'' | ||
| − | + | Casas Colgadas (‘Hanging Houses’) is a complex of houses located in Cuenca. They were built in the 14th century and are built over a rock | |
| + | '''Castile and Leon''' | ||
| − | + | Capital – Valladolid | |
| − | + | Castile and Leon is the largest autonomous community in Spain | |
| − | + | Burgos Cathedral is the burial place of Rodrigo Diaz de Vivar (El Cid) | |
| − | + | Segovia is famous for its historic buildings including three main landmarks: its midtown Roman aqueduct, its cathedral, and the castle, which served as one of the templates for Walt Disney's Cinderella Castle | |
| − | + | '''Catalonia''' | |
| − | + | Capital – Barcelona | |
| − | + | Catalonia is administratively divided into four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona | |
| − | + | Park Guell is in Barcelona. Garden complex designed by Gaudi | |
| − | + | Barcelona El-Prat airport is the second largest in Spain behind Madrid Barajas Airport | |
| + | |||
| + | Barcelona was known as Faventia in Roman times | ||
| + | |||
| + | A tree-lined pedestrian mall, La Rambla in Barcelona stretches for 1.2 km connecting Placa de Catalunya in the centre with the Christopher Columbus Monument at Port Vell | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dali Theatre and Museum is in Figueres, near Barcelona | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tarragona is a port city in Catalonia. The Roman ruins of Tarraco have been designated a World Heritage Site | ||
| + | |||
| + | Costa Brava is a coastal region of northeastern Catalonia, in the province of Girona. Costa is the Catalan and Spanish word for 'coast', and Brava means 'rugged' or 'wild'. It includes the town of Lloret de Mar | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Extremadura''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capital – Merida | ||
| + | |||
| + | Extremadura is formed by the two largest provinces of Spain: Caceres and Badajoz | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Galicia''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capital – Santiago de Compostela | ||
| + | |||
| + | Galicia takes its name from the Gallaeci, the Celtic peoples living north of the Douro river | ||
| + | |||
| + | Way of St James (Camino de Santiago) is the pilgrimage route to the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, where tradition has it that the remains of the apostle Saint James are buried. The scallop shell, often found on the shores in Galicia, has long been the symbol of the pilgrimage route | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vigo is a city in Galicia | ||
| + | |||
| + | A Coruna is the largest city in Galicia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lugo is the only city in the world to be surrounded by completely intact Roman walls | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tower of Hercules is the oldest extant lighthouse known. It has an ancient Roman origin on a peninsula near A Coruna | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''La Rioja''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capital – Logrono | ||
| + | La Rioja is the least populated autonomous community of Spain. It is well known for its wines | ||
| − | + | '''Madrid''' | |
| − | + | Madrid is the third largest city in the European Union, after London and Berlin, and its metropolitan area is the third largest in the European Union after Paris and London | |
| − | + | Madrid is the highest capital city in Europe | |
| − | + | Philip II named Madrid as the capital of Spain in 1561 | |
| − | + | Puerta del Sol is a square in Madrid | |
| − | + | Plaza de Colon is located in Madrid. This plaza and its fountain commemorate the explorer Christopher Columbus, whose name in Spanish was Cristóbal Colón | |
| − | + | Madrid is located on the Manzanares river | |
| − | + | Atocha railway station has a concourse with a tropical botanical garden | |
| − | River Dnieper flows from Russia, through Belarus and Ukraine (including | + | Terminal 4 at Madrid-Barajas Airport was designed by Richard Rogers |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Ciudad Real International Airport, previously known as Don Quixote Airport, was constructed at a cost of €1.1 billion. It was opened in 2009, but closed in 2012 when the management company filed for bankruptcy | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Las Ventas in Madrid is the largest bullring in Spain | |
| − | Seas | + | |
| − | + | '''Murcia''' | |
| − | Baltic Sea is the world’s largest pool of brackish water | + | |
| − | + | Capital – Murcia | |
| − | Gulf of Riga and Gulf of Finland are inlets of | + | |
| − | + | Murcia is the largest city | |
| − | Usedom is a Baltic Sea island since 1945 split between Germany and Poland | + | |
| − | + | Cartagena is the second largest city | |
| − | Market is an uninhabited island in the Baltic Sea divided between Sweden and Finland | + | |
| − | + | '''Navarre''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Capital – Pamplona | |
| − | Sea of | + | |
| − | + | Bull running in Pamplona is part of the San Fermin festival, held in July | |
| − | + | ||
| + | '''Valencian Community''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Valencia is known as the “city of 100 bell towers” | ||
| + | |||
| + | La Tomatina is a festival that is held in the Valencian town of Bunol, in which participants throw tomatoes at each other | ||
| + | |||
| + | Costa Blanca (English: White Coast) refers to the over 200 km of coastline belonging to the Province of Alicante. The name Costa Blanca was devised as a promotional name used by BEA when they launched their air service (for £38.16s.-) between London and Valencia in 1957. It includes the major tourist destinations of Benidorm and Alicante | ||
| + | |||
| + | Benidorm has the most high-rise buildings per capita in the world | ||
| + | |||
| + | Intempo in Benidorm consists of two parallel towers separated by a gap of 20 metres and connected by a cone-shaped structure between floors 38 and 44 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lladro is a company based in Valencia that produces high quality porcelain figurines | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Penon de Velez de la Gomera is a Spanish rock in North Africa off the Moroccan coast | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ebro is the longest river entirely in Spain | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rio Tinto river is notable for being very acidic (pH 2) and its deep reddish hue is due to iron dissolved in the water | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mulhacen is the highest mountain in continental Spain and in the Iberian Peninsula. It is part of the Sierra Nevada range | ||
| + | |||
| + | Picos de Europa is a mountain range in Spain | ||
| + | |||
| + | Faisans (Pheasant Island) in the Bidasoa river is an uninhabited river island that is formally controlled by Spain between 1 February and 31 July each year and by France for the following six months | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Autonomous cities === | ||
| + | '''Ceuta''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ceuta is an exclave located on the north coast of Africa, sharing a western border with Morocco. Ceuta, like Melilla, was a free port before Spain joined the European Union. Separated from the Iberian peninsula by the Strait of Gibraltar, Ceuta lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Melilla''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Melilla shares a border with Morocco and is and across the sea from the Spanish provinces of Granada and Almeria | ||
| + | == Sweden == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Sweden.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Stockholm | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Stockholm, Gothenburg, Malmo, Uppsala | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Krona | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Kebnekaise | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Stockholm is located where Lake Malaren flows into the Baltic Sea. The central parts of the city consist of fourteen islands that are continuous with the Stockholm archipelago | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vasa Museum in Stockholm displays the 64-gun warship ''Vasa'' that sank on her maiden voyage in 1628 | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for its decoration of the stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gamla Stan is the historic old town of Stockholm | ||
| + | |||
| + | Museum of World Culture is in Gothenburg | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gothenburg is situated by the Kattegat | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gota Canal provides a route from Gothenburg on the west coast to Soderkoping on the Baltic Sea, through the lakes Vanern and Vattern | ||
| + | |||
| + | Together with Copenhagen, Malmo constitutes the transnational Oresund Region | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Oresund Bridge is a combined two-track rail and four-lane road bridge across the Oresund strait. The bridge-tunnel is the longest combined road and rail bridge in Europe and connects Copenhagen and Malmo. The bridge ends in the middle of Oresund, on an artificially built island, called Peberholm. The connection between Peberholm and the nearest populated part of Denmark is through the Drogden Tunnel. Opened in 2000 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kiruna is the northernmost town in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland. The city's vicinity shares a long history with the indigenous Sami people. The town of Kiruna is being moved as an iron ore mine undermines the current town centre | ||
| + | |||
| + | ICEHOTEL near the village of Jukkasjarvi, Kiruna is the first and most famous of the ice hotels | ||
| + | |||
| + | Visby is main town of Gotland, which is Sweden’s largest island | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1999, the world's largest Viking silver treasure, the Spillings Hoard, was found in a field in Gotland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vanern is the largest lake in Sweden, the largest lake in the European Union and the third largest lake entirely in Europe after Ladoga and Onega in Russia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Oland is the second largest Swedish island and the smallest of the traditional provinces of Sweden | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sweden has more than 220,000 islands | ||
| + | |||
| + | Birka on the island of Bjorko was an important Viking Age trading centre | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ytterby is a village on the island of Resaro. Four chemical elements are named after the village | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Switzerland == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag of Switzerland.jpg|center|thumb|200x200px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Swiss flag is one of only two square sovereign-state flags, the other being the flag of Vatican City | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Berne | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Zurich, Geneva, Basel, Berne, Lausanne | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Swiss franc | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Dufourspitze | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Officially the Swiss Confederation (Latin: Confoederatio Helvetica, hence its abbreviation CH), is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Berne as the seat of the federal authorities, the so-called Bundesstadt ("federal city") | ||
| + | |||
| + | The establishment of the Swiss Confederation is traditionally dated to 1291 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Historically each canton in the then confederation was a sovereign state, with its own borders, army, and currency until the current federal structure was established in 1848 | ||
| + | [[File:Swiss cantons.png|center|thumb|600x600px|alt=]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Graubunden is the largest and easternmost canton of Switzerland. Also known as Grisons | ||
| + | |||
| + | Graubunden is the only canton where Romansh, Switzerland's fourth national language, has official status | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jura is the newest of the Swiss cantons. It was created in 1979 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Appenzell Innerrhoden is the smallest canton by population and the second smallest by area, with Basel-City being the smallest. It was the last Swiss canton to grant women the vote on local issues, in 1991 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Switzerland has four official languages – German, French, Italian, and Romansh | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zurich has the highest population of the cantons | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zurich was known as Turicum in Roman times | ||
| + | |||
| + | Most of Zurich's sites are located within the area on either side of the Limmat river, between the Main railway station and Lake Zurich | ||
| + | |||
| + | Geneva is located at the south-western end of Lake Geneva, where the lake flows back into the Rhone River. It is surrounded by two mountain chains, the Alps and the Jura | ||
| + | |||
| + | Geneva is known as ‘The Protestant Rome’ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Geneva is the headquarters of many of the agencies of the United Nations and the Red Cross | ||
| + | |||
| + | CERN is based in a suburb of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border | ||
| + | |||
| + | Palais des Nations in Geneva was built between 1929 and 1936 to serve as the headquarters of the League of Nations | ||
| + | |||
| + | Basel is on the Rhine, where the Swiss, French, and German borders meet | ||
| + | |||
| + | Basel has Switzerland’s only cargo port | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bayerler Foundation is an art museum in Riehen, near Basel | ||
| + | |||
| + | Canton of Berne is the second most populous of Switzerland's cantons | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Aare flows in a wide loop around the Old City of Berne | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lausanne is a city in Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland, and is the capital of the canton of Vaud. The city is situated on the shores of Lake Geneva | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kapellbrucke (Chapel Bridge) is a covered wooden footbridge spanning the river Reuss in Lucerne. The bridge was originally built in the 14th century | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lugano is in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest Italian-speaking city in Switzerland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bellinzona is the capital of Ticino | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vevey is the site of the world headquarters of the food giant Nestle, founded in 1867 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Suisse romande or Romandie is the area of French-speaking parts of western Switzerland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Interlaken is located between Lake Brienz to the east and Lake Thun to the west. The Aare River flows through the town connecting the lakes | ||
| + | |||
| + | Davos is the highest city in Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | Locarno is located on the northern tip of Lake Maggiore | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vindonissa was a Roman camp in Switzerland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Charles Kuonen Suspension Bridge is the longest hanging bridge for pedestrian use in the world. It is located in Randa and opened in 2017 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lotschberg Base Tunnel is a 21.5 mile long railway tunnel cutting through the Alps of Switzerland some 400 m below the existing Lotschberg Tunnel. It is the longest land tunnel in the world | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reichenbach Falls are near Meiringen. The falls are the location where Sherlock Holmes fights to the death with Professor Moriarty | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bernese Oberland is the higher part of the canton of Berne | ||
| + | |||
| + | Eiger is near Grindelwald in the Bernese Alps | ||
| + | |||
| + | Aletsch Glacier in the Bernese Alps is the largest Alpine glacier | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Neuchatel is the largest lake entirely in Switzerland, as the larger Lake Geneva (Lac Leman) is shared with France, and Lake Constance (German: Bodensee) with Germany and Austria | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Lucerne (‘Lake of the Four Forest Cantons’) is a lake in central Switzerland, the fifth largest in the country | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jungfraubahn is a rack railway which runs 9 km from Kleine Scheidegg to the highest railway station in Europe at Jungfraujoch. The railway runs almost entirely within a tunnel built into the Eiger and Monch mountains | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jungfrau is one of the main summits in the Bernese Alps. Together with the Eiger and Monch, the Jungfrau forms a massive wall overlooking the Bernese Oberland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jungfrau is German for maiden/virgin | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rhine Falls is the largest plain waterfall in Europe. The falls are located on the Upper Rhine near the town of Schaffhausen in northern Switzerland. Most powerful waterfall in Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zermatt lies at the foot of the Matterhorn | ||
| + | |||
| + | Monte Rosa is the highest mountain in Switzerland. Its main summit is named Dufourspitze | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Turkey == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Turkey.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Ankara | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Istanbul, Ankara, Izmir, Bursa | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Lira | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Mount Ararat | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Turkey is the only country to border the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, and has the longest border to the Black Sea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Istanbul is the most populous city in Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | Istanbul straddles the Bosporus Strait, which provides the only passage from the Black Sea to the Mediterranean via the Sea of Marmara | ||
| + | |||
| + | Taksim Square is considered the heart of modern Istanbul. Taksim is Arabic for ’division’ or ‘distribution’. The Taksim square was originally the point where the main water lines from the north of Istanbul were collected and branched off to other parts of the city (hence the name) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Grand Bazaar in Istanbul is among the world's most-visited tourist attractions | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fatih Sultan Mehmet Bridge and the Eurasia Tunnel are crossings across the Bosphorus | ||
| + | |||
| + | Golden Horn is a fresh-water estuary in Istanbul dividing the city of Istanbul. Crossed by several bridges, most notably the Galata Bridge. Galata was a colony of the Republic of Genoa between 1273 and 1453 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Galata Tower is a medieval stone tower in Istanbul | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Ankara was historically known as Angora | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ankara has many well-preserved remains of Ottoman and Roman architecture, the most remarkable being the Temple of Augustus and Rome | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hisarlik (‘Place of Fortresses’), is the modern Turkish name for the ancient site of Troy, also known as Ilion, and is located in Turkey (known throughout history as Anatolia) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Trabzon is a city on the Black Sea coast of northeastern Turkey, located on the Silk Road | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cappadocia region is largely underlain by sedimentary rocks formed in lakes and streams, and ignimbrite deposits erupted from ancient volcanoes approximately 9 to 3 million years ago | ||
| + | |||
| + | Goreme is a town in Cappadocia, located among the ‘fairy chimney’ volcanic tuff formations. Early homes were carved straight into the rock formations | ||
| + | |||
| + | Edirne is a city in Thrace, the westernmost part of Turkey, close to the borders with Greece and Bulgaria. Edirne served as the capital city of the Ottoman Empire from 1365 to 1457, when Constantinople (Istanbul) became the empire's new capital. Founded by the Romans as Adrianople | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Selimiye Mosque in Edirne was commissioned by Sultan Selim II and was built by architect Mimar Sinan between 1568 and 1574. It was considered by Sinan to be his masterpiece and is one of the highest achievements of Islamic architecture | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sardis was an ancient city at the location of modern Sart in Turkey. Sardis was the capital of the ancient kingdom of Lydia, one of the important cities of the Persian Empire, the seat of a proconsul under the Roman Empire, and the metropolis of the province Lydia in later Roman and Byzantine times | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gobekli Tepe (‘Potbelly Hill’) is a Neolithic (stone-age) hilltop sanctuary erected at the top of a mountain ridge in southeastern Anatolia. It is the oldest known human-made religious structure. This is where modern wheat was first domesticated | ||
| + | |||
| + | Catalhoyuk (‘Fork tumulus’) was a large Neolithic and Chalcolithic settlement in southern Anatolia, which existed from approximately 7500 BC to 6400 BC. The site was first excavated by James Mellaart in 1958 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Library of Celsus is an ancient Roman building in Ephesus, Anatolia, now part of Selcuk. It was built in honour of the Roman Senator Tiberius Julius Celsus Polemaeanus | ||
| + | |||
| + | The site of the temple of Artemis at Ephesus was discovered by John Turtle Wood in 1869 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Batman is a Kurdish-majority city | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rize is a tea producing province in Turkey | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hatay Province is the southernmost province of Turkey. Sovereignty over the province remains disputed with neighbouring Syria | ||
| + | |||
| + | Antakya, historically known as Antioch, is the capital of Hatay Province | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bosphorus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara. It is the world's narrowest strait used for international navigation | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dardanelles connects the Aegean and Sea of Marmara. Also known as the Strait of Gallipoli or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1915 Canakkale Bridge, the first bridge over the Dardanelles and the world's longest suspension bridge, opened in 2022 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Marmaray is an undersea rail tunnel that links the European and Asian sections of Istanbul, running under the Bosphorus strait. Completed in 2019, it is the world's deepest undersea immersed tube tunnel | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lycia was a geopolitical region in Anatolia in what are now the provinces of Antalya and Mugla on the southern coast of Turkey | ||
| + | |||
| + | Turquoise Coast is the southwest Mediterranean coast of Turkey. Also known as the Turkish Riviera | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tigris and Euphrates both rise in Turkey | ||
| + | |||
| + | Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey | ||
| + | |||
| + | Taurus Mountains are in southern Turkey, dividing the Mediterranean coastal region of southern Turkey from the central Anatolian Plateau | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mount Ararat overlooks the city of Yerevan | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pontic Mountains are a mountain range in northern Anatolia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Van is the largest lake in Turkey | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ceyhan is the Mediterranean terminus of the Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline which brings crude oil from the landlocked Caspian Sea | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Ukraine == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Ukraine.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Kyiv | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Kyiv, Kharkiv, Odesa, Dnipro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Hryvna | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Hoverla | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Ukraine is the largest wholly European country | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ukraine’s only mountains are the Carpathian Mountains in the west | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kyiv is also known as Kiev | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kyiv is on the Dnieper river | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kyiv Pechersk Lavra, also known as the Kyiv Monastery of the Caves, is a historic Orthodox Christian monastery. Since its foundation as the cave monastery in 1015 the Lavra has been a preeminent centre of the Eastern Orthodox Christianity in Eastern Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery is in Kyiv | ||
| + | |||
| + | The largest cave in Europe, Optymistychna, is a gypsum cave in Ukraine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Donbas refers to the Donetsk and Luhansk regions | ||
| + | |||
| + | Donetsk was founded by Welsh engineer and businessman John Hughes, for the building of metal works | ||
| + | |||
| + | Donetsk Sergei Prokofiev International Airport is a former airport that was destroyed in 2014 during the war in Donbas | ||
| + | |||
| + | Odesa is also known as Odessa | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dnipro, formerly Dnipropetrovsk, is located in the eastern part of Ukraine on the Dnieper River | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pripyat is a ghost town near the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in the Kyiv Oblast of northern Ukraine, near the border with Belarus | ||
| + | |||
| + | Slavutych was built for the evacuated personnel of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant following the 1986 disaster | ||
| + | |||
| + | Duga woodpecker was an over-the-horizon radar sited near Chernobyl | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lviv was previously known as Lemberg and Lwow. It has been occupied by Poland, Germany, and the Soviet Union | ||
| + | |||
| + | Crimea has a large Tatar population | ||
| + | |||
| + | Simferopol is the capital of Crimea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sevastopol is the largest city of Crimea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Livadia Palace was a summer retreat of the last Russian tsar, Nicholas II, and his family in Livadiya, in Crimea. The Yalta Conference was held there in 1945, when the palace housed the apartments of Franklin Delano Roosevelt and other members of the American delegation | ||
| + | |||
| + | Isthmus of Perekop connects Crimea to the mainland of Ukraine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Crimean Bridge, also called Kerch Strait Bridge or Kerch Bridge, is a pair of parallel bridges, one for a four-lane road and one for a double-track railway, spanning the Kerch Strait between Krasnodar Krai in Russia and the Kerch Peninsula of Crimea. Built by the Russian Federation after the annexation of Crimea at the start of 2014, the bridge cost has a length of 19 km, making it the longest bridge in Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | == United Kingdom == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-United-Kingdom.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | Flag of United Kingdom consists of the red cross of Saint George, superimposed on the Cross of St Patrick, which are superimposed on the Saltire of Saint Andrew | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |London | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |London, Birmingham, Manchester, Leeds, Glasgow | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Pound | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Ben Nevis | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | For further information see [[Civilisation/British Isles Geography|British Isles Geography]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Gibraltar === | ||
| + | [[File:Flag of Gibraltar.png|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Flag of Gibraltar is unique as it is the only British Overseas Territory which does not feature the Union Jack | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory. The United Kingdom considers Gibraltar to be under its sovereignty, but not as part of the United Kingdom itself | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gibraltar was awarded city status in 2022 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Strait of Gibraltar is 13 km wide | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gibraltar has been ruled by Britain since 1704. It was named ‘Jebel Tarik’ by Moorish settlers | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Rock of Gibraltar is a monolithic limestone promontory. It is one of the two traditional Pillars of Hercules | ||
| + | |||
| + | Europa Point is a lighthouse in Gibraltar | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gorham's Cave is a natural sea cave in Gibraltar, and is considered to be one of the last known habitations of the Neanderthals c. 25,000 years ago | ||
| + | |||
| + | North Front airport serves Gibraltar | ||
| + | |||
| + | GX11 1AA is the postcode for Gibraltar | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Barbary macaque population in Gibraltar is the only wild monkey population on the European continent | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Vatican City == | ||
| + | [[File:Flag-of-Vatican-City.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | Flag of Vatican City is a yellow and white square. On the white area is surmounted the Papal crown and two crossed keys, which represent the keys to the Kingdom of Heaven | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |Capital | ||
| + | |Vatican City | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Largest cities | ||
| + | |Vatican City | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Currency | ||
| + | |Euro | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Highest point | ||
| + | |Vatican Hill | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Vatican City is a walled enclave within the city of Rome. With an area of approximately 44 hectares (110 acres), and a population of around 450, it is the smallest internationally recognized independent state in the world by both area and population | ||
| + | |||
| + | The name ‘Vatican’ predates Christianity and comes from the Latin Mons Vaticanus, meaning Vatican Mount | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vatican City is one of a few widely recognized independent states that has not become a member of the United Nations. The Holy See, which is distinct from Vatican City State, has permanent observer status | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sistine Chapel is in the Apostolic Palace, the official residence of the Pope. Originally known as the Cappella Magna, the chapel takes its name from Pope Sixtus IV, who restored it between 1477 and 1480. There are five sibyls on the roof of the Sistine Chapel | ||
| + | |||
| + | St. Peter's Basilica is a Late Renaissance church located within Vatican City. It is the largest church in the world. Designed principally by Donato Bramante, Michelangelo, Carlo Maderno and Gian Lorenzo Bernini | ||
| + | |||
| + | Saint Peter's Square is a large plaza located directly in front of St. Peter's Basilica. At the centre of the square is an ancient Egyptian obelisk | ||
| + | |||
| + | Belvedere Torso is a marble fragment of a nude male statue, signed prominently on the front of the base by "Apollonios, son of Nestor, Athenian", who is unmentioned in ancient literature. It is now in the Vatican Museums | ||
| + | |||
| + | == States with limited recognition == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Abkhazia === | ||
| + | [[File:Flag of the Republic of Abkhazia.png|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | Abkhazia considers itself an independent state, called the Republic of Abkhazia. The Georgian government, United Nations and the majority of the world's governments consider Abkhazia a part of Georgia's territory, though Georgia is not in control of it. Sukhumi is the capital | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Artsakh === | ||
| + | [[File:Flag of Artsakh.png|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Artsakh (formerly known as the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic) declared its independence in 1991. It is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus supported by Armenia, whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan | ||
| + | |||
| + | In September 2020, fighting broke out between Armenia and Azerbaijan over Artsakh. Azerbaijan recaptured territories, primarily in the southern part of the region. A ceasefire agreement signed in November 2020 between Armenia, Azerbaijan and Russia declared an end to the renewed fighting, and established that Armenia would withdraw from remaining occupied territories surrounding the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast over the next month, while maintaining control over the areas of the former oblast that had not been captured during the war | ||
| + | |||
| + | Stepanakert is the capital and the largest city | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Northern Cyprus === | ||
| + | [[File:Flag of the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.png|center|thumb]] | ||
| + | Northern Cyprus is a self-declared state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Recognised only by Turkey, Northern Cyprus is considered by the international community as part of the Republic of Cyprus | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Transnistria === | ||
| + | [[File:Flag of Transnistria (state).svg.png|center|thumb|200x200px]] | ||
| + | Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic, is landlocked and borders Moldova to the west and Ukraine to the east. It is a narrow valley stretched in the north-south direction along the banks of the Dniester River | ||
| + | |||
| + | Transnistria is designated by the Republic of Moldova as the Transnistria autonomous territorial unit with special legal status. The capital and largest city is Tiraspol | ||
| + | |||
| + | === South Ossetia === | ||
| + | [[File:Flag of South Ossetia.png|center|thumb|200x200px]] | ||
| + | South Ossetia declared independence from Georgia in 1990, calling itself the Republic of South Ossetia. The Georgian government responded by abolishing South Ossetia's autonomy and trying to re-establish its control over the region by force. The crisis escalation led to the 1991–92 South Ossetia War. The capital is Tskhinvali | ||
| + | |||
| + | South Ossetia is officially the Republic of South Ossetia or the State of Alania | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Physical Geography == | ||
| + | <u>Regions</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west. This was the name by which Imperial Russia designated the eastern part of the Principality of Moldavia. Part of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Ukraine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cerdanya, or Cerdagne, is a historical region of the eastern Pyrenees divided between France and Spain | ||
| + | |||
| + | Galicia is currently divided between Poland and Ukraine, and was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jutland forms the mainland part of Denmark, and the German state of Schleswig-Holstein | ||
| + | |||
| + | Karelia is currently divided between the Russian Republic of Karelia, the Russian Leningrad Oblast, and Finland (the regions of South Karelia and North Karelia) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Livonia is a historic region along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. Currently split between Estonia and Latvia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lusatia is a historical region in Central Europe, today located within the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg, and Poland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Macaronesia consists of Azores, Madeira Islands, Canary Islands, and Cape Verde Islands | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pomerania is located on the south coast of the Baltic Sea, divided today between Germany in the west and Poland in the east by the Polish-German border. Pomerania stretches roughly from Stralsund in the west to Gdansk in the east, centered on the Oder River delta | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Mountains</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The highest mountain in Europe is Mount Elbrus, with a summit of 5,642 m. It is located in Russia and it the highest peak of the Caucasus Mountains | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dykh-Tau is the second highest of the Caucasus Mountains, after Mount Elbrus, and is the second highest peak in Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | Caucasus Mountains stretch from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tatra Mountains form a natural border between Slovakia and Poland. They are the highest mountain range in the Carpathian Mountains | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Urals run north-south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan. They are usually considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia. Mount Narodnaya is the highest peak of the Urals | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jura Mountains are a small mountain range located north of the Alps, separating the Rhine and Rhone rivers and forming part of the watershed of each. The mountain range is located in France, Switzerland, and Germany. Cret de la Neige is the highest mountain in the Jura Mountains | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pindus mountain range is located in northern Greece and southern Albania. Mount Smolikas is the highest of the Pindus Mountains, and the second highest mountain in Greece after Mount Olympus | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dinaric Alps are between Croatia and Albania | ||
| + | |||
| + | Matterhorn (German), Cervino (Italian) or Cervin (French), is a mountain in Switzerland and Italy and is one of the highest peaks in the Alps | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mont Blanc is the highest mountain in the Alps and the highest peak in Europe outside of the Caucasus range. It rises 4,810 m above sea level, lying on the border between France and Italy. It was part of the Duchy of Savoy between 1416 and 1792 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rhodopes are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, with over 83% of its area in southern Bulgaria and the remainder in Greece | ||
| + | |||
| + | Balkan Mountains are mainly in Bulgaria, but also cover part of Serbia. Botev Peak is the highest mountain | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cantabrian Mountains stretch for over 300 km across northern Spain | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vosges are a range of mountains in eastern France. The highest peak is Grand Ballon | ||
| + | |||
| + | Julian Alps stretch from north-eastern Italy to Slovenia, where they rise to 2864 metres at Triglav. They are named after Julius Caesar and are part of the Southern Limestone Alps | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pyrenees is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. The highest point is Aneto, in the Spanish region of Aragon | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Alpine Tunnels</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mont Blanc Tunnel links Chamonix, Haute-Savoie, France with Courmayeur, Aosta Valley, Italy. Opened in 1965 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gotthard Tunnel is a railway tunnel and forms the summit of the Gotthard Railway in Switzerland. Opened in 1882 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gotthard Road Tunnel runs from Goschenen in the canton of Uri at its northern portal, to Airolo in Ticino to the south. At time of construction, in 1980, it was the longest road tunnel in the world | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gotthard Base Tunnel opened in 2016. With a route length of 57 km it is the world's longest railway and deepest traffic tunnel | ||
| + | |||
| + | Simplon Tunnel is a railway tunnel on the Simplon railway that connects Brig, Switzerland and Domodossola, Italy, through the Alps. East tunnel opened in 1906. West tunnel opened in 1921 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Frejus Rail Tunnel links Bardonecchia in Italy to Modane in France under Col du Frejus. Opened in 1871 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Frejus Road Tunnel opened in 1980 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lotschberg Base Tunnel is a 34 km railway base tunnel cutting through the Bernese Alps of Switzerland | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Rivers</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Longest rivers in Europe – Volga, Danube, Ural, Dnieper, Don | ||
| + | |||
| + | Danube flows from the Black Forest into the Black Sea, and connects 10 countries | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capital cities that lie on the Danube – Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bratislava | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sava is a tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia, along the northern border of Bosnia and Herzegovina, through Serbia, discharging into the Danube in Belgrade | ||
| + | |||
| + | Iron Gates is a gorge on the Danube River. It forms part of the boundary between Romania and Serbia. The tallest rock sculpture in Europe, a 42.9 m carving in rock of the face of Decebalus, is a sculpture of the last king of Dacia on a rocky outcrop near the Iron Gates | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ural river rises in the southern Ural Mountains and ends at the Caspian Sea. Its total length is 1511 miles making it the third longest river in Europe after the Volga and the Danube | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dnieper flows from Russia, through Belarus and Ukraine (including Kyiv), to the Black Sea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rhone rises in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Arles, near its mouth, the river divides into the Great Rhone and the Little Rhone. The resulting delta forms the Camargue region | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rhine rises in the Swiss canton of Graubunden, and flows through Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, France, and Netherlands where it empties into the North Sea. It is the second longest river in Central and Western Europe, after the Danube. Vaduz is the only capital city that lies on the Rhine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Meuse rises in France and flows through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea. The Meuse is one of the oldest rivers in the world | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tagus is the longest river on the Iberian Peninsula. It is 1,038 km long, 716 km in Spain, 47 km along the border between Portugal and Spain and 275 km in Portugal, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean near Lisbon | ||
| + | |||
| + | Douro flows from its source near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province across northern-central Spain and Portugal to its outlet at Porto. It is the third-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula after the Tagus and Ebro | ||
| + | |||
| + | Daugava rises in Russia and drains into the Gulf of Riga in Latvia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Garonne flows from the central Spanish Pyrenees to the Gironde estuary at the French port of Bordeaux | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Lakes</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Maggiore is the second largest lake of Italy and largest of southern Switzerland. It is divided between the Italian regions of Piedmont and Lombardy and the Swiss canton of Ticino. The Borromean Islands and Brissago Islands are located in Lake Maggiore | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Lugano is a glacial lake which is situated on the border between southern Switzerland and northern Italy. The lake, named after the city of Lugano, is situated between Lake Como and Lake Maggiore | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Constance (German: Bodensee) is a lake on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps, and consists of three bodies of water: the Obersee (‘upper lake’), the Untersee (‘lower lake’), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Seerhein. The lake is situated in Germany, Switzerland and Austria | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Geneva (Lac Leman) is the largest alpine lake, and lies on the border between France and Switzerland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Ohrid straddles the mountainous border between North Macedonia and Albania. It is one of Europe's deepest and oldest lakes | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Peipus is the biggest transboundary lake in Europe and lies on the border between Estonia and Russia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Sevan is the largest body of water in Armenia and the Caucasus region | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Skadar is the largest lake in the Balkans. It lies on the border of Albania and Montenegro | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake Prespa is located on the tripoint of North Macedonia, Albania, and Greece | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Seas</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Baltic Sea is the world’s largest pool of brackish water | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gulf of Bothnia is the northernmost arm of the Baltic Sea, between Finland's west coast and Sweden's east coast. The Finnish region of Aland lies in the south of the gulf | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gulf of Riga and Gulf of Finland are inlets of theBaltic Sea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Usedom is a Baltic Sea island that since 1945 has been split between Germany and Poland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Market is an uninhabited island in the Baltic Sea divided between Sweden and Finland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Skagerrak is a strait running between the southeast coast of Norway, the southwest coast of Sweden, and the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area, which leads to the Baltic Sea | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kattegat separates Sweden and Denmark, and is a continuation of the Skagerrak | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denmark Strait separates Iceland and Greenland | ||
| + | |||
| + | Barents Sea is located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bering Strait is 53 miles across at the narrowest point | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chukchi Sea lies north of the Bering Strait | ||
| + | |||
| + | Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean off the coast of Siberia | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia, between the Barents Sea and the Laptev Sea | ||
| + | |||
| + | North Sea was known as the German Sea | ||
| − | + | Graeco-Roman tradition refers to the Black Sea as the ‘Hospitable Sea’ | |
| − | + | Sea of Azov is a northern section of the Black Sea, linked to the larger body through the Strait of Kerch. It is bounded on the north by Ukraine, on the east by Russia and on the west by the Crimean Peninsula | |
| − | + | Caspian Sea borders Russia, Iran and Azerbaijan. It is the is the world's largest inland body of water | |
| − | + | Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Apennine peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges | |
Istria is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner. Istria lies in three countries: Croatia, Slovenia and Italy | Istria is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner. Istria lies in three countries: Croatia, Slovenia and Italy | ||
| Line 2,481: | Line 3,838: | ||
Aegean Sea is a sea arm of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey respectively. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus | Aegean Sea is a sea arm of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey respectively. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus | ||
| − | + | Ionian Sea is connected to the Tyrrhenian Sea by the Strait of Messina, and to the Adriatic Sea by the Strait of Otranto | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Ionian Sea | ||
Calypso Deep, located in the Ionian Sea south-west of Pylos, Greece, is the deepest part of the Mediterranean Sea. At the Calypso Deep, the African Plate slides under the Eurasian Plate, creating the Hellenic Trench | Calypso Deep, located in the Ionian Sea south-west of Pylos, Greece, is the deepest part of the Mediterranean Sea. At the Calypso Deep, the African Plate slides under the Eurasian Plate, creating the Hellenic Trench | ||
| Line 2,491: | Line 3,844: | ||
Strait of Otranto separates Italy from Corfu and Albania | Strait of Otranto separates Italy from Corfu and Albania | ||
| − | + | Strait of Sicily lies between Sicily and Tunisia | |
| − | |||
| − | Strait of Sicily | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Alboran Sea is the westernmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, lying between the Iberian Peninsula and the north of Africa. Alboran Island is a small islet of Spain in the Alboran Sea | |
Latest revision as of 21:29, 23 July 2023
Albania
The symbol on the flag of Albania is a double-headed eagle
| Capital | Tirana |
| Largest cities | Tirana, Durres |
| Currency | Lek |
| Highest point | Mount Korab |
Albania is officially the Republic of Albania (Albanian: Republika e Shqipërisë)
Tirana was founded as a city in 1614 by the Ottoman Albanian general Sylejman Pasha Bargjini
Durres is the main port of Albania
Vlore is the old capital of Albania. It is the city where the Albanian Declaration of Independence was proclaimed in 1912
Karaburun peninsula is located along the Albanian Ionian Sea Coast
Albania is the only European country with a 20th century Muslim monarch
In 1967 Enver Hoxha proclaimed Albania the world's first 'atheist state'
Andorra
| Capital | Andorra la Vella |
| Largest cities | Andorra la Vella |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Coma Pedrosa |
Andorra is a parliamentary co-principality with the President of France and the Bishop of Urgell (Catalonia, Spain), as co-princes. This peculiarity makes the President of France, in his capacity as Prince of Andorra, an elected reigning monarch
Andorra la Vella is the highest capital city in Europe
Catalan is the official language of Andorra
Andorra is divided into seven parishes
Andorra is the largest country in the world which does not have an airport
Armenia
| Capital | Yerevan |
| Largest cities | Yerevan |
| Currency | Dram |
| Highest point | Mount Aragats |
In August 1990, Armenia declared independence, becoming the first non-Baltic republic to secede from the Soviet Union
Armenia supports the de facto independent Artsakh
Armenia was the first country to adopt Christianity as its state religion
Armenia is the smallest ex-Soviet republic
Austria
According to legend, the flag of Austria was invented by Duke Leopold V as a consequence of his fighting during the Crusades. After a fierce battle, his white battle dress was completely drenched in blood. When he removed his belt, the cloth underneath was untouched by it, revealing the combination of red-white-red
| Capital | Vienna |
| Largest cities | Vienna, Graz, Linz, Salzburg, Innsbruck |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Grossglockner |
Austria is a federal republic made up of nine states, known in German as Länder
Vindobona was the Roman name for Vienna
Ringstrasse is a circular road surrounding the Innere Stadt district of Vienna
Graben is one of the most famous streets in Vienna's first district, the city centre
Prater is a large public park in Vienna. Oldest amusement park in the world
Zentralfriedhof (German for "Central Cemetery") is one of the largest cemeteries in the world, largest by number of interred in Europe and most famous cemetery among Vienna's nearly 50 cemeteries. Beethoven is interred in this cemetery
Vienna Zoo (Tiergarten Schonbrunn) was founded as an imperial menagerie in 1752 and is the oldest continuously operating zoo in the world
Graz is the capital of Styria
Lower Austria is the largest state in Austria
Linz is the capital of Upper Austria. It lies on the River Danube. In 2009, it was a European Capital of Culture
Salzburg (Geman: ‘salt castle’) lies on the site of the Roman settlement of Iuvavum. Salzburg's historic centre is renowned for its Baroque architecture
Innsbruck is the capital of Tyrol. It lies on the River Inn
Semmering is a mountain pass in the Eastern Northern Limestone Alps connecting Lower Austria and Styria, between which it forms a natural border
Brenner Pass is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria
Azerbaijan
The star on the flag of Azerbaijan has eight points
| Capital | Baku |
| Largest cities | Baku, Ganja |
| Currency | Manat |
| Highest point | Mount Bazardudu |
Baku is the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region
Baku is located 28 m below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world
Maiden Tower was built in the 12th century as part of the walled city of Baku. Together with the Shirvanshahs' Palace, dated to the 15th century, it forms an ensemble of historic monuments inscribed in 2001 under the UNESCO World Heritage List of Historical Monuments as cultural property
By the beginning of the 20th century almost half of world production of oil was being extracted in Baku
Oil Rocks is a town on the Caspian Sea, and was the first oil platform in Azerbaijan
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers 5,500 km2 and borders Armenia, Iran and Turkey
Lachin corridor is a mountain pass within de-jure borders of Azerbaijan, It is the shortest route which connects Armenia with Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
Belarus
| Capital | Minsk |
| Largest cities | Minsk, Homyel |
| Currency | Ruble |
| Highest point | Dzyarzhynskaya Hara |
Belarus is Europe’s biggest landlocked country
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed in Brest
From 1919 to 1991, after the Russian Revolution, Minsk was the capital of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic within the Soviet Union
Pinsk Marsges (also known as Pripet Marches) occupy most of the southern part of Belarus and the north-west of Ukraine
Belarus is the last country in Europe to still retain and use the death penalty
Belarus is the only newly-independent country to keep the Ruble as its currency after 1993
Homyel is also known as Gomel
Belgium
The colours of the flag of Belgium were taken from the coat of arms of the Duchy of Brabant
| Capital | Brussels |
| Largest cities | Brussels, Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liege |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Signal de Botrange |
Belgium's two largest regions are the Dutch-speaking region of Flanders in the north and the French-speaking southern region of Wallonia. The Brussels-Capital Region, officially bilingual, is a mostly French-speaking enclave within the Flemish Region
Luxembourg is the largest of the ten provinces in Belgium
Flemish, French and German are the official languages of Belgium
NATO Headquarters are in Brussels
Brussels is on River Zenne/Senne, a tributary of the Scheldt
Grand Place or Grote Markt is the central square of Brussels. It is surrounded by Baroque guildhalls of the former Guilds of Brussels and two larger edifices; the city's Flamboyant Town Hall, and the neo-Gothic King's House or Bread House building, containing the Brussels City Museum
In the centre of Brussels, the River Zenne was completely covered up and major boulevards were built over top in the 19th and early 20th centuries
Menin Gate is at Ypres
Tyne Cot is a Commonwealth War Graves Commission burial ground for the dead of the First World War in the Ypres Salient
Zeebrugee is also known as Bruges-sur-mer
Antwerp is on the River Scheldt
Rubenshuis is the former home and studio of Peter Paul Rubens in Antwerp. It is now a museum
Ghent is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province
Belgium was known as “The Cockpit of Europe”, due to the number of battles fought there
Leuven is the capital of Flemish Brabant
Waterloo is in the province of Walloon Brabant
Lion's Mound is a large conical artificial hill raised on the battlefield of Waterloo to commemorate the location where William II of the Netherlands (the Prince of Orange) was knocked from his horse during the battle. It was ordered constructed in 1820 by his father, King William I of The Netherlands
Liege is situated in the valley of the Meuse River, near Belgium's eastern borders with the Netherlands and Germany. The city is the principal economic and cultural centre of Wallonia. Liege is the second most populous city in Wallonia, after Charleroi
Mechelen is a Dutch-speaking city and municipality in the province of Antwerp. It is one of Flanders' prominent cities of historical art
Baarle-Hertog is a Flemish municipality of Belgium, much of which consists of a number of small Belgian exclaves in the Netherlands. Baarle-Hertog is noted for its complicated borders with Baarle-Nassau, Netherlands
Bosnia and Herzegovina
The white stars on a blue background on the flag of Bosnia and Herzegovina represent links with the EU
| Capital | Sarajevo |
| Largest cities | Sarajevo, Banja Luka |
| Currency | Mark |
| Highest point | Maglic |
Republika Srpska is one of the two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located in the north and east of the country. Its largest city and administrative centre is Banja Luka
Mostar Bridge (Stari Most, ‘old bridge’) is a 16th century Ottoman bridge that crosses the River Neretva in Bosnia and Herzegovina and connects two parts of the city. The Old Bridge stood for 427 years, until it was destroyed in 1993 during the Croat-Bosniak War. Subsequently, a project was set in motion to reconstruct it, and the rebuilt bridge opened in 2004
Miljacka River passes through Sarajevo
Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for 20 km of coastline on the Adriatic Sea surrounding the city of Neum
Brcko District is a self-governing administrative unit in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bulgaria
| Capital | Sofia |
| Largest cities | Sofia, Plovdiv, Varna |
| Currency | Lev |
| Highest point | Musala |
Sofia was originally a Thracian settlement
St. Alexander Nevsky Cathedral is a Bulgarian Orthodox cathedral in Sofia
National Palace of Culture and Vitosha Boulevard are in Sofia
Plovdiv was the European Capital of Culture in 2019
Varna is the largest city and seaside resort on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. It was named Stalin between 1949 and 1956
The three national parks in Bulgaria are Pirin National Park, Rila National Park and Central Balkan National Park
Musala is the highest point in the Rila Mountains, in the Balkan Peninsula
Croatia
| Capital | Zagreb |
| Largest cities | Zagreb, Split, Rijeka |
| Currency | Kuna |
| Highest point | Dinara |
Zagreb lies on the Sava river
Zagreb Airport is named after Franjo Tudman, the first President of Croatia
Split is the largest city in the region of Dalmatia. Diocletian’s Palace is a World Heritage Site
Rijeka is the largest port in Croatia. because of its strategic position and its excellent deep-water port, the city was fiercely contested, especially between the Holy Roman Empire, Hungary (serving as the Kingdom of Hungary's largest and most important port, known as Fiume), Italy and Croatia
Trogir is a historic town and harbour on the Adriatic coast. The centre of Trogir is a World Heritage Site
Lord Byron called Dubrovnik the “pearl of the Adriatic”
Dubrovnik was known as Ragusa until 1909
Zadar is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatian city
Slavonia, Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria are the four historical regions of Croatia
Cres and Krk are the largest Croatian islands
Korkula is the second most populous Adriatic island after Krk
Plitvice Lakes National Park is the oldest national park in Southeast Europe and the largest national park in Croatia
The Danube runs through the city of Vukovar in the extreme east and forms part of the border with Serbia
Karst topography makes up about half of Croatia and is especially prominent in the Dinaric Alps
Cyprus
The outline of the island on the flag of Cyprus is a copper-orange colour, symbolising the large deposits of copper ore on the island
| Capital | Nicosia |
| Largest cities | Nicosia, Limassol |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Mount Olympus |
Cyprus is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean
Mount Olympus is the highest point of the Troodos Mountains
Pedieos is the longest river on Cyprus
United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus is a demilitarised zone that was established in 1974 following the Turkish invasion of Cyprus. The zone runs for more than 180 km along what is colloquially known as the Green Line. Turkish forces built a barrier on the zone's northern side – this line is also referred to as the Attila Line
Ledra Street is a major shopping thoroughfare in central Nicosia. It is the site of the former Ledra Street barricade, across the United Nations buffer zone
Limassol, on the southern coast, was built between two ancient Greek cities, Amathus and Kourion, and during Byzantine rule it was known as Neapolis
Karpas Peninsula is the long peninsula of northeast Cyprus
Akrotiri and Dhekelia is a British Overseas Territory on Cyprus
Czech Republic (Czechia)
| Capital | Prague |
| Largest cities | Prague, Brno, Ostrava |
| Currency | Koruna |
| Highest point | Sněžka |
Czechia is the official short name of Czech Republic
Kraj is the highest-level administrative unit in the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic
Prague is known as the ‘City of a Hundred Spires’
Charles Square in Prague is one of the largest squares in the world and was the largest town square of the medieval Europe
Charles Bridge is a medieval stone arch bridge that crosses the Vltava river in Prague. Its construction started in 1357
Wenceslas Square is one of the main city squares and the centre of the business and cultural communities in the New Town of Prague
Prague astronomical clock, or Prague orloj was first installed in 1410, making it the oldest astronomical clock in the world still working
Karlovy Vary, known in English as Carlsbad, is a spa city situated in Bohemia, the western part of the Czech Republic, on the confluence of the rivers Ohře and Teplá. Part of the Spa Triangle, along with Marinnske Lazne and Frantiskovy Lizne. Carlsbad is named after Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV, who founded the city in 1370. Moser is a luxury, high-quality glass manufacturer based in Carlsbad
Moravia occupies most of the eastern third of the Czech Republic
Czech Silesia is one of the three Czech lands and a section of the Silesian historical region. It is located in the north-east of the Czech Republic
Vltava is the longest river in the Czech Republic, running north from its source near the German Border, through Prague, merging with the Elbe at Melník
Denmark
The flag of Denmark, the Dannebrog, holds the world record of being the oldest continuously used national flag. Adopted in 1219
| Capital | Copenhagen |
| Largest cities | Copenhagen, Aarhus, Odense |
| Currency | Krone |
| Highest point | Mollehoj |
Denmark consists of the peninsula of Jutland and an archipelago of 443 named islands
Tivoli, also known as Tivoli Gardens, is an amusement park and pleasure garden in Copenhagen. The park opened in 1843
Bakken is an amusement park near Copenhagen. It opened in 1583 and is the world's oldest operating amusement park
Copenhagen is located partly on the islands of Zealand and Amager
Kastrup Airport serves Copenhagen
Aarhus is located on the eastern shore of Jutland in the Kattegat sea
The island of Bornholm is part of Denmark
Odense is the largest city on the island of Funen
Billund is a town in Jutland that is home to the Lego Group head office and the Legoland theme park
Roskilde Cathedral is the burial site for Danish monarchs
Viking Ship Museum in Roskilde is the Danish national museum for ships. Around 1070, five Viking ships were deliberately sunk at Skuldelev in Roskilde Fjord in order to block the most important fairway and to protect Roskilde from enemy attack from the sea
The Vikingemuseet Ladby in Denmark is the only place in the world where a Viking burial ship may be seen in its original position inside a burial mount
Kronborg is a castle in the town of Helsingor. Immortalized as Elsinore in Hamlet
Capital Region of Denmark is the easternmost administrative region of Denmark
Denmark generates 40% of its electricity from wind power
Samso is a carbon-neutral island in the Kattegat. All of its electricity comes from wind power and biomass
Great Belt Fixed Link is a multi-element fixed link crossing the Great Belt strait between the Danish islands of Zealand and Funen (Fyn). It consists of a road suspension bridge and a railway tunnel between Zealand and the small island Sprogø in the middle of the Great Belt, and a box-girder bridge for both road and rail traffic between Sprogø and Funen
Limfjord is a shallow part of the sea that has been regarded as a fjord ever since Viking times
Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands have been a self-governing country within the Danish Realm since 1948
Streymoy and Esturoy are the largest of the Faroe Islands
Torshavn is the capital of the Faroe Islands and is situated on the island of Streymoy
Estonia
| Capital | Tallinn |
| Largest cities | Tallinn, Tartu |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Suur Munamagi |
From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known as Reval, its historical Danish name
Soomaa (‘land of bogs’) National Park is a Ramsar site of protected wetlands
Suur Munamagi is the highest point in the Baltic states
Saaremaa and Hiiumaa are the two largest islands of Estonia
Peipus is the largest lake in Estonia, and the fifth largest lake in Europe
Finland
| Capital | Helsinki |
| Largest cities | Helsinki, Espoo, Tampere |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Halti |
Uusimaa is the region of Finland that contains Helsinki
Helsinki was founded by Gustav I of Sweden
Helsinki is known as Helsingfors in Sweden
Helsinki Metro has bright orange trains and is is the world's northernmost subway
Turku was the capital of Finland until 1812
Rovaniemi is the capital of Lapland. It is home to the Santa Claus Village at the Arctic Circle and SantaPark Arctic World
Finland is the most sparsely populated country in the European Union
Finland has about 168,000 lakes and 179,000 islands. Its largest lake, Saimaa, is the fourth largest in Europe
Kemijoki is the longest river in Finland
Archipelago Sea is a part of the Baltic Sea between the Gulf of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland and the Sea of Aland, within Finnish territorial waters. By some definitions it contains the largest archipelago (island group) in the world by the number of islands
Aland Islands form an archipelago in the Baltic Sea. They are situated at the entrance to the Gulf of Bothnia and form an autonomous Swedish-speaking region of Finland. Mariehamm is the capital
France
Flag of France has a variant with lighter shades
| Capital | Paris |
| Largest cities | Paris, Marseille, Lyon, Toulouse, Nice |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Mont Blanc |
France is the largest country in the EU
Due to its shape, France is often referred to as l'Hexagone (‘The Hexagon’)
There are 18 regions, of which 13 are in continental metropolitan France
In 2016 the number of metropolitan regions was reduced from 22 to 13
Gascony is currently divided between the Aquitaine region and the Midi-Pyrenees region
Auvergne-Rhone-Alpes
Former regions – Auvergne (capital – Clermont Ferrand) and Rhone-Alpes (capital – Lyon)
Capital – Lyon
Auvergne is part of the Massif Central
Vichy is a spa town, famous for thermal baths. Connects the Garonne to the Mediterranean
Lyon is at the confluence of the Rhone and Saone
Lyon was historically known as an important area for the production and weaving of silk
Roman name for Lyon was Lugdunum
Chauvet Cave in the Ardeche department of southern France became famous in 1994 after speleologists found that its walls were richly decorated with Paleolithic artwork, that it contained the fossilized remains of many animals, including those that are now extinct
Val Thorens is Europe’s highest skiing resort
Isere rises in the Alps and flows through Grenoble
Bourgogne-Franche-Comte
Former regions – Burgundy (capital – Dijon) and Franche-Comte (capital – Besancon)
Capital – Dijon
Dijon holds an International and Gastronomic Fair every year
Beaune is the wine capital of Burgundy in the Cote d'Or department
Franche-Comte was part of the Kingdom of Burgundy
Brittany
Capital – Rennes
Rennes is the historic capital of Brittany
Brest is an important harbour and the second French military port after Toulon
Brest is noted for poultry
Saint-Malo is a walled port city in Brittany
Carnac is famous as the site of more than 3000 prehistoric standing stones. The stones were hewn from local rock and erected by the pre-Celtic people of Brittany
Rance tidal power station was opened in 1966 and was the largest tidal power station in the world by installed capacity until the South Korean Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Station surpassed it in 2011
Ushant is an island in the English Channel which marks the north-westernmost point of metropolitan France
Centre-Val de Loire
Capital – Orleans
The Cathedral of Our Lady of Chartres is considered one of the finest examples in all France of the Gothic style of architecture. It has two contrasting spires – one, a 105 metre plain pyramid dating from the 1140s, and the other a 113 metre tall early 16th century flamboyant spire on top of an older tower
Chartres Cathedral was reconstructed after a fire in 1194
Fontevraud Abbey, near Chinon, was the site of the graves of King Henry II of England, his wife Eleanor of Aquitaine, their son King Richard I of England, their daughter Joan, their grandson Raymond VII of Toulouse, and Isabella of Angouleme, wife of Henry and Eleanor's son King John
Canal de Briare is one of the oldest canals in France. It connects the Loire and Seine valleys
Corsica
Capital – Ajaccio
Corsica is known as ‘The Scented Isle’
Corsica is the fourth largest island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily, Sardinia and Cyprus
Bastia was the capital of Corsica until 1791. It is the second largest city of Corsica
Corsica is divided in two departments: Corse-du-Sud and Haute-Corse
Napoleon Bonaparte Airport is the main airport serving Ajaccio
Porto-Vecchio is a commune in Corsica
Monte Cinto is the highest mountain on Corsica
Grand Est
Former regions – Alsace (capital – Strasbourg), Champagne-Ardenne (capital – Chalons-en-Champagne) and Lorraine (capital – Metz)
Capital – Strasbourg
Strasbourg is principal city of the Alsace region and is the official seat of the European Parliament. It is the capital of the Bas-Rhin department
EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg is located in France, on the administrative territory of the commune of Saint-Louis near the Swiss and German borders. The airport has a Swiss customs area connected to Basel
Reims played a prominent ceremonial role in French monarchical history as the traditional site of the crowning of the kings of France
Sedan is known for its castle that is claimed to be the largest fortified medieval castle in Europe
Metz is the first regional outpost of the Pompidou Centre, opened in 2010
Metz is the capital of Lorraine, on the River Moselle
The last working coalfield in France was in Lorraine
Nancy was formerly the capital of the Duchy of Lorraine
Mulhouse is the second largest city in Alsace
Verdun Memorial is situated on the battlefield, close to the destroyed village of Fleury-devant-Douaumont in the department of Meuse
Clairvaux Abbey is a Cistercian monastery founded in 1115
Hauts-de-France
Former regions – Nord-Pas-de-Calais (capital – Lille) and Picardy (capital – Amiens)
Capital – Lille
Pas-de-Calais is a department in northern France. Its name is the French equivalent of the Strait of Dover, which it borders
Arras is the capital of the Pas-de-Calais department
Nord is the most populous French department
Canadian National Vimy Memorial is a memorial site dedicated to the memory of Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War
Amiens Cathedral is the tallest Gothic cathedral in France
Aisne, Oise, and Somme are departments of Picardy
Thiepval Memorial to the Missing of the Somme is a major war memorial to 72,191 missing British and South African men who died in the Battles of the Somme with no known grave. Designed by Edwin Lutyens
Musee Conde is an art gallery located inside the Chateau de Chantilly
During the Hundred Years' War, Ponthieu, now part of Picardy, changed hands a number of times
Ile-de-France
Capital – Paris
Ile-de-France is the wealthiest and most populated of the 27 administrative regions of France. It consists mostly of the Paris metropolitan area
Paris is known the ‘City of Light’
Distances from Paris are measured from Notre Dame Cathedral
Gare du Nord is the busiest railway station in Europe
Gare de Lyon is the second-busiest railway station in France
Gare St Lazare opened in 1837. First station in Paris
Charles de Gaulle-Etoile is a Paris Metro station
Place de la Concorde is the largest Place in Paris. During the French Revolution the statue of Louis XV of Franc was torn down and the area renamed ‘Place de la Revolution’. Marie Antoinette was executed there
Place Charles de Gaulle, historically known as the Place de l'Etoile, is a large road junction in Paris, the meeting point of twelve straight avenues (hence its historic name, which translates as ‘Place of the Star’) including the Champs-Elysees which continues to the east. In the centre is the Arc de Triomphe
Pere Lachaise takes its name from Pere François de la Chaise, the confessor of Louis XIV, who lived in the Jesuit house rebuilt in 1682 on the site of the chapel. The cemetery was established by Napoleon in 1804
Flooding in Paris is measured by the height of the water against the Zouave statue on Pont de l'Alma
Champs-Elysees was designed by Andre Le Notre
Monparnasse Cemetery is the second largest cemetery in Paris. Interments include Jean Paul Sartre, Simone de Beauvoir, Charles Baudelaire, and Camille Saint-Seans
Montmartre Ceremony is the final resting place of many famous artists. Interments include Vaslav Nijinsky, Hector Berlioz, and Edgar Degas
Reseau Express Regional (RER) is a hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit system serving Paris and its suburbs
Shakespeare and Company is an English-language bookstore located on the Left Bank
Prix d'Amerique is a harness race held at the Hippodrome de Vincennes in Paris. It is widely considered the most prestigious harness race in the world
Place Vendome was begun in 1698. The original Vendome Column at the centre of the square was erected by Napoleon I to commemorate the Battle of Austerlitz
Ponf Neuf is the oldest standing bridge across the river Seine
The Bastille was a castle built in the 14th century in response to a threat to Paris during the Hundred Years' War. The Place de la Bastille is a square where the Bastille prison once stood until the storming of the Bastille in 1789 and its subsequent destruction
Bois de Vincennes is the largest public park in Paris
Bois de Boulognes is the second largest public park in Paris
Place de la Concorde was known as Place Louis XV until 1795
Latin Quarter is an area in the 5th and the 6th arrondissements of Paris. It is situated on the left bank of the Seine, around the Sorbonne
Palace of Fontainbleau is one of the largest French royal chateaux. The medieval castle and subsequent palace served as a residence for the French monarchs from Louis VII to Napoleon III
Normandy
Former regions – Upper Normandy (capital – Rouen) and Lower Normandy (capital – Caen)
Capital – Rouen
Rouen Cathedral is a Roman Catholic Gothic cathedral. Claude Monet produced a series of paintings of the cathedral
Etretat is a resort in Normandy frequently painted by impressionist artists
Mont-Saint-Michel is a tidal island and mainland commune. The island lies approximately one kilometre off France's north-western coast. It is visited by more than three million people each year
During the Hundred Years' War, the English made repeated assaults on the island of Mont-Saint-Michel, but were unable to seize it due to the abbey's improved fortifications
Bayeux is a commune in the Calvados department
Thierville is the only village in all of France with no men lost from World War I
Le Havre is situated on the estuary of the Seine. The city and port were founded by King Francis I in 1517
River Seine is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen
Honfleur is located on the southern bank of the estuary of the Seine across from Le Havre and very close to the exit of the Pont de Normandie
Nouvelle-Aquitaine
Former regions – Aquitaine (capital – Bordeaux), Limousin (capital – Limoges) and Poitou-Charantes (capital – Poitiers)
Capital – Bordeaux
Nouvelle-Aquitaine is the largest French region
Bordeaux is on River Garonne. It is the prefecture of the Gironde department
Cite du Vin is a wine theme park in Bordeaux
Lascaux is the setting of a complex of caves in southwestern France famous for its cave paintings. The original caves are located near the village of Montignac, in the department of Dordogne. They contain some of the best-known Upper Paleolithic art. Since 1998 the cave has been beset with a fungus
Medoc is well known as a wine growing region on the left bank of the Gironde estuary, north of Bordeaux
Limoges is famous for porcelain
Limousin is situated largely in the Massif Central
The port of La Rochelle is in Poitou-Charantes
Futuroscope is a French theme park based upon multimedia, cinematographic and audio-visual techniques. It is located 10 km north of Poitiers
Gironde estuary is formed from the meeting of the rivers Dordogne and Garonne just downstream of Bordeaux
Ile d’Oleron is an island west of Rochefort. It is the second largest island of Metropolitan France, after Corsica
Occitanie
Former regions – Midi-Pyrenees (capital – Toulouse) and Languedoc-Roussillon (capital – Montpellier)
Capital – Toulouse
Musee Fabre is an art and sculpture museum in Montpellier
Pont du Gard is an aqueduct constructed by the Roman Empire, and located near Remoulins, in the Gard department, close to Nimes
Odeillo solar furnace is the world largest solar furnace
Toulouse lies on the River Garonne
Millau Viaduct is 270 m high and is the largest cable-stayed bridge in the world. Largest pylon is 343 m high. A75 road over the River Tarn. Designed by Norman Foster and Michel Virlogeux
Pech Merle, a hillside opening in the Lot department of Midi-Pyrenees region, is the site of one of the prehistoric cave paintings remaining in France
Cathedral Basilica of Saint Cecilia, also known as Albi Cathedral, was constructed from 1282 to 1480, built in the wake of the Albigensian heresy of the Cathars and the brutal crusade brought against it. This crusade, led by Simon de Montfort, involved the burning of 400 Cathars. It is claimed to be the largest brick building in the world
Cevennes range of mountains is on the southeast edge of the Massif Central
Pays-de-la-Loire
Capital – Nantes
Nantes is on the banks of the River Loire
Angers is a city in the Maine-et-Loire department and is the historical capital of Anjou
Chantiers de l'Atlantique, one of the largest shipyards in the world, is located in Saint-Nazaire
Sarthe is a department, named after the river Sarthe. Le Mans is a city in Sarthe
Provence-Alpes-Cote d’Azur
Capital – Marseille
Nice is the capital of the Alpes-Maritimes department
The largest Orthodox cathedral in Western Europe is in Nice
Promenada des Anglais is in Nice
Marc Chagall National Museum and Musee Matisse are in Nice
Alpes-Maritimes was created by Octavian as a Roman military district in 14 BC
Marseille was founded in 600 BC by Greeks from Phocaea as a trading port. Oldest city in France
Marseille is Europe’s largest Muslim city
Miramar restaurant is in Marseille
La Ciotat, near Marseille, was the setting of one the very first projected motion pictures, L'Arrivée d'un train en gare de La Ciotat filmed by the Lumiere brothers in 1895
L'Estaque is a fishing village just west of Marseille. Many artists of the Impressionist and Post-Impressionist periods visited or resided there or in the surrounding area
Menton is a commune in the Alpes-Maritimes department in the Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur region. It is nicknamed ‘The Pearl of France’
Pont Saint-Benezet, also known as the Pont d'Avignon, is a famous medieval bridge in the town of Avignon, in southern France. The bridge originally spanned the Rhone River between Avignon and Villeneuve-les-Avignon on the left bank. It was built between 1171 and 1185
The first museum in the world to be dedicated to Pablo Picasso is in Antibes
The military port of Toulon is the major naval centre on France's Mediterranean coast
Built in 90 AD, the Arles Amphitheatre was capable of seating over 20,000 spectators
Mont Ventoux is a mountain in Provence. Mistral wind speeds can reach 200 mph. Mont Ventoux has become legendary as the scene of one of the most grueling climbs in the Tour de France
The river Rhone forks into two branches just upstream of Arles, forming the Camargue delta. Because the Camargue is for a large part administratively part of Arles, the commune is the largest commune in Metropolitan France in terms of territory
River Loire is the longest river entirely in France. It rises in the Massif Central in the Cevennes range; it flows north through Nevers to Orléans, then west through Tours and Nantes until it reaches the Bay of Biscay at Saint-Nazaire
River Seine is the second longest river entirely in France. It rises northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre
Tarn and Lot are tributaries of the Garonne
River Dordogne rises in Massif Central and unites with the Garonne to form the Gironde estuary
Bay of Biscay is known in France as the Gulf of Gascony
Canal du Midi runs from the city of Toulouse down to the Mediterranean port of Sete
Malpas tunnel was excavated in 1679, allowing the passage of the Canal du Midi. It was Europe's first navigable canal tunnel
Mer de Glace ("Sea of Ice") is a valley glacier located on the northern slopes of the Mont Blanc massif, in the French Alps. It is the second longest in the Alps after the Aletsch Glacier
Overseas regions
The five overseas regions of France are Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion
The overseas collectivities are first-order administrative divisions of France. The five collectivities are Saint Barthelemy, Saint Martin, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Wallis and Futuna, and French Polynesia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France
The term overseas territory is an administrative division of France and is currently only applied to the French Southern and Antarctic Lands. Includes Kerguelen Islands and Amsterdam Island
Georgia
Flag of Georgia, known as the Five Cross Flag, was adopted in 2004
| Capital | Tbilisi |
| Largest cities | Tbilisi, Batumi |
| Currency | Lari |
| Highest point | Shkhara |
Georgia contains two de facto independent regions, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, which gained limited international recognition after the 2008 Russo-Georgian War
Georgia is known as Sakartvelo in Georgia
Tbilisi is on the River Kura
Tbilisi was also capital of the Democratic Republic of Georgia from 1918 to 1921, the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic from 1921 to 1991, and the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic from 1922 to 1936
Veryovkina Cave and Krubera Cave are the deepest-known caves on Earth. They are located in Abkhazia
Germany
| Capital | Berlin |
| Largest cities | Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, Cologne, Frankfurt |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Zugspitze |
Germany is a Federal Republic made up of 16 States, known as Lander. The term Bundeslander (‘states of the federation’) is commonly used as it is more specific. Three cities (Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg) are states in their own right, termed Stadtstaaten (‘city states’). The remaining 13 states are termed Flachenlander (‘area states’)
Nine countries share a land border with Germany. The longest land border is with Austria
City states
Berlin
Unter den Linden (‘under the lime trees’) is an area east of Brandenburg Gate
Brandenburg Gate is located on the Pariser Platz. It consists of 12 Doric columns, and above the gate is the Quadriga consisting of the goddess of peace driving a four-horse chariot, a design based on the Propylea (the gateway to the Acropolis). Designed by Carl Langhans
Kaufhaus des Westens, or KaDeWe, is the second largest department store in Europe after Harrods
Tiergarten is an inner-city park in Berlin
Kulturforum is a collection of cultural buildings in Berlin
Oberhaum Bridge is a double-deck bridge crossing the Spree river
Berlin Central Station (Berlin Hauptbahnhof) began full operation in 2006. It is located on the site of the historic Lehrter Bahnhof
Tempelhof was designated as an airport in 1923. Tempelhof was one of Europe's three iconic pre-World War II airports, the others being London’s Croydon Airport and the old Paris–Le Bourget Airport
Tegel airport was built in 1948 for the Berlin airlift. Tegel Airport is named after Otto Lilienthal, the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful gliding flights
Berlin Brandenburg Airport is named after Willy Brandt. The new airport replaced Tempelhof, Schonefeld, and Tegel airports, and opened in 2020
Berlin orbital motorway (BAB 10) is 196 km long, and is the longest orbital in Europe
Bremen
The state consists of two cities (Bremen and Bremerhaven) and is the smallest German state
River Weser flows through Bremen and Bremerhaven
Town Musicians of Bremen is a statue depicting a donkey, a dog, a cat, and a rooster from a fairy tale by the Brothers Grimm
Hamburg
Hamburg is officially known as the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg
The port of Hamburg, on the river Elbe, is the second largest port in Europe (after the Port of Rotterdam)
The area of Reeperbahn in the quarter St. Pauli is Europe's largest red-light district
Hamburg is the largest non-capital city in the European Union
Miniatur Wunderland is the world's largest model railway museum
Hamburg's rivers and canals are crossed by around 2,500 bridges, making it the city with the highest number of bridges in Europe
Area states
Baden-Wurttemberg
Capital – Stuttgart
Restaurant Top Air in Stuttgart Airport has a Michelin star
Stuttgart is on the Neckar river
Ulm is primarily known for its Ulm Munster (a Lutheran cathedral and the tallest church in the world, its steeple measuring 530 ft high) and as the birthplace of Albert Einstein. It lies on the Danube
Ruins of Heidelberg Castle are among the most important Renaissance structures north of the Alps
Heidelberg is on the Neckar river
The Rhine joins the Necker at Mannheim
Hockenheimring race track was built in 1932
Busingen is a German exclave surrounded by Switzerland
Europa-Park is located in Rust. It is the second most popular theme park in Europe, after Disneyland Paris
Bavaria
Capital – Munich
Bavaria is the largest state in Germany
Neuschwanstein Castle is a 19th century neo-romantic castle. Located near Hohenschwangau and Fussen in southwest Bavaria, the castle was built by Ludwig II, King of Bavaria, as a retreat and as homage to Richard Wagner, the King's inspiring muse
Frauenkirche (‘Cathedral of Our Dear Lady’) is the cathedral of the Archbishop of Munich and Freising. It is a landmark and is considered a symbol of the Bavarian State Capital
Olympic Stadium in Munich was designed by the German architect Günther Behnisch and the engineer Frei Otto. Design included large sweeping canopies of acrylic glass stabilized by steel cables that were used for the first time in a large scale
Munich is on the River Isar
Pilgrimage Church of Wies is an oval rococo church in Bavaria, designed in the 1740s by Dominikus Zimmermann
Lindau is a Bavarian major town and an island on the eastern side of Lake Constance
Nuremberg is in Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia
Coburg was one of the capitals of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha until 1918
Augsburg was named after Emperor Augustus
Regensburg, historically also Ratisbon, is a city in Bavaria
Wurzburg Residence is a palace in Wurzburg. Balthasar Neumann, architect of the court of the Bishop of Wurzburg, was the principal architect. Giovanni Tiepolo, assisted by his son, Domenico, painted frescoes in the building
Rhine–Main–Danube Canal connects the North Sea and Atlantic Ocean to the Black Sea
Brandenburg
Capital – Potsdam
Sanssouci is the former summer palace of Frederick the Great, King of Prussia, in Potsdam. Sanssouci means ‘without worries’
Cecilienhof Palace is built in the layout of an English Tudor manor house. It was the location of the Potsdam Conference in 1945
Glienicke Bridge across the Havel River connects the Wannsee district of Berlin with Potsdam. Known as the “Bridge of Spies” during the Cold War
Hesse
Capital – Wiesbaden
Wiesbaden is one of the oldest spa towns in Europe. Its name literally means ‘meadow baths’
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main, is the largest city in Hesse
Frankfurt is home to the European Central Bank and the German Federal Bank
Frankfurt Stock Exchange is the largest in Germany
Frankfurt is known as “Mainhattan” due to the large number of skyscrapers
Commerzbank Tower is the tallest building in Germany. It was designed by Norman Foster
Messel Pit is a disused quarry near the village of Messel, close to Frankfurt. Bituminous shale was mined there. Because of its abundance of fossils, it has significant geological and scientific importance
Lower Saxony
Capital – Hanover
Hanover is the largest city in Lower Saxony
Hanover is on the River Leine
The northwestern area of Lower Saxony, which lies on the coast of the North Sea, is called East Frisia
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
State is also known as Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania in English
Capital – Schwerin
Mecklenburg is the region between Berlin and Hamburg
Rostock is the largest city and the principal overseas port of the former GDR
Mecklenburg Lake District is sometimes called "the land of a thousand lakes"
Rugen is Germany's largest island. It is located in the Baltic Sea
Prora is a beach resort on the island of Rugen, known especially for its colossal Nazi-planned touristic structures. The massive building complex was built between 1936 and 1939
North-Rhine Westphalia
Capital – Dusseldorf
North-Rhine Westphalia is the most populous lander
Cologne became acknowledged as a city by the Romans in 50 AD
Cologne Bonn Airport is named after Konrad Adenauer
Museum Lugwig is a modern art museum in Cologne
Bonn is the second official seat and second official residence of the President of Germany, the Chancellor of Germany, the Bundesrat, and the first official seat and first official residence of six German federal ministries
Bonn was the capital of West Germany from 1949 to 1990
Duisburg lies on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers and is the largest inland port in Europe
Charlemagne is buried in Aachen Cathedral, the oldest cathedral in northern Europe
Bielefeld is well known for the Bielefeld conspiracy, which satirises conspiracy theories by claiming that Bielefeld does not exist
Wuppertal Schwebebahn is a suspension railway (a form of elevated monorail) that started operations in 1901
Neuss is primarily known for its historic Roman sites. Neuss and Trier share the title of "Germany's oldest city"
Rhineland-Palatinate
Capital – Mainz
To celebrate the 400th anniversary of his death, the Gutenberg Museum was founded in 1900 in Johannes Gutenberg’s hometown of Mainz
Trier lies on the banks of the Moselle. It was founded by the Celts in the 4th century BC as Treuorum and conquered 300 years later by the Romans
Porta Nigra (Latin for ‘black gate’) is a large Roman city gate in Trier. It is today the largest Roman city gate north of the Alps and has been designated a World Heritage Site
Koblenz is at the confluence of Rhine and Moselle
Stolzenfels Castle is a castle near Koblenz on the Rhine
Lorelei – a rock on the eastern bank of the Rhine near St. Goarshausen, which soars some 120 metres above the water line. It marks the narrowest part of the river between Switzerland and the North Sea
The wine festival called Wurstmarkt in Bad Durkheim is the largest wine festival in the world
Saarland
Capital – Saarbrucken
Apart from the city states, it is Germany's smallest federal state. It has borders with France and Luxembourg
Saxony
Capital – Dresden
Dresden is known as the ‘Florence of the Elbe’ and the ‘Florence of the North’
Frauenkirche (Church of Our Lady) is a Lutheran church in Dresden. It was destroyed in the bombing of Dresden during World War II, and the ruins were left for 50 years as a war memorial. The church was rebuilt after the reunification of Germany
Zwinger is a palace in Dresden and a major landmark of German baroque architecture
Leipzig is the largest city in Saxony
Oflag IV-C (often referred to as Colditz Castle because of its location) was situated on a cliff overlooking the town of Colditz in Saxony
Chemnitz was known as Karl-Marx-Stadt between 1953 and 1990
In 2009, UNESCO voted to remove the status of World Heritage Site from the Dresden Elbe Valley on the basis of the Waldschlosschen Bridge that was under construction and would bisect the valley. The bridge opened in 2013
Saxony-Anhalt
Capital – Magdeburg
Magdeburg lies on the Elbe River and was one of the most important medieval cities of Europe. Emperor Otto I lived during most of his reign in the town and was buried in the cathedral after his death
Brocken – the highest peak of the Harz mountain range and also the highest peak of Northern Germany
Schleswig-Holstein
Capital – Kiel
Kiel is known for a variety of international sailing events, including the annual Kiel Week, which is the biggest sailing event in the world. It is a major high-tech shipbuilding centre
Lubeck was the largest and most powerful member of the Hanseatic League
Lubeck is the second-largest German Baltic port after the port of Rostock
St. Mary's Church in Lubeck was built in Gothic architecture style using north German brick. It has the tallest brick vault in the world
Holsten Gate is a city gate marking off the western boundary of the old centre of Lubeck. It is known for its two-round towers and arched entrance
Heligoland – German island in the North Sea. Matches the description of Azkaban in the Harry Potter books
Kiel Canal links the North Sea with the Baltic Sea. It is the world’s busiest artificial waterway
Sylt is the northernmost island of Germany and is known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It is one of the North Frisian Islands in the Wadden Sea
Thuringia
Capital – Erfurt
Weimar was a focal point of the German Enlightenment. The Bauhaus movement was founded in Weimar in 1919
Jena is the second largest city in Thuringia, after Erfurt
Wartburg Castle is in Eisanach
The Bachhaus in Eisanach was the first museum worldwide to be dedicated to the life and work of Johann Sebastian Bach, who was born there
Danube river originates in the Black Forest in Germany as two smaller rivers: the Brigach and the Breg rivers
Meissen, Pardubice, Wittenberg, Dessau, Magdeburg and Cuxhaven are on the Elbe river
Swabia is normally thought of as comprising the former German state of Wurttemberg (with the Prussian Hohenzollern Province) and the administrative region of Bavarian Swabia
Harz National Park is a nature reserve in the federal states of Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt. It comprises large portions of the western Harz mountain range
Reichenau Island lies in Lake Constance. It was declared a World Heritage Site in 2000 because of its monastery, the Abbey of Reichenau
Teutoburg forest – range of low forested mountains in Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia
Fulda Gap is an area between the Hesse-Thuringian border and Frankfurt. During the Cold War, the Fulda Gap offered a route for a hypothetical Soviet tank attack on West Germany
Greece
| Capital | Athens |
| Largest cities | Athens, Thessaloniki |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Mount Olympus |
Parthenon is a temple of the Greek goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their protector. Its construction began in 447 BC and was completed in 438 BC on the Athenian Acropolis, although decorations of the Parthenon continued until 431 BC. It is the most important surviving building of Classical Greece, generally considered to be the culmination of the development of the Doric order
Syntagma Square (English: Constitution Square), is located in central Athens. The Square is named after the Constitution that King Otto was forced to grant to the people, after a popular and military uprising in 1843
Plaka is the old historical neighborhood of Athens, clustered around the northern and eastern slopes of the Acropolis, and incorporating labyrinthine streets and neoclassical architecture
Athens is known as the “violet crowned city”
Panathenaic Stadium in Athens is the only stadium made entirely of marble
The Philippeion in the Altis of Olympia was an Ionic circular memorial of ivory and gold, which contained statues of Philip's family and Alexander the Great. It was made by the Athenian sculptor Leochares in celebration of Philip's victory at the battle of Chaeronea (338 BC)
Thessaloniki or Salonica is Greece’s second-largest city and the capital of Macedonia, the largest region of Greece
Great Thessaloniki Fire of 1917 destroyed two thirds of the city
The region of Argos, in Greece is called the Argolid. The inhabitants of Argos were called Argives
Cape Matapan is the southernmost point of Greek mainland
Piraeus is the largest port in Europe (and third largest in the world) in terms of passenger transportation, servicing 19 million passengers annually
Gulf of Corinth is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece. In medieval times, the gulf was known as the Gulf of Lepanto
Corinth Canal connects the Gulf of Corinth with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea. It cuts through the narrow Isthmus of Corinth and separates the Peloponnesian peninsula from the Greek mainland. Completed in 1893. The canal has been closed since the beginning of 2021 after a landslide
Corinth was founded as New Corinth in 1858 after an earthquake destroyed the existing settlement of Corinth
Rion-Antirion Bridge is one of the world's longest multi-span cable-stayed bridge. It crosses the Gulf of Corinth near Patras, linking the town of Rion on the Peloponnese to Antirion on mainland Greece
Cadmea was the citadel of ancient Thebes, named after Cadmus
Apidima cave is located on the Mani Peninsula. Neanderthal and Homo sapiens fossils have been found at the cave
Meteora is a rock formation in Greece that is host to six Eastern Orthodox monasteries
Mount Athos in Macedonia is a self-governed state in the Hellenic Republic. Referred to in Greek as the ‘Holy Mountain’
Athos is an important centre of Eastern Orthodox monasticism
Arcadia is a region of Greece in the Peloponnese. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas
Mycanae, in the Peloponnese, was Agamemnon’s capital, and is the site of the Lion Gate, the main entrance of the Mycanae citadel
The city of Pavlopetri, underwater off the coast of southern Laconia in Peloponnese, is about 5000 years old, and is the oldest submerged archeological town site. It is unique in having an almost complete town plan
Delphi is both an archaeological site and a modern town in Greece on Mount Parnassus
Greek Islands
Largest islands – Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes, Chios
Crete is the most populous of the Greek islands
Palace of Knossos is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and probably the ceremonial and political centre of the Minoan civilization and culture
Heraklion is the capital of Crete
Mount Ida is the highest point in Crete
Chania is an old city and port on Crete
The island of Gavdos is located to the south of Crete. it is the southernmost point of Europe
Euboea, also known as Evia, is the second largest of the Aegean Islands, after Crete. The chief town is Chalcis, that was known as Negroponte In the Late Middle Ages
Lesbos is located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. Capital city is Mytilene. Home of the ancient Greek poet Sappho
Chios is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mastic gum. It was the site of the Chios massacre during the Greek War of Independence in 1822
Lemnos is an island in the northern part of the Aegean Sea. The principal town is Myrina
Ionian Islands are in the Ionian Sea, west of Mainland Greece. They are known as the Hepanese (‘seven islands’) but the group includes many smaller islands
Kefalonia is the largest of the Ionian Islands
Argostoli is the capital of Kefalonia
Corfu or Kerkyra is the second largest island. The northeastern edge of Corfu lies off the coast of Sarande, Albania
The other major islands are Cythera, Ithaca, Lefkas, Paxos, and Zante
Cyclades are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece
Naxos is the largest of the Cyclades. The island is famous as a source of emery
Syros is the most populous island. Ermoupoli, the capital of the Cyclades, is on the island
Andros is the northernmost island of the Cyclades, 10 km southeast of Euboea
Santorini is the southernmost island of the Cyclades. The island was the site of the Minoan eruption, that was one of the largest volcanic eruptions in recorded history
Akrotiri is an ancient city buried, and preserved by, the volcanic ash on the island of Santorini
Milos and Mykanos are islands in the Cyclades
Dodecanese (‘twelve islands’) are a group of islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia
Rhodes is the largest of the Dodecanese Islands. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Rhodes. Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem ruled the island from 1310 to 1522
Colossus of Rhodes was a statue of the Greek sun-god Helios, erected by Chares of Lindos in 280 BC. One of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
Faliraki is the primary seaside resort village on Rhodes
Acropolis of Lindos on Rhodes is a natural citadel
Kos is the third largest of the Dodecanese by area, after Rhodes and Karpathos, and the second largest by population
Patmos is famous as the location where John of Patmos received the visions found in the Book of Revelation of the New Testament, and where the book was written
Monastery of Saint John the Theologian is a Greek Orthodox monastery founded in 1088 on the island of Patmos
Sporades are a group of 24 islands northeast of Euboea. There are four permanently inhabited islands – Alonnisos, Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros
Rupert Brooke is buried on Skyros
Saronic Islands are named after the Saronic Gulf in which they are located. The main inhabited islands of this group are Salamis, Aegina, Agistri, and Poros
Hungary
| Capital | Budapest |
| Largest cities | Budapest, Debrecen, Szeged |
| Currency | Forint |
| Highest point | Kekes |
Budapest is the combination of the city names Buda and Pest, which were (together with Obuda) united into a single city in 1873
Budapest Metro is the second oldest underground metro system in the world after the London Underground. Opened in 1896
Szechenyi Lanchid Chain Bridge in Budapest was the first permanent bridge across the Danube. Designed by William Tierney Clark. Opened in 1849
Gellert Hotel is a spa hotel in Budapest
Keleti is the main railway station in Budapest
Memento Park is a museum in Budapest, including Statue Park with monumental statues from Hungary's Communist period
The ancient city of Aquincum was situated on the North-Eastern borders of the Pannonia province within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found today in Budapest
Shoes on the Danube Bank is a memorial to honour the Jews who were massacred by fascist Hungarian militia in Budapest during the Second World War
Szeged is known as the home of paprika
Pecs was a 2010 European Capital of Culture
Kelenfold Power Station was the largest electrical generation plant in the world after its construction in 1912
Lake Balaton is the largest lake in Central Europe
Iceland
| Capital | Reykjavik |
| Largest cities | Reykjavik, Kopavogur |
| Currency | Krona |
| Highest point | Hvannadalshnjukur |
Iceland observes Greenwich Mean Time all year round
Keflavik International is the largest airport in Iceland
Reykjavik is the most northerly capital in the world
Mount Hekla is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes
Vatnajokull (meaning ‘Glacier of Rivers’), also known as the Vatna Glacier, is the largest and most voluminous Icelandic glacier
Eyjafjallajokull lies 25 km west of another subglacial volcano, Katla, which is much more active and known for its powerful subglacial eruptions and its large magma chamber. Each of the eruptions of Eyjafjallajokull in 920, 1612, and 1821–1823 has preceded an eruption of Katla
Eyjafjallajokull erupted in 2010, causing enormous disruption to air travel across northern and western Europe for a week
Katla last erupted in 1918
Laki is a volcanic fissure situated in the south of Iceland. The system erupted over an 8 month period during 1783–84 from the Laki fissure and the adjoining Grímsvotn volcano, pouring out basalt lava and clouds of poisonous hydrofluoric acid/sulfur-dioxide compounds that killed over 50% of Iceland's livestock population, leading to famine which killed approximately 25% of the population
Iceland is located on both the Iceland hotspot and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which runs right through it
The Iceland Plume is an upwelling of anomalously hot rock in the Earth's mantle beneath Iceland whose origin probably lies at the boundary between the core and the mantle at c. 2880 km depth. It is generally thought to be the cause of the formation of Iceland and its volcanism
In 1973 a volcanic eruption of the mountain Eldfell began on Heimaey. Townspeople constantly sprayed the lava with cold seawater, causing some of it to solidify and much to be diverted, thus saving the harbour from destruction
Silfra is a rift formed in the divergent tectonic boundary between the North American and Eurasian plates. It is popular with scuba divers
Karahnjukar is Europe’s biggest dam and is part of a hydroelectricity plant
Surtsey, one of the youngest islands in the world, is part of Iceland. It rose above the ocean in a series of volcanic eruptions between 1963 and 1968
Dettifoss is a waterfall in Vatnajokull National Park, and is reputed to be the most powerful waterfall in Europe
Blue Lagoon is a geothermal spa supplied by water used in the nearby Svartsengi geothermal power station. The water's milky blue shade is due to its high silica content
Gullfoss and Skogafoss are waterfalls in Iceland
Ireland
| Capital | Dublin |
| Largest cities | Dublin, Cork, Limerick, Galway, Waterford |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Carrauntoohil |
Ireland has historically been divided into four provinces: Connacht, Leinster, Munster and Ulster. There were once five; the fifth province, Meath, was incorporated into Leinster, with parts going to Ulster
Ireland is divided into 32 ‘traditional counties’
Connacht is in the west of Ireland, and is the smallest province in terms of area and population. The province is divided into five traditional counties – Galway, Leitrim, Mayo, Roscommon and Sligo
Galway has an International Oyster Festival every September
The Claddagh is a beach area in the western part of Galway. People have been gathering seafood and fishing from the area for millennia. Historically, its existence has been recorded since the arrival of Christianity in the 5th century. Claddagh ring is a traditional Irish ring
The Twelve Bens or Twelve Pins is a mountain range in Connemara
Benbulben is a large rock formation in County Sligo
Aran Islands are a group of three islands located at the mouth of Galway Bay. The islands are Inishmore, Inishmaan and Inisheer
Knock Shrine is a pilgrimage site in County Mayo, where it is claimed there was an apparition of the Blessed Virgin Mary, Saint Joseph, John the Evangelist, angels and Jesus Christ in 1879
Croagh Patrick '(Saint) Patrick's stack') is a mountain and an important site of pilgrimage in County Mayo
Achill Island is the largest of the Irish isles and lies off the coast of County Mayo
Leinster is in the east of Ireland, and is the largest province in terms of population. The province is divided into 12 traditional counties – Carlow, Dublin, Kildare, Kilkenny, Laois, Longford, Louth, Meath, Offaly, Westmeath, Wexford and Wicklow
Dublin means ‘dark pool’. Baile Atha Cliath is the Irish name for Dublin
Abbey Theatre was founded by Lady Gregory, Edward Martyn and W.B. Yeats in 1899 and opened in 1904
Olympia Theatre in Dublin was opened as ‘The Star of Erin’ music hall in 1879
Halfpenny Bridge is a pedestrian bridge across the River Liffey in Dublin. It is so called because this was the toll for pedestrians. The official name is Wellington Bridge
The Custom House is a neoclassical 18th century building in Dublin which houses the Department of the Environment, Heritage and Local Government
Temple Bar is promoted as ‘Dublin's cultural quarter’
O’Connell Street was known as Sackville Street until 1924
Spire of Dublin is a 121 m stainless steel monument on O’Connell Street, also known as ‘Bertie’s Pole’. Designed by Ian Ritchie Architects. It is a replacement for Nelson’s Pillar, which was destroyed by the IRA in 1966
Book of Kells is an illuminated manuscript, containing the four Gospels. The manuscript takes its name from the Abbey of Kells. It is on permanent display at Trinity College Library
St. James's Gate Brewery was founded in 1759 by Arthur Guinness
Mountjoy prison has the largest prison population in Ireland
The Chester Beatty Library was established in Dublin in 1950, to house the collections of mining magnate, Sir Alfred Chester Beatty
Heuston and Connolly stations are the two main railway termini in Dublin
Donnybrook Fair was held annually from 1204 to 1855. It ceased due to disorderly behaviour
Anna Livia is a bronze monument in Dublin known as ‘the Floozie in the Jacuzzi’. The monument is a personification of the River Liffey. Moved from O’Connell Street to Croppies Memorial Park in 2006. Named after a character in Finnegan’s Wake
Molly Malone is commemorated in a statue designed by Jeanne Rynhart, erected to celebrate the city's first millennium in 1988. Originally placed at the bottom of Grafton Street, the statue is known as ‘The Tart with the Cart’
Newgrange is a passage tomb in County Meath. Newgrange was built in such a way that at dawn on the shortest day of the year, the winter solstice, a narrow beam of sunlight for a very short time illuminates the floor of the chamber at the end of the long passageway. Newgrange is the main monument in the Brú na Bóinne complex, a World Heritage Site
Hill of Tara, located near the River Boyne, is an archaeological complex in County Meath. It contains a number of ancient monuments and, according to tradition, was the seat of the High King of Ireland
Louth is the smallest county in Ireland
Munster is in the southwest of Ireland and is the largest province in terms of area. The province is divided into six traditional counties – Clare, Cork, Kerry, Limerick, Tipperary and Waterford
Cork is the largest county in Ireland
Cork is the second largest city in Ireland. The city is built on the River Lee
In 2005, Cork was selected as the European Capital of Culture
Cork is home to the Heineken Brewery that brews Murphy’s Irish Stout
Brow Head in County Cork is the most southerly point of mainland Ireland
Cobh was first called Cove (‘The Cove of Cork’) in 1750. It was renamed Queenstown in 1850 to commemorate a visit by Queen Victoria. This remained the town's name until 1922 when it was renamed Cobh with the foundation of the Irish Free State. Queenstown was the final port of call for the RMS Titanic
Bantry Bay is located in County Cork
Blarney Stone is a block of limestone built into the battlements of Blarney Castle, about five miles from Cork. According to legend, kissing the stone endows the kisser with ‘the gift of gab’. The stone was set into a tower of the castle in 1446
Limerick lies on the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King’s Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and the Abbey River
Tipperary was divided into North (capital – Nenagh) and South (capital – Clonmel) Ridings in 1838
Rock of Cashel in County Tipperary was the traditional seat of the kings of Munster for several hundred years prior to the Norman invasion
Carrantuohill is the highest peak in Ireland. Located in County Kerry, it is 1,038 metres (3,406 ft) tall and is the central peak of the Macgillycuddy's Reeks range
Dingle Peninsula is in County Kerry
Burren is a karst limestone region of approximately 300 sq km which lies in the northwest corner of County Clare
Cliffs of Moher are sea cliffs located at the southwestern edge of the Burren region
Skellig Michael is an island off the coast of Kerry and is a World Heritage Site
Gap of Dunloe is a mountain pass in County Kerry
Tralee Bay is located off the coast of County Kerry
In 1947, the ‘Customs Free Airport Act’ established Shannon as the world's first duty-free airport. Shannon Airport is in County Clare
Ulster is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three (Cavan, Donegal, and Monaghan) are in the Republic of Ireland
Malin Head in Donegal is the northernmost point in Ireland
River Shannon is 360 km in length and is the longest river in Ireland and the British Isles. It rises in County Cavan and empties into the Atlantic Ocean near Limerick. Athlone is located on the Shannon
River Barrow is one of The Three Sisters; the other two being the River Suir and the River Nore. The Barrow is the longest of the three rivers. At 192 km, it is the second-longest river in Ireland
River Boyne flows through Leinster. Drogheda is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea
M1 – Dublin to Dundalk
M50 – Dublin ring road
Fastnet Rock is the most southerly point of Ireland. Due to its location, Fastnet was known as ‘Ireland's Teardrop’, because it was the last part of Ireland that 19th century Irish emigrants saw as they sailed to North America
Celtic Sea is the area of the Atlantic Ocean off the south coast of Ireland bounded to the east by Saint George's Channel; other limits include the Bristol Channel, the English Channel, and the Bay of Biscay
Italy
| Capital | Rome |
| Largest cities | Rome, Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Mont Blanc |
Italy is subdivided into 20 regions
Abruzzo
Capital – L’Aquila
Located on the Adriatic coast, Pescara is the most populated city in Abruzzo
Aosta Valley
Capital – Aosta
Aosta Valley is a mountainous semi-autonomous region in northwestern Italy. It is the smallest, least populous, and least densely populated region of Italy
Apulia
Capital – Bari
Apulia (Italian: Puglia) is a region in southeastern Italy bordering the Adriatic Sea in the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Otranto and Gulf of Taranto in the south. Its southern portion known as Salento, a peninsula, forms a high heel on the ‘boot’ of Italy
Taranto is a coastal city in Apulia and is the main Italian naval base
Basilicata
Capital – Potenza
Sassi settlements in Matera are known for their ancient cave dwellings inhabited since the Paleolithic period
Calabria
Capital – Catanzaro
Calabria is known as the ‘toe of Italy’s boot’. It is separated from Sicily by the Strait of Messina
Campania
Capital – Naples
Capri is located in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the Sorrentine Peninsula, on the south side of the Gulf of Naples in the Campania region
Villa Jovis is a Roman palace on Capri built by Roman emperor Tiberius
Blue Grotto is a cave off the island of Capri
Teatro di San Carlo is in Naples. It is the oldest continuously active venue for public opera in the world, opening in 1737
Sorrento overlooks the Bay of Naples as the key place of the Sorrentine Peninsula, and many viewpoints allow sight of Naples itself, Vesuvius and the Isle of Capri
Museo di Capodimonte in Naples is the prime repository of Neapolitan painting and decorative art
Castel dell'Ovo is the oldest standing fortification in Naples
Castel Nuovo is a medieval castle located in front of Piazza Municipio and the city hall in central Naples
Salerno is mostly known for its Schola Medica Salernitana, the first University of Medicine in the world
Paestum was a major ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea in Magna Graecia
Pompeii and Herculaneum were destroyed when Vesuvius erupted in 79 AD
Vesuvius last erupted in 1944
Amalfi Coast is a stretch of coastline on the southern side of the Sorrentine Peninsula of Italy (Province of Salerno), extending from Positano in the west to Vietri sul Mare in the east
Lake Avernus is a volcanic crater lake. Avernus was of major importance to the Romans, who considered it to be the entrance to Hades
Emilia-Romagna
Capital – Bologna
Bologna is known as the Fat, Red, and the Learn'd City due to its rich cuisine, red Spanish tiled rooftops, left wing politics, and being home to the oldest university in the western world
Towers of Bologna are a group of medieval structures. The two most prominent ones remaining, known as the Two Towers, are a landmark of the city
Bologna Guglielmo Marconi Airport is an international airport serving the city of Bologna
Rimini Airport is named after Federico Fellini
Ravenna is known as ‘city of the mosaic’
Faience pottery was originally associated by French speakers with wares exported from Faenza in the province of Ravenna
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Capital – Trieste
As a prosperous seaport in the Mediterranean region, Trieste became the fourth largest city of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (after Vienna, Budapest, and Prague). Trieste was the main seaport of the Austro-Hungarian empire
Lazio
Capital – Rome
The seven hills of Rome east of the river Tiber form the geographical heart of Rome, within the walls of the city. The seven hills are: Aventine Hill, Caelian Hill, Capitoline Hill, Esquiline Hill, Palatine Hill, Quirinal Hill, and Viminal Hill. Tradition holds that Romulus and Remus founded the original city on the Palatine Hill in 753 BC
Trevi fountain was constructed in1762. Trevi means ‘three roads’. An estimated 3,000 Euros are thrown into the fountain each day. Designed by Nicola Salvi
Spanish Steps is a monumental stairway of 138 steps was built with French diplomat Étienne Gueffier’s bequeathed funds of 20,000 scudi, in 1723–1725, linking the Bourbon Spanish Embassy, and the Trinita dei Monti church that was under the patronage of the Bourbon kings of France
Fontana dei Quattro Fiumi (Fountain of the Four Rivers) is a fountain in the Piazza Navona in Rome. It was designed in 1651 by Gian Lorenzo Bernini for Pope Innocent X. River gods represent four major rivers of the four continents through which papal authority had spread: the Nile representing Africa, the Danube representing Europe, the Ganges representing Asia, and the Río de la Plata representing the Americas
Monte Mario is the highest hill in the modern city of Rome, Monte Mario is not one of the Seven Hills of Rome, being outside the boundaries of the ancient city
Roma Termini is the central railway station in Rome
Via Sacra was the main street of ancient Rome, leading from the top of the Capitoline Hill to the Colosseum
Victor Emmanuel II Monument in Rome is known as the ‘Wedding Cake’
Tarpeian Rock was a steep cliff of the southern summit of the Capitoline Hill, overlooking the Roman Forum. It was used during the Roman Republic as an execution site
Ostia was the port city of Ancient Rome
Fiumicino–Leonardo da Vinci International Airport in Rome is the main hub for Alitalia
At the time of the Emperor Augustus, Rome was the largest city in the world: with a population of about one million people
Portus was a large artificial harbour of Ancient Rome. Sited on the north bank of the north mouth of the Tiber, it was established by Claudius and enlarged by Trajan to supplement the nearby port of Ostia
Tivoli, the classical Tibur, is an ancient Italian town in Lazio, about 30 km east of Rome
Lake Nemi is a small circular volcanic lake. The lake is most famous for its sunken Roman ships
Via Flaminia was an ancient road from Rome to Rimini
Via Appia was an ancient road from Rome to Brindisi
Liguria
Capital – Genoa
Genoa is the largest commercial port in Italy
Imperia is a coastal city and commune in the region of Liguria
Sanremo Music Festival was first held in 1951
Lombardy
Capital –Milan
Biblioteca Ambrosiana is a historic library in Milan, also housing the Pinacoteca Ambrosiana art gallery. Named after Ambrose, the patron saint of Milan, it was founded by Cardinal Federico Borromeo
Brera Art Gallery is the main public gallery for paintings in Milan
Latin name for Milan was Mediolanum
Milan Cathedral is the largest church in the Italian Republic. Construction began in 1386 and was completed in 1965
La Scala opened in 1778 with a performance of Antonio Salieri's Europa riconosciuta
UniCredit tower in Milan is the tallest building in Italy. Designed by Cesar Pelli
Pirelli Tower in Milan was hit by a plane in 2002
Quadrilatero della moda ("fashion square"), or Via Montenapoleone fashion district, is a high-class shopping district in the centre of Milan
Ducal Palace, Mantua was built between the 14th and the 17th century mainly by the noble family of Gonzaga as their royal residence in the capital of their Duchy
Stone carvings of Val Camonica constitute one of the largest collections of prehistoric petroglyphs in the world. The collection was recognized by UNESCO in 1979 and was Italy's first recognized World Heritage Site. Include the world’s earliest map, known as the Bedolina Map
Monza race track is 15 km north of Milan
Marche
Capital – Ancona
Palazzo Ducale (‘Ducal Palace’) in Urbino is a World Heritage site
Rossini Opera Festival takes place in Pesaro, the birthplace of Rossini
Molise
Capital – Campobasso
Until 1963, Molise formed part of the region of Abruzzi e Molise together with Abruzzo. The split, which did not become effective until 1970, makes Molise the newest region in Italy
Piedmont
Capital – Turin
Piedmont means ‘foot of the mountains’
Turin was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is mainly on the western bank of the Po River
Turin was the political and intellectual centre of the Risorgimento that led to the unification of Italy
Turin Shroud is kept in the royal chapel of the Cathedral of Saint John the Baptist in Turin
Carnival of Ivrea includes a tradition of throwing of oranges between organized groups, known as the Battle of the Oranges
Sardinia
Capital – Cagliari
Sassari is the second-largest city of Sardinia
Costa Smeralda is a resort in Sardinia. Development of the area started in 1961, and was financed by a consortium of companies led by Aga Khan
Alghero is a town in Sardinia. The Catalan language is co-official in the city, unique in Italy
Nuraghe is the main type of ancient megalithic edifice found in Sardinia, developed during the Nuragic Age between 1900 and 730 BC
Sicily
Capital - Palermo
Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean
Catania is the second-largest city in Sicily
Trapani is an important fishing port
Marsala in Sicily is famous for the landing of Garibaldi in 1860 (the Expedition of the Thousand) and its wine
Mount Etna is known as Mongibello (‘beautiful mountain’) in Italian
Mount Etna is an active stratovolcano lying between the cities of Messina and Catania
Messina was destroyed by an earthquake and tsunami in 1908
Syracuse was founded by Ancient Greek Corinthians and became a very powerful city-state. Syracuse was allied with Sparta and Corinth, exerting influence over the entire Magna Graecia area of which it was the most important city
Villa Romana del Casale is a large Roman villa. Excavations have revealed one of the richest, largest, and varied collections of Roman mosaics in the world
Trentino-South Tyrol
Capital – Trento
Bolzano, commonly known as South Tyrol, is an autonomous province. 64% of the population is Austro-Bavarian or Tyrolean and speaks German. Less than a quarter of the population speak Italian as their first language
Trentino is the other autonomous province of Trentino-South Tyrol
Tuscany
Capital – Florence
Ponte Vecchio (‘old bridge’) spans the River Arno in Florence
Piazza della Signoria is an L-shaped square in front of the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence
Florence Airport, Peretola, was formerly Amerigo Vespucci Airport
Carrara is a city in Tuscany notable for the white or blue-grey marble quarried there
Ducal palace of Mantua was built between the 14th and the 17th century mainly by the noble family of Gonzaga as their royal residence
Pisa Botanical Garden was established in 1544 under Cosimo I de' Medici as the first university botanical garden in Europe
Pisa International Airport was formerly Galileo Galilei Airport
Siena Cathedral, begun in the 12th century, is a masterpiece of Italian Romanesque-Gothic architecture
Palio is a horse race that is held twice each year in Siena. The horses represent ten of the seventeen contrade, or city wards. The race circles the Piazza del Campo
Livorno is a port on the Ligurian Sea. It is known in English as Leghorn
Elba is the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago and the third-largest island of Italy
Umbria
Capital – Perugia
Umbria is bordered by Tuscany to the west, the Marche to the east and Lazio to the south. The main towns are Perugia and Terni
Umbria is the only region not to have a coastline or a border with another country
The Basilica of San Francesco d'Assisi (Saint Francis), the mother church of the Franciscan Order, is a World Heritage Site in Assisi. The foundation stone was laid by Pope Gregory IX in 1228. The church displays works by Giotto and Cimabue
Veneto
Capital – Venice
Venice is built on 118 islands
Venice is known as La Serinissima and Bride of the Sea
Venice is divided into six areas or sestiere and is built on 118 islands
The banks of the Grand Canal are lined with more than 170 buildings. At one end the canal leads into the lagoon near Santa Lucia railway station and the other end leads into Saint Mark Basin: in between it makes a large S-shape through the central districts of Venice
Rialto Bridge is one of the four bridges spanning the Grand Canal in Venice. It is the oldest bridge across the canal, and was the dividing line for the districts of San Marco and San Polo. The present stone bridge, a single span designed by Antonio da Ponte, was completed in 1591
Triumphal Quadriga or Horses of Saint Mark is a set of Roman or Greek bronze statues of four horses, originally part of a monument depicting a quadriga. It was originally erected in the Hippodrome of Constantinople, possibly on a triumphal arch, and is now in St Mark's Basilica in Venice
Piazza San Marco, often known in English as Saint Mark's Square, is the principal public square of Venice
Santa Maria della Salute was one of five plague-churches built in Venice. The church is dedicated to Our Lady of Health (or of Deliverance, Italian: Salute)
Museo Correr is a museum in St. Mark’s Square. It covers both the art and history of Venice
Constitution Bridge is the fourth bridge over the Grand Canal. It was designed by Santiago Calatrava
Marciana Library or Library of Saint Mark is one of the earliest surviving public libraries and repositories for manuscripts in Italy and holds one of the world's most significant collections of classical texts
Venice Biennale was founded in 1895. It is now known as the Art Biennale
San Michele is Venice’s cemetery island
Venice is served by Marco Polo Airport
MOSE project is intended to protect Venice from flooding. It is due to be completed in 2025
Lido is a barrier island in the Venetian Lagoon
Sant'Erasmo is an island in the Venetian Lagoon lying north of the Lido and north east of Venice
Murano is an island just north of Venice. Murano became Europe's luxury glassmaking centre in the 15th and 16th centuries
Mestre is a neighborhood of Venice on the mainland
Traghetto is a large gondola used to ferry passengers across the Grand Canal
Vaporetto is a public waterbus
Padua is 40 km west of Venice
Padua Botanical Garden was founded in 1545
Prato della Valle is an elliptical square in Padua. It is the largest square in Italy
Islands
Aeolian Islands are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily. The largest island is Lipari, and the entire archipelago is known as the Lipari Islands. The other islands include Vulcano and Stromboli
Stromboli is known the ‘lighthouse of the Mediterranean’. Mount Stromboli has been in almost continuous eruption for the past 2,000–5,000 years; its last serious one occurred in 1921
The island of Lampedusa belongs to Italy and is the largest of the Pelagie Islands, situated 205 km from Sicily and 113 km from Tunisia. Since the early 2000s, the island has become a primary European entry point for migrants, mainly coming from Libya
Ponza is the largest island of the Italian Pontine Islands archipelago, located in the Tyrrhenian Sea
Santo Stefano is an island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, and is part of the Pontine Islands. It is dominated by an old prison built by the Bourbons, completed in 1797 and in use until 1965
Ischia is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples
Ferdinandea is a submerged volcanic island (also known as Graham Island) that forms part of the underwater volcano Empedocles 30 km south of Sicily. Currently a seamount, eruptions have raised it above sea level several times before erosion has caused it to submerge again. It last rose above sea level after erupting in 1831
Mountains
Apennines are a mountain range extending 1,200 km (750 miles) along the length of peninsular Italy
Corno Grande in Abruzzo is the highest point in the Apennines
Dolomites are a mountain range in northeastern Italy. They form part of the Southern Limestone Alps
The Dolomites take their name from the rock dolomite which was named after French mineralogist Deodat Gratet de Dolomieu
Marmolada is the highest point in the Dolomites
Cortina d’Ampezzo is in the Dolomites
Lakes
Largest lakes of Italy – Garda, Maggiore, Como
Lake Garda is located in Northern Italy, about half-way between Brescia and Verona, and between Venice and Milan
Lake Maggiore lies on the border of Italy and Switzerland
Lake Como is a lake of glacial origin in Lombardy. At over 400 m (1320 ft) deep it is one of the deepest lakes in Europe
Lake Como is shaped much like the character ‘Y’. The northern branch begins at the town of Colico, while the towns of Como and Lecco sit at the ends of the southwestern and southeastern branches respectively
Lake Lugano is between Como and Maggiore
Lake Orta is west of Lake Maggiore. Basilica di San Giulio is a Roman Catholic church on the San Giulio Island in the centre of Lake Orta
Lake Trasimeno in Umbria is the largest lake on the Italian peninsula south of the Po River
Lake Avernus is a volcanic crater lake located in the Avernus crater in the Campania region
Lake Bolsena is a crater lake in central Italy and is the largest volcanic lake in Europe
Seas
Tyrrhenian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy
Ligurian Sea lies between Corsica and Genoa
Strait of Messina is the strait between Sicily and Calabria
Strait of Bonifacio is the strait between Corsica and Sardinia
Rivers
Po flows 405 miles eastward across northern Italy, from Monviso (in the Cottian Alps) to the Adriatic Sea near Venice. It is the longest river in Italy, and passes through many important Italian towns, including Turin
Adige is the second longest river in Italy. It rises in the province of South Tyrol and flows 250 miles through most of northeastern Italy to the Adriatic Sea
Tiber rises in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flows through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio to the Tyrrhenian Sea. Tiber flows through Rome
Arno passes through Florence, Empoli, and Pisa
Kazakhstan
Flag of Kazakhstan has a gold sun with 32 rays above a soaring golden steppe eagle, both centered on a sky blue background
| Capital | Astana |
| Largest cities | Almaty, Astana |
| Currency | Tenge |
| Highest point | Khan Tengri |
Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country by land area and the ninth largest country in the world
Kazakhstan was the last of the Soviet republics to declare independence following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991
After the capital of Kazakhstan was moved from Almaty to Akmola in 1997, the city was consequently renamed Astana in 1998
Astana was renamed Nur-Sultan in honour of President Nursultan Nazarbayev in 2019, and reverted to the name Astana in 2022
Bayterek is the most famous landmark in Astana. The legend behind this tower as a symbol is that it represents a poplar tree, where the magic bird Samruk laid its egg
Lake Balkhash is shrinking due to diversion and extraction of water from its feeders. The lake's western part is fresh water. The lake's eastern half is saline
Kazakhstan produces 39% of the world’s uranium
Kosovo
Flag of Kosovo uses a map of the country as a design element; the flag of Cyprus is the only other to do so
| Capital | Pristina |
| Largest cities | Pristina, Prizren |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Velika Rudoka |
Note: Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence in 2008. Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. Kosovo has gained diplomatic recognition as a sovereign state by 114 member states of the United Nations
The city of Mitrovica is mainly Albanian, with a Serbian population in the north of the city
Kosovo is the only mainland European country which does not border the European Union
Latvia
| Capital | Riga |
| Largest cities | Riga, Daugavpils |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Gaizinkalns |
Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League member
Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states
Riga lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Baltic Sea
Riga has one of the largest collection of Art Nouveau buildings in the world
Yarni is a pagan festival in Latvia
Courland is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia
Liechtenstein
The crown was added to the flag of Liechtenstein in 1937, after it was discovered by Liechtenstein's team at the 1936 Summer Olympics that the flag then in use was identical to the flag of Haiti
| Capital | Vaduz |
| Largest cities | Schaan, Vaduz |
| Currency | Swiss franc |
| Highest point | Grauspitz |
Liechtenstein is a constitutional monarchy with the rank of principality, headed by the Prince of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked country bordered by Austria and Switzerland. The entire western border of Liechtenstein is formed by the Rhine
The principality of Liechtenstein is divided into 11 communes called Gemeinden. Five of them fall within the electoral district Unterland (the lower county), and the remainder within Oberland (the upper county)
Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in the world with more registered companies than citizens
Vaduz is the only capital city on the Rhine
Lithuania
| Capital | Vilnius |
| Largest cities | Vilnius, Kaunas |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Aukstojas Hill |
Lithuania is known as Lietuva in Lithuania
On 11 March 1990, a year before formal break-up of the Soviet Union, Lithuania became the first Soviet republic to declare itself independent
The Old Town of Vilnius is one of the largest surviving medieval old towns in Northern Europe. It was declared a World Heritage Site in 1994
Vilnius was a European Capital of Culture in 2009
In 1995, the world's first bronze cast of Frank Zappa was installed in Vilnius
Luxembourg
Flag of Luxembourg is very similar to the flag of the Netherlands, but the light blue stripe and red stripe on the Luxembourg flag are a lighter shade
| Capital | Luxembourg City |
| Largest cities | Luxembourg City |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Kneiff |
Luxembourg was founded by Count Siegfried I in 963
Luxembourg comprises two principal regions: the Oesling in the north as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south
As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by a grand duke, Henri, Grand Duke of Luxembourg, and is the world's only remaining grand duchy
European Court of Justice is in Luxembourg
Luxembourg was known as the “Gibraltar of the North”
Three languages are recognized as official in Luxembourg: French, German, and Luxembourgish
Luxembourg City lies at the confluence of the Alzette and Petrusse rivers
Luxembourg American Cemetery and Memorial is the final resting place of 5,076 American military dead, including General George S. Patton
Schengen is near the tripoint where the borders of Germany, France, and Luxembourg meet. The Schengen Agreement of 1985 led to the creation of Europe's borderless Schengen Area
Malta
A representation of the George Cross, awarded to Malta in 1942, is carried in the canton of the white stripe on the flag of Malta
| Capital | Valletta |
| Largest cities | Birkirkara |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Ta' Dmejrek |
Malta is an archipelago 80 km south of Sicily across the Malta Channel. Only the three largest islands – Malta, Gozo and Comino – are inhabited
Malta is the closest commonwealth country to the United Kingdom
Malta has two official languages: Maltese and English
Valletta, at 0.8 km2, is the smallest national capital in the European Union
Valletta is named after Jean Parisot de la Valette, a French nobleman and Grand Master of the Order of Malta
Valletta contains buildings from the 16th century onwards, built during the rule of the Order of St. John of Jerusalem, also known as Knights Hospitaller
Mdina served as the island's capital from antiquity until 1530, when the capital was moved to Birgu
Megalithic Temples of Malta are the oldest free-standing structures on Earth, even older than the Pyramids
The megalithic temple of Ggantija is on the island of Gozo
Three Cities is a collective description of the three fortified cities of Birgu, Senglea and Cospicua
Dghajsa is a traditional water taxi
Moldova
The tricolour of Moldova is identical to the flag of Romania, but on Moldova's flag the yellow stripe is charged with the coat of arms
| Capital | Chisinau |
| Largest cities | Chisinau, Tiraspol (see note below) |
| Currency | Leu |
| Highest point | Balanesti Hill |
Note: Tiraspol is a city in Transnistria
The name Moldova is derived from the Moldova River
Moldova declared itself an independent state in 1991. It is the poorest country in Europe
The largest part of the nation lies between two rivers, the Dniester and the Prut
The English language name for Chisinau is Kishinev
Monaco
| Capital | Monaco |
| Largest cities | Monaco |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Chemin des Revoires |
Monaco is a sovereign city-state and microstate. It is the second smallest and the most densely populated country in the world
Monaco is a principality governed under a form of constitutional monarchy, with Prince Albert II as head of state
The traditional national language is Monegasque, now spoken by only a minority of residents
Monte Carlo officially refers to an administrative area of the Principality of Monaco; informally the name also refers to a larger district, the Monte Carlo Quarter
Opera de Monte-Carlo was designed by Charles Garnier
Monte Carlo Casino opened in 1863
Montenegro
| Capital | Podgorica |
| Largest cities | Podgorica |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Zla Kolata |
Montenegro means “black mountain”
Montenegro declared itself independent of Serbia in 2006
The country has a segment of the Karst of the western Balkan Peninsula
Podgorica was known as Titograd from 1946 to 1992
Podgorica means “under the small hill”
Bay of Kotor is the southernmost part of the region of Dalmatia. The bay has been inhabited since antiquity. Its medieval towns are major tourist attractions
Cetinje is the former royal capital of Montenegro
Netherlands
| Capital | Amsterdam |
| Largest cities | Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht, Eindhoven |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Vaalserberg (see note below) |
Note: Vaalserberg is the highest point on the Dutch mainland. The highest point of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is Mount Scenery on the island of Saba in the Caribbean Netherlands
Netherlands is divided into twelve provinces and three overseas public bodies (Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba)
Amsterdam is the largest city in North Holland province
Amsterdam is colloquially referred to as the ‘Venice of the North’, for its large number of canals
Amsterdam was founded at the mouth of the Amstel River that was dammed to control flooding
Dam Square lies in the historical center of Amsterdam
De Wallen, also known as Walletjes or Rosse Buurt, is a designated area for legalised prostitution and is Amsterdam's largest and most well-known red-light district
Vondelpark has around 10 million visitors annually
Natura Artis Magistra, commonly known just as Artis, is a zoo in Amsterdam. It is the oldest zoo in the Netherlands
Rotterdam is the largest city of South Holland province
The port of Rotterdam is the largest cargo port in Europe. Rotterdam is known as the “Gateway to Europe”
The Erasmus Bridge is a cable stayed bridge across the Nieuwe Maas river, linking the northern and southern halves of the city of Rotterdam. It was designed by Ben van Berkel and completed in 1996. The bridge has a 139 metre-high asymmetrical pylon, earning the bridge its nickname of “The Swan”
The Hague is the capital of South Holland province
The Hague is the seat of Dutch government
International Court of Justice is located at Peace Palace in The Hague, and was funded by Andrew Carnegie
Mauritshaus art museum in The Hague houses the Royal Cabinet of Paintings which consists of 841 objects, mostly Dutch Golden Age paintings
Haarlem is the capital of North Holland province
Maastrict is on River Maas and is the capital of Limburg province
The presence of the Philips electronics company is probably the largest single contributing factor to the major growth of Eindhoven
Limburg is the southernmost of the provinces of the Netherlands
Vlissingen is also known as Flushing
Aalsmeer flower auction is the largest flower auction in the world. Around 43 million flowers are sold daily
Alkmaar is known for its traditional cheese market
Leeuwarden is the capital of Friesland
Randstat is a conurbation consisting primarily of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague and Utrecht); their suburbs, and many towns in between, that all grew and merged into each other
Efteling is a fantasy-themed amusement park in North Brabant. In 2020, it was the most visited theme park in Europe
Flevoland is the 12th and youngest province of the Netherlands, established in 1986
Zeeland is the westernmost and least populous province. Large parts of Zeeland are below sea level
Zuider Zee was dammed using boulder clay in 1932
Many dykes were breached in the North Sea flood of 1953
Vaalserberg is the location of the tripoint between Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands
Ijsselmeer is a shallow artificial lake of 1100 km² in the central Netherlands. It is the largest lake in Western Europe
North Macedonia
| Capital | Skopje |
| Largest cities | Skopje |
| Currency | Denar |
| Highest point | Mount Korab |
North Macedonia is officially the Republic of North Macedonia. It became a member of the United Nations in 1993, but, as a result of an ongoing dispute with Greece over use of the name Macedonia, it was admitted under the provisional description of "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (FYROM). The name was changed from Macedonia to North Macedonia in 2019
Skopje is on the River Vardar
Skopje was known in the Roman period under the name Scupi
In 2018 Skopje Alexander the Great Airport was renamed Skopje International Airport to improve relations with Greece
Norway
| Capital | Oslo |
| Largest cities | Oslo, Bergen, Trondheim, Stavanger |
| Currency | Krone |
| Highest point | Galdhopiggen |
Bygdoy in Oslo has several museums, including the Kon-Tiki Museum; the Norwegian Museum of Cultural History (Norsk Folkemuseum); the Viking Ship Museum; the Norwegian Maritime Museum and the ship Fram, used by Roald Amundsen
The main attractions at the Viking Ship Museum in Oslo are the Oseberg ship, Gokstad ship and Tune ship
Frogner Park is a public park in Oslo that contains the Vigeland installation, a permanent sculpture installation created by Gustav Vigeland
Oseberg ship is a well-preserved Viking ship discovered in a large burial mound at the Oseberg farm in Norway. The characteristic motif of the Oseberg style of animal ornamentation is gripping beasts
Kings of Norway were traditionally crowned at Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim
Edvard Grieg Museum Troldhaugen is in Bergen
Tromso is a city in Troms og Finnmark, the largest county by area in Norway
Sarpsfossen has the greatest flow of any waterfall in Europe. It is the last waterfall in the river Glomma, which is the longest river in Norway
Cape Nordkinn is the northernmost point of mainland Norway, and by extension the northernmost point of mainland Europe. It is in the county of Finnmark
Laerdal Tunnel is a 15 mile long road tunnel connecting Laerdal and Aurland in Sogn. It is the longest road tunnel in the world
Ryfylke Tunnel the world's longest and deepest subsea road tunnel, although it will be superceded by Rogfast that is projected to open in 2033
Lofoten is an archipelago in the county of Nordland. Though lying within the Arctic Circle, the archipelago experiences one of the world's largest elevated temperature anomalies relative to its high latitude. Target of oil and gas exploration
Utsira is a municipality in Rogaland county. Utsira (under the spelling Utsire) gives its name to North Utsire and South Utsire, two of the sea areas of the Shipping Forecast
Hammerfest claims to be the northernmost city in the world
Hurtigruten (“the Express Route”) is a daily passenger and freight shipping service along Norway's western and northern coast between Bergen and Kirkenes. Sometimes referred to as the Norwegian Coastal Express
Galdhopiggen is the highest mountain in Norway, Scandinavia and Northern Europe
Hornindalsvatnet is the deepest lake in Europe
Vinnufossen is the highest waterfall in Europe
Troll Wall, composed of gneiss, is the tallest vertical rock face in Europe
Jostedal Glacier (Norwegian: Jostedalsbreen) is the largest glacier in continental Europe
Saltstraumen and Moskstraumen are the sources of the strongest whirlpools in the world
E6 is the main north-south road through Norway, and is 1,919 miles long
North Cape is the northernmost point in Europe that can be accessed by car
Svalbard (formerly known by its Dutch name Spitsbergen) is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. It is about midway between continental Norway and the North Pole
Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century and several permanent communities were established
Longyearbyen, in Svalbard, is the world’s northernmost town
Bear Island is the southernmost island of the Norwegian Svalbard archipelago
Jan Mayen is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and a part of the Kingdom of Norway
The Antarctic Peter I Island is a dependent territory and thus not considered part of the Kingdom. Norway also lays claim to a section of Antarctica known as Queen Maud Land
Bouvet Island is an uninhabited subantarctic volcanic island and dependency of Norway located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is the most remote island in the world
Poland
| Capital | Warsaw |
| Largest cities | Warsaw, Lodz, Krakow, Wroclaw, Poznan |
| Currency | Zloty |
| Highest point | Rysy |
Voivodeship is the highest-level administrative division in Poland
Warsaw international airport is named after Frederic Chopin
Warsaw is known as the “Phoenix City”
Warsaw is located on the Vistula river
Palace of Culture and Science in Warsaw is the tallest building in Poland. It was a gift from the Soviet Union to the people of Poland
Royal Castle was the official residence of the Polish monarchs. It is located in the Castle Square, at the entrance to the Warsaw Old Town
Krakow's John Paul II International airport in Balice is Poland’s second busiest after Warsaw
The main landmarks of Krakow include the St. Mary's Basilica and the Sukiennice Cloth Hall, the Wawel Castle, the Zygmunt Bell at the Wawel Cathedral, and the medieval St Florian's Gate with the Barbican along the Royal Coronation Route
Wieliczka salt mine, near Krakow, was built in the 13th century. It produced table salt continuously until 2007, as one of the world's oldest salt mines still in operation
Lodz translates literally as “boat” It is an industrial city
Wroclaw is the capital of Lower Silesia in southwestern Poland, situated on the Oder River
Wroclaw is served by Copernicus Airport
Wroclaw is known as Breslau in Germany
Lublin is the largest Polish city east of the Vistula River
Malbork Castle is a 13th century Teutonic castle and fortress. It is the largest castle in the world measured by land area
Poznan has the oldest cathedral in the country, which contains the tombs of the first Polish rulers
Containing the painting known as the Black Madonna, the Jasna Gora monastery in the city of Czestochowa is a centre for Catholic pilgrims
Vistula river empties into the Baltic Sea near Gdansk
Suwalki Gap is a sparsely populated area immediately southwest of the border between Lithuania and Poland, between Belarus and the Russian exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast. It is of great strategic and military importance
Masurian Lakes in northeastern Poland contains more than 2,000 lakes
Bledow desert is a sandy desert in Silesia
Bialowieza Forest is a World Heritage Site straddling the border between Poland and Belarus. It is one of the last and largest remaining parts of the immense primeval forest that once stretched across the European Plain
Portugal
Flag of Portugal has a simple version of the national coat of arms (armillary sphere and Portuguese shield)
| Capital | Lisbon |
| Largest cities | Lisbon, Porto |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Serra da Estrela (see note below) |
Note: Serra da Estrela is the highest point on the Portuguese mainland. The highest point of Portugal is Mount Pico on Pico Island in the Azores
Aside from continental Portugal, the Portuguese Republic holds sovereignty over the Atlantic archipelagos of Azores and Madeira, which are autonomous regions of Portugal
The country is named after its second largest city, Porto
In 27 BC, Lusitania gained the status of Roman province. Later, a northern province of Lusitania was formed, known as Gallaecia, with the capital in Bracara Augusta, today's Braga
Lisbon was built on seven hills
Belem Tower was commissioned by King John II to be both part of a defence system at the mouth of the Tagus River and a ceremonial gateway to Lisbon. It was built in the early 16th century and is a prominent example of the Portuguese Manueline style
Lisbon was known to the Romans as Felicitas Julia Olissipo
Calouste Gulbenkian Museum in Lisbon houses one of the world's most important private art collections
Vasco da Gama Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge that spans the Tagus River in Lisbon. It is the second longest bridge in Europe. It was built to alleviate the congestion on Lisbon's other bridge (25 of April Bridge)
Lisbon is served by Humberto Delgado Airport
Gare do Oriente station was opened in 1998
25th of April Bridge is a suspension bridge connecting Lisbon to Almada on the left bank of the Tagus river. Named after the date of the Carnation Revolution in 1974
Braga Munipical Stadium was carved out of a quarry (Monte Castro) that overlooks the city of Braga
Douro enters the Atlantic near Porto
Mondego is the longest river wholly within Portugal
Serra da Estrela (English: Mountain Range of the Star) is the highest mountain range in Continental Portugal
Sintra is a World Heritage Site on account of its 19th century Romantic architecture
Fatima is associated with the Marian apparitions that were purportedly witnessed by three local shepherd children at the Cova da Iria in 1917
Most westerly point in mainland Europe is Cabo da Roca
Algarve is the southernmost region of mainland Portugal. Faro is the administrative centre
Praia do Norte (North Beach) at Nazare is listed on the Guinness World Records for the biggest waves ever surfed
Autonomous regions
Azores
Azores is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands 1,400 km west of Lisbon
Largest islands – Sao Miguel, Pico, Terceira
Ponta Delgada is the capital of the Azores and is on the island of Sao Miguel
Madeira
Madeira is an archipelago located in the north Atlantic Ocean, west and slightly south of Portugal. It includes the islands of Madeira, Porto Santo, and the Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands
Madeira is famous for Madeira wine and embroidery
The main harbour is in Funchal, the capital of Madeira
Funchal is served by Cristiano Ronaldo International Airport
Monte in a town in Funchal with a toboggan run that uses large wicker baskets
Romania
| Capital | Bucharest |
| Largest cities | Bucharest, Cluj, Timisoara |
| Currency | Leu |
| Highest point | Moldoveanu Peak |
Modern Romania emerged within the territories of the ancient Roman province of Dacia, and was formed in 1859 through a personal union of the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia. The new state, officially named Romania since 1866, gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1877
The Palace of the Parliament in Bucharest is the world's heaviest building and the world's second largest administrative building, after the Pentagon
Carpathian Mountains dominate the centre of Romania
Transylvania was part of Hungary until 1918
Bran Castle is a national monument and landmark in Transylvania. Commonly known outside Transylvania as Dracula's Castle
Danube empties in Romania's Danube Delta
Danube Delta has three distributaries
Russia
| Capital | Moscow |
| Largest cities | Moscow, St Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Kazan |
| Currency | Ruble |
| Highest point | Mount Elbrus |
Russia is the largest country in the world, covering more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area. Russia is also the world's ninth most populous nation
Russia is a federation which, since 2008, consisted of 83 federal subjects. In 2014, Sevastopol and the Republic of Crimea became the 84th and 85th federal subjects
Federal subjects are divided into 46 oblasts, 22 republics, 9 krais, 4 autonomous okrugs, 3 federal cities (Moscow, Saint Petersburg, and Sevastopol) and 1 autonomous oblast (Jewish Autonomous Oblast)
There are 11 time zones in Russia, ranging from UTC+02:00 (Kaliningrad) to UTC+12:00 (Kamchatka)
Russia is the only country that borders the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea
Moscow was founded in 1147
Boulevard Ring is Moscow's second centremost ring road (the first is formed by the Central Squares of Moscow running along the former walls of Kitai-gorod)
Sheremetyevo and Domodedovo are the international airports in Moscow
Moscow Metro was opened in 1935 with one line and 13 stations. It was the first underground railway system in the Soviet Union. As of 2023, the Moscow Metro has 258 stations. The Moscow Metro is the busiest metro system in Europe
The underground stations being constructed under Stalin's regime, in the style of socialist classicism, were meant as underground ‘palaces of the people’
Moscow is known as the ‘Port of the Five Seas’
Tverskaya Street in Moscow was named Gorky Street from 1935 to 1990
Arbat Street in the historical centre of Moscow has existed since at least the 15th century
Europe's largest shopping centre, Aviapark, is in Moscow
Moskva River passes through central Moscow
Dubna is a town in Moscow Oblast. It is home to the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, an international nuclear physics research centre and one of the largest scientific foundations in the country
Saint Petersburg was founded by Tsar Peter the Great in 1703. It was known as Petrograd from 1914 to 1924, and Leningrad from 1924 to 1991
Saint Petersburg is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea
Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents
Nevsky Prospect is a main street in Saint Petersburg
Novosibirsk is the most populous city in Asian Russia. It lies on the Ob river
Yekaterinburg is the largest city in Urals and is the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk. The city was formerly known as Sverdlovsk
Kazan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan. It is the most populous city on the Volga
Nizhny Novgorod was known as Gorky from 1932 to 1990
Volgograd was known as Tsaritsyn from 1598 to 1925, and Stalingrad from 1925 to 1961
The Motherland Calls is a statue in Mamayev Kurgan in Volgograd commemorating the Battle of Stalingrad. Sculpted by Vevgeny Vuchetich
Astrakhan is the principal port on River Volga
Arkhangelsk, also known as Archangel, is on the White Sea. It was the chief seaport of Russia until 1703, when it was replaced by the newly-founded Saint Petersburg
Krasnoyarsk is located on the Yenisei River. It is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk and Omsk
Anadyr is a town in far northeastern Russia. It lies on the southern shore of the estuary of the Anadyr River, which empties into the Bering Sea
Norilsk in Siberia is known for nickel mining
Birobidzhan is a town and the administrative centre of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, located on the Trans-Siberian Railway
Sakha Republic, also known as Yakutia, is the largest subnational governing body by area in the world at 1,190,555 sq miles and the eighth largest territory in the world. Its capital is Yakutsk
Yakutsk is the coldest city on earth
Great Patriotic War Monument is a large statue in Murmansk
Samara lies on the River Volga. Chosen to be the capital of the USSR should Moscow fall to the invading Germans during World War II
Taymyr Peninsula, in the Siberian Federal District, forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Lake Taymyr and the Byrranga Mountains are located within the vast Taymyr Peninsula. Cape Chelyuskin, the northernmost point of the Eurasian continent, is located at the northern end of the Taymyr Peninsula
Samara lies on the River Volga. Chosen to be the capital of the USSR should Moscow fall to the invading Germans during World War II
Mount Narodnaya is the highest peak of the Urals in Russia
Kamchatka has around 30 active volcanoes
Kalmykia is the only region in Europe where Buddhism is the main religion
Vladikavkaz is the capital of North Ossetia-Alania
Magas is the capital of Ingushetia
Grozny is the capital of Chechnya
Makhachkala is the capital of Dagestan
Derbent is a city in the Republic of Dagestan. It is the southernmost city in Russia. Often identified with the legendary Gates of Alexander, Derbent claims to be the oldest city in Russia
Kaliningrad Oblast is an exclave of Russia surrounded by Poland, Lithuania and the Baltic Sea
Konigsberg was renamed Kaliningrad in 1946
Museum of the World’s Ocean is in Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad is situated on the Pregolya River
Rostov-on-Don is a port city 30 km from the Sea of Azov
Franz Josef Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It was discovered in 1873 and named in honour of the Austro-Hungarian emperor Franz Joseph I
Solovki was the first Gulag. Located on the Solovetsky Islands, in the White Sea
Novaya Zemlya (Russian: New Land) is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky. Novaya Zemlya consists of two major islands, separated by the narrow Matochkin Strait. The two main islands are Severny (northern) and Yuzhny (southern). Novaya Zemlya separates the Barents Sea from the Kara Sea. It was used as a nuclear test site in the Cold War. It was the site of the 1961 explosion of Tsar Bomba, the largest, most powerful nuclear weapon ever detonated
Khanty-Mansiysk is an oil boom town in West Siberia
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the capital of Kamchatka
Power of Siberia is a Gazprom-operated pipeline in Eastern Siberia that transports natural gas from Yakutia to China
Mirny mine is an open pit diamond mine located in Mirny, Sakha Republic. The mine is more than 525 m deep
Novorossiysk is a city in Krasnodar Krai. It is the largest port on the Black Sea and the largest Russian port
Magnitogorsk is a city in the Chelyabinsk Oblast. It contains the largest iron and steel works in Russia
Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains is a site of paleoarcheological remains
Kola Peninsula is part of the Murmansk Oblast. Kola Superdeep Borehole is the result of a scientific drilling project that attempted to drill as deeply as possible into the Earth’s crust. The deepest reached over 12,000 metres
Trans-Siberian Railway is the longest railway line in the world, with a length of over 9,289 kilometres (5,772 miles), from Moscow to Vladivostok. Construction started in 1891
Kolyma Highway in Siberia is known as the Road of Bones in reference to the hundreds of thousands of forced labourers who were interred in the road after dying during its construction
Beringia is the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula
Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. Woolly mammoths survived until c. 2000 BC
Big Diomede or “Tomorrow Island” is the larger of the two Diomede Islands located in the middle of the Bering Strait between the Alaska mainland and Siberia. Little Diomede Island is part of the United States and is east of the International Date Line
Rivers
Volga is the longest river in Europe (2,290 miles) and empties into the Caspian Sea
Neva is the only river flowing from Lake Ladoga
Ob, Yenisei, and Lena are the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean
Ob is the westernmost of the Siberian rivers. The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary
Yenisei is the largest river system flowing to the Arctic Ocean
Lena is the easternmost of the three rivers. It flows into the Laptev Sea and is the longest river entirely within Russia
Lena Pillars is a natural rock formation along the banks of the Lena River. The pillars are 150–300 metres high
Don river rises southeast of Moscow, and flows for a distance of about 1,220 miles to the Sea of Azov
Kolyma river is in northeastern Siberia and is 1,323 miles long. It is frozen for 250 days each year
Angara is the only river flowing out of Lake Baikal
Svir connects Lake Onega to Lake Lagoda
Lakes
Lake Baikal, in Southern Siberia is the deepest and oldest lake in the world as well as the largest (by volume) freshwater lake. It contains over 20% of the world's liquid fresh surface water and more than 90% of Russia's liquid fresh surface water. It is a World Heritage Site. Olkhon, by far the largest island in Lake Baikal, is the second largest lake-bound island in the world (the largest being Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron)
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, not far from Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake in Europe
Lake Onega is the second largest lake in Europe. Kizhi Island in Lake Onega is known for its wooden churches
Lake Karachay in the Ural Mountains was used as a dumping site for radioactive waste. Today the lake is completely infilled
San Marino
| Capital | San Marino |
| Largest cities | Serraville (see note below), Borgo Maggiore, San Marino |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Monte Titano |
Note: Though it is the biggest town of the Republic, Dogana is not an autonomous castello (municipality) but belongs to the castello of Serravalle
San Marino is also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino
San Marino is a microstate enclaved by Italy. It claims to be the oldest surviving sovereign state and constitutional republic in the world, as the continuation of the monastic community founded in 301, by stonecutter Marinus from the Croatian island of Rab
San Marino has more vehicles than people
The Captains Regent are the two heads of state of the Republic of San Marino. They are elected every six months by the Grand and General Council, the country's legislative body
Serbia
| Capital | Belgrade |
| Largest cities | Belgrade, Novi Sad, Nis |
| Currency | Dinar |
| Highest point | Velika Rudoka (see note below) |
Note: Velika Rudoka is in Kosovo, but Serbia claims Kosovo as part of its own sovereign territory
Serbia became landlocked after Montenegro declared independence in 2006
The province of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia in 2008. Serbia immediately condemned the declaration and continues to deny any statehood to Kosovo
Air Serbia is the flag carrier and largest airline of Serbia. The airline was formerly known as Jat Airways until it was renamed in 2013. The airline has its hub at Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport
Belgrade lies at the confluence of the Sava and Danube Rivers. Means “white city”
House of Flowers is the mausoleum of Josip Broz Tito in Belgrade
Several Roman emperors were born in Nis
Slovakia
| Capital | Bratislava |
| Largest cities | Bratislava, Kosice |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Gerlach |
Slovakia became an independent state on 1 January 1993 after the dissolution of Czechoslovakia
Bordering Austria and Hungary, Bratislava is the only national capital that borders two independent countries
Bratislava was known as Pressburg until 1919
Pressburg flourished during the 18th century reign of Queen Maria Theresa, becoming the largest and most important town in “the Kingdom of Hungary”
Vah is the longest river in Slovakia
Gerlachov Peak, informally referred to as Gerlach, is the highest peak in the High Tatras, in Slovakia, and in the Carpathians
Slovenia
The coat of arms on the flag of Slovenia is a shield with the image of Mount Triglav, Slovenia's highest peak
| Capital | Ljubljana |
| Largest cities | Ljubljana, Maribor |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Mount Triglav |
In 1991, Slovenia became the first country to split from Yugoslavia and become an independent country. In 2004, it entered NATO and the European Union; in 2007 it became the first former Communist country to join the Eurozone
Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport is named after the leader of the Democratic Opposition of Slovenia between 1989 and 1992
In the Middle Ages, both the river and the town of Ljubljana were also known by the German name Laibach
Piran is a town on the Adriatic Sea known for its medieval architecture
Planica is an alpine valley famous for ski jumping
Lake Cerknica is an intermittent lake. When full, it is the largest lake in the country
Lake Bled is a tourist destination in the Julian Alps. The lake surrounds Bled Island which has several buildings, the main one being the pilgrimage church dedicated to the Assumption of Mary
Mount Triglav is the highest peak of the Julian Alps and of the former Yugoslavia
Spain
| Capital | Madrid |
| Largest cities | Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Zaragoza |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Mulhacen (see note below) |
Note: Mulhacen is the highest point on the Spanish mainland. The highest point of Spain is Mount Teide on Tenerife in the Canary Islands
Spain is divided into 17 autonomous communities and two autonomous cities
Andalusia
Capital – Seville
Cordoba is known as the “Athens of the west”
In the 10th century Cordoba was the most populous city in the world, and under the rule of Caliph Al Hakam II it had also become a centre for education under its Islamic rulers
Cordoba has more World Heritage Sites than any other city in the world
Mezquita is a mosque in Cordoba, completed in the 11th century. The building is most notable for its giant arches, with over 1,000 columns of jasper, onyx, marble, and granite
Alhambra (“red castle”) is an ancient palace and fortress complex of the Moorish monarchs of Granada, in southern Spain (known as Al-Andalus when the fortress was constructed during the mid-14th century). It was the residence of the Muslim kings of Granada and their court, and is currently a museum exhibiting Islamic architecture. Court of the lions is a fountain supported by the figures of twelve lions in white marble
Federico Garcia Lorca airport serves Grenada
Seville is on the Guadalquivir river
Hispalis was the Roman name for Seville
Seville Cathedral is the largest Gothic cathedral in the world. Giralda is the bell tower
Almeria is a province of the Autonomous Community of Andalucia. It is bordered by the provinces of Granada and Murcia, and the Mediterranean Sea. Its capital is the city of Almeria
Almeria is the driest region of Europe, with the continent's only true desert climate. A number of spaghetti westerns were shot here
Tabernas Desert is in Almeria
Malaga–Costa Del Sol airport has a Pablo Ruiz Picasso terminal
Costa del Sol (“Sun Coast”) is a region comprising the coastal towns along the Mediterranean coastline of the Malaga province. It includes the towns of Torremolinos and Marbella
The most southerly point in mainland Europe is Punta de Tarifa
Aragon
Capital – Zaragosa
Zaragoza is on the river Ebro
Zaragoza was founded by Emperor Augustus
Belchite is a ghost town left as a memorial to the Spanish Civil War
Pico d’Aneto is the highest point in the Pyrenees and in Aragon
Asturias
Capital – Oviedo
Gijon is a seaport and the largest city in Asturias
Balearic Islands
Capital – Palma de Mallorca
Palma de Mallorca is on Majorca
The four largest islands are Majorca, Minorca, Ibiza and Formentera. There are many minor islands and islets in close proximity to the larger islands, including Cabrera, Dragonera and S'Espalmador
Miro Mallorca Foundation is a museum in Palma de Mallorca, dedicated to the work of the artist Joan Miro
Pityusic Islands, or commonly but informally the Pine Islands, is the name given collectively to Ibiza, Formentera and a number of small islands
Ibiza is closest to the mainland
Large portions of Ibiza are registered as World Heritage Sites
Privilege Ibiza is the world’s largest nightclub
Mahon is the capital of Minorca
Basque Country
Capital – Vitoria (de facto)
Basque Country includes the Basque provinces of Alava, Biscay and Gipuzkoa, also called Historical Territories
Almost half of the inhabitants of the Basque Autonomous Community live in Greater Bilbao
Guggenheim Museum Bilbao was designed by Frank Gehry and was opened in 1997
San Sebastian is also known as Donostia
Canary Islands
Capital – Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, commonly known as Las Palmas is the capital (jointly with Santa Cruz de Tenerife) and the most populous city in the Autonomous Community of the Canary Islands and the ninth largest city in Spain
Santa Cruz de Tenerife is also a capital of the Canary Islands
The name Islas Canarias is likely derived from the Latin name Canariae Insulae, meaning ‘Islands of the Dogs’
Tenerife is the largest and most populous island of the seven Canary Islands
Playa de las Américas is a purpose-built holiday resort in Arona Municipio, in the south of Tenerife
Mount Teide is a volcano on Tenerife. Its 3,718 m summit is the highest point in Spain
La Gomera is a mountainous island of volcanic origin on Tenerife
Fuerteventura is the oldest island in the Canary Islands dating back 20 million years to a volcanic eruption from the Canary hotspot. It is the second largest island and the closest to Africa
El Hierro is the smallest and westernmost of the main Canary Islands
Lanzarote is the easternmost Canary Island
Fire Mountain is on Lanzarote
Arrecife is main town on Lanzarote
La Palma is the most north-westerly of the Canary Islands
Cumbre Vieja is an active volcanic ridge on the volcanic ocean island of Isla de La Palma in the Canary Islands. A future failure of the western flank of the Cumbre Vieja may cause a mega-tsunami
Cantabria
Capital – Santander
Altamira is a cave famous for its Upper Paleolithic cave paintings featuring drawings and polychrome rock paintings of wild mammals and human hands. It is located near the town of Santillana del Mar in Cantabria. The cave with its paintings has been declared a World Heritage Site
Castile-La Mancha
Capital – Toledo
Toledo is known as the ‘City of the Three Cultures’ for the cultural influences of Christians, Muslims, and Jews reflected in its history
Toledo is located on the banks of the River Tagus, and is known for the production of swords
La Mancha is the largest continuous wine growing region in the world
La Mancha's windmills were immortalized in the novel Don Quixote
Casas Colgadas (‘Hanging Houses’) is a complex of houses located in Cuenca. They were built in the 14th century and are built over a rock
Castile and Leon
Capital – Valladolid
Castile and Leon is the largest autonomous community in Spain
Burgos Cathedral is the burial place of Rodrigo Diaz de Vivar (El Cid)
Segovia is famous for its historic buildings including three main landmarks: its midtown Roman aqueduct, its cathedral, and the castle, which served as one of the templates for Walt Disney's Cinderella Castle
Catalonia
Capital – Barcelona
Catalonia is administratively divided into four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona
Park Guell is in Barcelona. Garden complex designed by Gaudi
Barcelona El-Prat airport is the second largest in Spain behind Madrid Barajas Airport
Barcelona was known as Faventia in Roman times
A tree-lined pedestrian mall, La Rambla in Barcelona stretches for 1.2 km connecting Placa de Catalunya in the centre with the Christopher Columbus Monument at Port Vell
Dali Theatre and Museum is in Figueres, near Barcelona
Tarragona is a port city in Catalonia. The Roman ruins of Tarraco have been designated a World Heritage Site
Costa Brava is a coastal region of northeastern Catalonia, in the province of Girona. Costa is the Catalan and Spanish word for 'coast', and Brava means 'rugged' or 'wild'. It includes the town of Lloret de Mar
Extremadura
Capital – Merida
Extremadura is formed by the two largest provinces of Spain: Caceres and Badajoz
Galicia
Capital – Santiago de Compostela
Galicia takes its name from the Gallaeci, the Celtic peoples living north of the Douro river
Way of St James (Camino de Santiago) is the pilgrimage route to the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, where tradition has it that the remains of the apostle Saint James are buried. The scallop shell, often found on the shores in Galicia, has long been the symbol of the pilgrimage route
Vigo is a city in Galicia
A Coruna is the largest city in Galicia
Lugo is the only city in the world to be surrounded by completely intact Roman walls
Tower of Hercules is the oldest extant lighthouse known. It has an ancient Roman origin on a peninsula near A Coruna
La Rioja
Capital – Logrono
La Rioja is the least populated autonomous community of Spain. It is well known for its wines
Madrid
Madrid is the third largest city in the European Union, after London and Berlin, and its metropolitan area is the third largest in the European Union after Paris and London
Madrid is the highest capital city in Europe
Philip II named Madrid as the capital of Spain in 1561
Puerta del Sol is a square in Madrid
Plaza de Colon is located in Madrid. This plaza and its fountain commemorate the explorer Christopher Columbus, whose name in Spanish was Cristóbal Colón
Madrid is located on the Manzanares river
Atocha railway station has a concourse with a tropical botanical garden
Terminal 4 at Madrid-Barajas Airport was designed by Richard Rogers
Ciudad Real International Airport, previously known as Don Quixote Airport, was constructed at a cost of €1.1 billion. It was opened in 2009, but closed in 2012 when the management company filed for bankruptcy
Las Ventas in Madrid is the largest bullring in Spain
Murcia
Capital – Murcia
Murcia is the largest city
Cartagena is the second largest city
Navarre
Capital – Pamplona
Bull running in Pamplona is part of the San Fermin festival, held in July
Valencian Community
Valencia is known as the “city of 100 bell towers”
La Tomatina is a festival that is held in the Valencian town of Bunol, in which participants throw tomatoes at each other
Costa Blanca (English: White Coast) refers to the over 200 km of coastline belonging to the Province of Alicante. The name Costa Blanca was devised as a promotional name used by BEA when they launched their air service (for £38.16s.-) between London and Valencia in 1957. It includes the major tourist destinations of Benidorm and Alicante
Benidorm has the most high-rise buildings per capita in the world
Intempo in Benidorm consists of two parallel towers separated by a gap of 20 metres and connected by a cone-shaped structure between floors 38 and 44
Lladro is a company based in Valencia that produces high quality porcelain figurines
Penon de Velez de la Gomera is a Spanish rock in North Africa off the Moroccan coast
Ebro is the longest river entirely in Spain
Rio Tinto river is notable for being very acidic (pH 2) and its deep reddish hue is due to iron dissolved in the water
Mulhacen is the highest mountain in continental Spain and in the Iberian Peninsula. It is part of the Sierra Nevada range
Picos de Europa is a mountain range in Spain
Faisans (Pheasant Island) in the Bidasoa river is an uninhabited river island that is formally controlled by Spain between 1 February and 31 July each year and by France for the following six months
Autonomous cities
Ceuta
Ceuta is an exclave located on the north coast of Africa, sharing a western border with Morocco. Ceuta, like Melilla, was a free port before Spain joined the European Union. Separated from the Iberian peninsula by the Strait of Gibraltar, Ceuta lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean
Melilla
Melilla shares a border with Morocco and is and across the sea from the Spanish provinces of Granada and Almeria
Sweden
| Capital | Stockholm |
| Largest cities | Stockholm, Gothenburg, Malmo, Uppsala |
| Currency | Krona |
| Highest point | Kebnekaise |
Stockholm is located where Lake Malaren flows into the Baltic Sea. The central parts of the city consist of fourteen islands that are continuous with the Stockholm archipelago
Vasa Museum in Stockholm displays the 64-gun warship Vasa that sank on her maiden voyage in 1628
The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for its decoration of the stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world
Gamla Stan is the historic old town of Stockholm
Museum of World Culture is in Gothenburg
Gothenburg is situated by the Kattegat
Gota Canal provides a route from Gothenburg on the west coast to Soderkoping on the Baltic Sea, through the lakes Vanern and Vattern
Together with Copenhagen, Malmo constitutes the transnational Oresund Region
The Oresund Bridge is a combined two-track rail and four-lane road bridge across the Oresund strait. The bridge-tunnel is the longest combined road and rail bridge in Europe and connects Copenhagen and Malmo. The bridge ends in the middle of Oresund, on an artificially built island, called Peberholm. The connection between Peberholm and the nearest populated part of Denmark is through the Drogden Tunnel. Opened in 2000
Kiruna is the northernmost town in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland. The city's vicinity shares a long history with the indigenous Sami people. The town of Kiruna is being moved as an iron ore mine undermines the current town centre
ICEHOTEL near the village of Jukkasjarvi, Kiruna is the first and most famous of the ice hotels
Visby is main town of Gotland, which is Sweden’s largest island
In 1999, the world's largest Viking silver treasure, the Spillings Hoard, was found in a field in Gotland
Vanern is the largest lake in Sweden, the largest lake in the European Union and the third largest lake entirely in Europe after Ladoga and Onega in Russia
Oland is the second largest Swedish island and the smallest of the traditional provinces of Sweden
Sweden has more than 220,000 islands
Birka on the island of Bjorko was an important Viking Age trading centre
Ytterby is a village on the island of Resaro. Four chemical elements are named after the village
Switzerland
The Swiss flag is one of only two square sovereign-state flags, the other being the flag of Vatican City
| Capital | Berne |
| Largest cities | Zurich, Geneva, Basel, Berne, Lausanne |
| Currency | Swiss franc |
| Highest point | Dufourspitze |
Officially the Swiss Confederation (Latin: Confoederatio Helvetica, hence its abbreviation CH), is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Berne as the seat of the federal authorities, the so-called Bundesstadt ("federal city")
The establishment of the Swiss Confederation is traditionally dated to 1291
Historically each canton in the then confederation was a sovereign state, with its own borders, army, and currency until the current federal structure was established in 1848
Graubunden is the largest and easternmost canton of Switzerland. Also known as Grisons
Graubunden is the only canton where Romansh, Switzerland's fourth national language, has official status
Jura is the newest of the Swiss cantons. It was created in 1979
Appenzell Innerrhoden is the smallest canton by population and the second smallest by area, with Basel-City being the smallest. It was the last Swiss canton to grant women the vote on local issues, in 1991
Switzerland has four official languages – German, French, Italian, and Romansh
Zurich has the highest population of the cantons
Zurich was known as Turicum in Roman times
Most of Zurich's sites are located within the area on either side of the Limmat river, between the Main railway station and Lake Zurich
Geneva is located at the south-western end of Lake Geneva, where the lake flows back into the Rhone River. It is surrounded by two mountain chains, the Alps and the Jura
Geneva is known as ‘The Protestant Rome’
Geneva is the headquarters of many of the agencies of the United Nations and the Red Cross
CERN is based in a suburb of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border
Palais des Nations in Geneva was built between 1929 and 1936 to serve as the headquarters of the League of Nations
Basel is on the Rhine, where the Swiss, French, and German borders meet
Basel has Switzerland’s only cargo port
Bayerler Foundation is an art museum in Riehen, near Basel
Canton of Berne is the second most populous of Switzerland's cantons
The Aare flows in a wide loop around the Old City of Berne
Lausanne is a city in Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland, and is the capital of the canton of Vaud. The city is situated on the shores of Lake Geneva
Kapellbrucke (Chapel Bridge) is a covered wooden footbridge spanning the river Reuss in Lucerne. The bridge was originally built in the 14th century
Lugano is in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest Italian-speaking city in Switzerland
Bellinzona is the capital of Ticino
Vevey is the site of the world headquarters of the food giant Nestle, founded in 1867
Suisse romande or Romandie is the area of French-speaking parts of western Switzerland
Interlaken is located between Lake Brienz to the east and Lake Thun to the west. The Aare River flows through the town connecting the lakes
Davos is the highest city in Europe
Locarno is located on the northern tip of Lake Maggiore
Vindonissa was a Roman camp in Switzerland
Charles Kuonen Suspension Bridge is the longest hanging bridge for pedestrian use in the world. It is located in Randa and opened in 2017
Lotschberg Base Tunnel is a 21.5 mile long railway tunnel cutting through the Alps of Switzerland some 400 m below the existing Lotschberg Tunnel. It is the longest land tunnel in the world
Reichenbach Falls are near Meiringen. The falls are the location where Sherlock Holmes fights to the death with Professor Moriarty
Bernese Oberland is the higher part of the canton of Berne
Eiger is near Grindelwald in the Bernese Alps
Aletsch Glacier in the Bernese Alps is the largest Alpine glacier
Lake Neuchatel is the largest lake entirely in Switzerland, as the larger Lake Geneva (Lac Leman) is shared with France, and Lake Constance (German: Bodensee) with Germany and Austria
Lake Lucerne (‘Lake of the Four Forest Cantons’) is a lake in central Switzerland, the fifth largest in the country
Jungfraubahn is a rack railway which runs 9 km from Kleine Scheidegg to the highest railway station in Europe at Jungfraujoch. The railway runs almost entirely within a tunnel built into the Eiger and Monch mountains
Jungfrau is one of the main summits in the Bernese Alps. Together with the Eiger and Monch, the Jungfrau forms a massive wall overlooking the Bernese Oberland
Jungfrau is German for maiden/virgin
Rhine Falls is the largest plain waterfall in Europe. The falls are located on the Upper Rhine near the town of Schaffhausen in northern Switzerland. Most powerful waterfall in Europe
Zermatt lies at the foot of the Matterhorn
Monte Rosa is the highest mountain in Switzerland. Its main summit is named Dufourspitze
Turkey
| Capital | Ankara |
| Largest cities | Istanbul, Ankara, Izmir, Bursa |
| Currency | Lira |
| Highest point | Mount Ararat |
Turkey is the only country to border the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, and has the longest border to the Black Sea
Istanbul is the most populous city in Europe
Istanbul straddles the Bosporus Strait, which provides the only passage from the Black Sea to the Mediterranean via the Sea of Marmara
Taksim Square is considered the heart of modern Istanbul. Taksim is Arabic for ’division’ or ‘distribution’. The Taksim square was originally the point where the main water lines from the north of Istanbul were collected and branched off to other parts of the city (hence the name)
Grand Bazaar in Istanbul is among the world's most-visited tourist attractions
Fatih Sultan Mehmet Bridge and the Eurasia Tunnel are crossings across the Bosphorus
Golden Horn is a fresh-water estuary in Istanbul dividing the city of Istanbul. Crossed by several bridges, most notably the Galata Bridge. Galata was a colony of the Republic of Genoa between 1273 and 1453
Galata Tower is a medieval stone tower in Istanbul
Ankara was historically known as Angora
Ankara has many well-preserved remains of Ottoman and Roman architecture, the most remarkable being the Temple of Augustus and Rome
Hisarlik (‘Place of Fortresses’), is the modern Turkish name for the ancient site of Troy, also known as Ilion, and is located in Turkey (known throughout history as Anatolia)
Trabzon is a city on the Black Sea coast of northeastern Turkey, located on the Silk Road
Cappadocia region is largely underlain by sedimentary rocks formed in lakes and streams, and ignimbrite deposits erupted from ancient volcanoes approximately 9 to 3 million years ago
Goreme is a town in Cappadocia, located among the ‘fairy chimney’ volcanic tuff formations. Early homes were carved straight into the rock formations
Edirne is a city in Thrace, the westernmost part of Turkey, close to the borders with Greece and Bulgaria. Edirne served as the capital city of the Ottoman Empire from 1365 to 1457, when Constantinople (Istanbul) became the empire's new capital. Founded by the Romans as Adrianople
The Selimiye Mosque in Edirne was commissioned by Sultan Selim II and was built by architect Mimar Sinan between 1568 and 1574. It was considered by Sinan to be his masterpiece and is one of the highest achievements of Islamic architecture
Sardis was an ancient city at the location of modern Sart in Turkey. Sardis was the capital of the ancient kingdom of Lydia, one of the important cities of the Persian Empire, the seat of a proconsul under the Roman Empire, and the metropolis of the province Lydia in later Roman and Byzantine times
Gobekli Tepe (‘Potbelly Hill’) is a Neolithic (stone-age) hilltop sanctuary erected at the top of a mountain ridge in southeastern Anatolia. It is the oldest known human-made religious structure. This is where modern wheat was first domesticated
Catalhoyuk (‘Fork tumulus’) was a large Neolithic and Chalcolithic settlement in southern Anatolia, which existed from approximately 7500 BC to 6400 BC. The site was first excavated by James Mellaart in 1958
Library of Celsus is an ancient Roman building in Ephesus, Anatolia, now part of Selcuk. It was built in honour of the Roman Senator Tiberius Julius Celsus Polemaeanus
The site of the temple of Artemis at Ephesus was discovered by John Turtle Wood in 1869
Batman is a Kurdish-majority city
Rize is a tea producing province in Turkey
Hatay Province is the southernmost province of Turkey. Sovereignty over the province remains disputed with neighbouring Syria
Antakya, historically known as Antioch, is the capital of Hatay Province
Bosphorus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara. It is the world's narrowest strait used for international navigation
Dardanelles connects the Aegean and Sea of Marmara. Also known as the Strait of Gallipoli or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont
1915 Canakkale Bridge, the first bridge over the Dardanelles and the world's longest suspension bridge, opened in 2022
Marmaray is an undersea rail tunnel that links the European and Asian sections of Istanbul, running under the Bosphorus strait. Completed in 2019, it is the world's deepest undersea immersed tube tunnel
Lycia was a geopolitical region in Anatolia in what are now the provinces of Antalya and Mugla on the southern coast of Turkey
Turquoise Coast is the southwest Mediterranean coast of Turkey. Also known as the Turkish Riviera
Tigris and Euphrates both rise in Turkey
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey
Taurus Mountains are in southern Turkey, dividing the Mediterranean coastal region of southern Turkey from the central Anatolian Plateau
Mount Ararat overlooks the city of Yerevan
Pontic Mountains are a mountain range in northern Anatolia
Lake Van is the largest lake in Turkey
Ceyhan is the Mediterranean terminus of the Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline which brings crude oil from the landlocked Caspian Sea
Ukraine
| Capital | Kyiv |
| Largest cities | Kyiv, Kharkiv, Odesa, Dnipro |
| Currency | Hryvna |
| Highest point | Hoverla |
Ukraine is the largest wholly European country
Ukraine’s only mountains are the Carpathian Mountains in the west
Kyiv is also known as Kiev
Kyiv is on the Dnieper river
Kyiv Pechersk Lavra, also known as the Kyiv Monastery of the Caves, is a historic Orthodox Christian monastery. Since its foundation as the cave monastery in 1015 the Lavra has been a preeminent centre of the Eastern Orthodox Christianity in Eastern Europe
St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery is in Kyiv
The largest cave in Europe, Optymistychna, is a gypsum cave in Ukraine
Donbas refers to the Donetsk and Luhansk regions
Donetsk was founded by Welsh engineer and businessman John Hughes, for the building of metal works
Donetsk Sergei Prokofiev International Airport is a former airport that was destroyed in 2014 during the war in Donbas
Odesa is also known as Odessa
Dnipro, formerly Dnipropetrovsk, is located in the eastern part of Ukraine on the Dnieper River
Pripyat is a ghost town near the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in the Kyiv Oblast of northern Ukraine, near the border with Belarus
Slavutych was built for the evacuated personnel of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant following the 1986 disaster
Duga woodpecker was an over-the-horizon radar sited near Chernobyl
Lviv was previously known as Lemberg and Lwow. It has been occupied by Poland, Germany, and the Soviet Union
Crimea has a large Tatar population
Simferopol is the capital of Crimea
Sevastopol is the largest city of Crimea
Livadia Palace was a summer retreat of the last Russian tsar, Nicholas II, and his family in Livadiya, in Crimea. The Yalta Conference was held there in 1945, when the palace housed the apartments of Franklin Delano Roosevelt and other members of the American delegation
Isthmus of Perekop connects Crimea to the mainland of Ukraine
Crimean Bridge, also called Kerch Strait Bridge or Kerch Bridge, is a pair of parallel bridges, one for a four-lane road and one for a double-track railway, spanning the Kerch Strait between Krasnodar Krai in Russia and the Kerch Peninsula of Crimea. Built by the Russian Federation after the annexation of Crimea at the start of 2014, the bridge cost has a length of 19 km, making it the longest bridge in Europe
United Kingdom
Flag of United Kingdom consists of the red cross of Saint George, superimposed on the Cross of St Patrick, which are superimposed on the Saltire of Saint Andrew
| Capital | London |
| Largest cities | London, Birmingham, Manchester, Leeds, Glasgow |
| Currency | Pound |
| Highest point | Ben Nevis |
For further information see British Isles Geography
Gibraltar
Flag of Gibraltar is unique as it is the only British Overseas Territory which does not feature the Union Jack
Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory. The United Kingdom considers Gibraltar to be under its sovereignty, but not as part of the United Kingdom itself
Gibraltar was awarded city status in 2022
Strait of Gibraltar is 13 km wide
Gibraltar has been ruled by Britain since 1704. It was named ‘Jebel Tarik’ by Moorish settlers
The Rock of Gibraltar is a monolithic limestone promontory. It is one of the two traditional Pillars of Hercules
Europa Point is a lighthouse in Gibraltar
Gorham's Cave is a natural sea cave in Gibraltar, and is considered to be one of the last known habitations of the Neanderthals c. 25,000 years ago
North Front airport serves Gibraltar
GX11 1AA is the postcode for Gibraltar
The Barbary macaque population in Gibraltar is the only wild monkey population on the European continent
Vatican City
Flag of Vatican City is a yellow and white square. On the white area is surmounted the Papal crown and two crossed keys, which represent the keys to the Kingdom of Heaven
| Capital | Vatican City |
| Largest cities | Vatican City |
| Currency | Euro |
| Highest point | Vatican Hill |
Vatican City is a walled enclave within the city of Rome. With an area of approximately 44 hectares (110 acres), and a population of around 450, it is the smallest internationally recognized independent state in the world by both area and population
The name ‘Vatican’ predates Christianity and comes from the Latin Mons Vaticanus, meaning Vatican Mount
Vatican City is one of a few widely recognized independent states that has not become a member of the United Nations. The Holy See, which is distinct from Vatican City State, has permanent observer status
Sistine Chapel is in the Apostolic Palace, the official residence of the Pope. Originally known as the Cappella Magna, the chapel takes its name from Pope Sixtus IV, who restored it between 1477 and 1480. There are five sibyls on the roof of the Sistine Chapel
St. Peter's Basilica is a Late Renaissance church located within Vatican City. It is the largest church in the world. Designed principally by Donato Bramante, Michelangelo, Carlo Maderno and Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Saint Peter's Square is a large plaza located directly in front of St. Peter's Basilica. At the centre of the square is an ancient Egyptian obelisk
Belvedere Torso is a marble fragment of a nude male statue, signed prominently on the front of the base by "Apollonios, son of Nestor, Athenian", who is unmentioned in ancient literature. It is now in the Vatican Museums
States with limited recognition
Abkhazia
Abkhazia considers itself an independent state, called the Republic of Abkhazia. The Georgian government, United Nations and the majority of the world's governments consider Abkhazia a part of Georgia's territory, though Georgia is not in control of it. Sukhumi is the capital
Artsakh
Artsakh (formerly known as the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic) declared its independence in 1991. It is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus supported by Armenia, whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan
In September 2020, fighting broke out between Armenia and Azerbaijan over Artsakh. Azerbaijan recaptured territories, primarily in the southern part of the region. A ceasefire agreement signed in November 2020 between Armenia, Azerbaijan and Russia declared an end to the renewed fighting, and established that Armenia would withdraw from remaining occupied territories surrounding the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast over the next month, while maintaining control over the areas of the former oblast that had not been captured during the war
Stepanakert is the capital and the largest city
Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus is a self-declared state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Recognised only by Turkey, Northern Cyprus is considered by the international community as part of the Republic of Cyprus
Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic, is landlocked and borders Moldova to the west and Ukraine to the east. It is a narrow valley stretched in the north-south direction along the banks of the Dniester River
Transnistria is designated by the Republic of Moldova as the Transnistria autonomous territorial unit with special legal status. The capital and largest city is Tiraspol
South Ossetia
South Ossetia declared independence from Georgia in 1990, calling itself the Republic of South Ossetia. The Georgian government responded by abolishing South Ossetia's autonomy and trying to re-establish its control over the region by force. The crisis escalation led to the 1991–92 South Ossetia War. The capital is Tskhinvali
South Ossetia is officially the Republic of South Ossetia or the State of Alania
Physical Geography
Regions
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west. This was the name by which Imperial Russia designated the eastern part of the Principality of Moldavia. Part of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Ukraine
Cerdanya, or Cerdagne, is a historical region of the eastern Pyrenees divided between France and Spain
Galicia is currently divided between Poland and Ukraine, and was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Jutland forms the mainland part of Denmark, and the German state of Schleswig-Holstein
Karelia is currently divided between the Russian Republic of Karelia, the Russian Leningrad Oblast, and Finland (the regions of South Karelia and North Karelia)
Livonia is a historic region along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. Currently split between Estonia and Latvia
Lusatia is a historical region in Central Europe, today located within the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg, and Poland
Macaronesia consists of Azores, Madeira Islands, Canary Islands, and Cape Verde Islands
Pomerania is located on the south coast of the Baltic Sea, divided today between Germany in the west and Poland in the east by the Polish-German border. Pomerania stretches roughly from Stralsund in the west to Gdansk in the east, centered on the Oder River delta
Mountains
The highest mountain in Europe is Mount Elbrus, with a summit of 5,642 m. It is located in Russia and it the highest peak of the Caucasus Mountains
Dykh-Tau is the second highest of the Caucasus Mountains, after Mount Elbrus, and is the second highest peak in Europe
Caucasus Mountains stretch from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea
Tatra Mountains form a natural border between Slovakia and Poland. They are the highest mountain range in the Carpathian Mountains
The Urals run north-south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan. They are usually considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia. Mount Narodnaya is the highest peak of the Urals
Jura Mountains are a small mountain range located north of the Alps, separating the Rhine and Rhone rivers and forming part of the watershed of each. The mountain range is located in France, Switzerland, and Germany. Cret de la Neige is the highest mountain in the Jura Mountains
Pindus mountain range is located in northern Greece and southern Albania. Mount Smolikas is the highest of the Pindus Mountains, and the second highest mountain in Greece after Mount Olympus
Dinaric Alps are between Croatia and Albania
Matterhorn (German), Cervino (Italian) or Cervin (French), is a mountain in Switzerland and Italy and is one of the highest peaks in the Alps
Mont Blanc is the highest mountain in the Alps and the highest peak in Europe outside of the Caucasus range. It rises 4,810 m above sea level, lying on the border between France and Italy. It was part of the Duchy of Savoy between 1416 and 1792
Rhodopes are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, with over 83% of its area in southern Bulgaria and the remainder in Greece
Balkan Mountains are mainly in Bulgaria, but also cover part of Serbia. Botev Peak is the highest mountain
Cantabrian Mountains stretch for over 300 km across northern Spain
Vosges are a range of mountains in eastern France. The highest peak is Grand Ballon
Julian Alps stretch from north-eastern Italy to Slovenia, where they rise to 2864 metres at Triglav. They are named after Julius Caesar and are part of the Southern Limestone Alps
Pyrenees is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. The highest point is Aneto, in the Spanish region of Aragon
Alpine Tunnels
Mont Blanc Tunnel links Chamonix, Haute-Savoie, France with Courmayeur, Aosta Valley, Italy. Opened in 1965
Gotthard Tunnel is a railway tunnel and forms the summit of the Gotthard Railway in Switzerland. Opened in 1882
Gotthard Road Tunnel runs from Goschenen in the canton of Uri at its northern portal, to Airolo in Ticino to the south. At time of construction, in 1980, it was the longest road tunnel in the world
Gotthard Base Tunnel opened in 2016. With a route length of 57 km it is the world's longest railway and deepest traffic tunnel
Simplon Tunnel is a railway tunnel on the Simplon railway that connects Brig, Switzerland and Domodossola, Italy, through the Alps. East tunnel opened in 1906. West tunnel opened in 1921
Frejus Rail Tunnel links Bardonecchia in Italy to Modane in France under Col du Frejus. Opened in 1871
Frejus Road Tunnel opened in 1980
Lotschberg Base Tunnel is a 34 km railway base tunnel cutting through the Bernese Alps of Switzerland
Rivers
Longest rivers in Europe – Volga, Danube, Ural, Dnieper, Don
Danube flows from the Black Forest into the Black Sea, and connects 10 countries
Capital cities that lie on the Danube – Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bratislava
Sava is a tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia, along the northern border of Bosnia and Herzegovina, through Serbia, discharging into the Danube in Belgrade
Iron Gates is a gorge on the Danube River. It forms part of the boundary between Romania and Serbia. The tallest rock sculpture in Europe, a 42.9 m carving in rock of the face of Decebalus, is a sculpture of the last king of Dacia on a rocky outcrop near the Iron Gates
Ural river rises in the southern Ural Mountains and ends at the Caspian Sea. Its total length is 1511 miles making it the third longest river in Europe after the Volga and the Danube
Dnieper flows from Russia, through Belarus and Ukraine (including Kyiv), to the Black Sea
Rhone rises in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Arles, near its mouth, the river divides into the Great Rhone and the Little Rhone. The resulting delta forms the Camargue region
Rhine rises in the Swiss canton of Graubunden, and flows through Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, France, and Netherlands where it empties into the North Sea. It is the second longest river in Central and Western Europe, after the Danube. Vaduz is the only capital city that lies on the Rhine
Meuse rises in France and flows through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea. The Meuse is one of the oldest rivers in the world
Tagus is the longest river on the Iberian Peninsula. It is 1,038 km long, 716 km in Spain, 47 km along the border between Portugal and Spain and 275 km in Portugal, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean near Lisbon
Douro flows from its source near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province across northern-central Spain and Portugal to its outlet at Porto. It is the third-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula after the Tagus and Ebro
Daugava rises in Russia and drains into the Gulf of Riga in Latvia
Garonne flows from the central Spanish Pyrenees to the Gironde estuary at the French port of Bordeaux
Lakes
Lake Maggiore is the second largest lake of Italy and largest of southern Switzerland. It is divided between the Italian regions of Piedmont and Lombardy and the Swiss canton of Ticino. The Borromean Islands and Brissago Islands are located in Lake Maggiore
Lake Lugano is a glacial lake which is situated on the border between southern Switzerland and northern Italy. The lake, named after the city of Lugano, is situated between Lake Como and Lake Maggiore
Lake Constance (German: Bodensee) is a lake on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps, and consists of three bodies of water: the Obersee (‘upper lake’), the Untersee (‘lower lake’), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Seerhein. The lake is situated in Germany, Switzerland and Austria
Lake Geneva (Lac Leman) is the largest alpine lake, and lies on the border between France and Switzerland
Lake Ohrid straddles the mountainous border between North Macedonia and Albania. It is one of Europe's deepest and oldest lakes
Lake Peipus is the biggest transboundary lake in Europe and lies on the border between Estonia and Russia
Lake Sevan is the largest body of water in Armenia and the Caucasus region
Lake Skadar is the largest lake in the Balkans. It lies on the border of Albania and Montenegro
Lake Prespa is located on the tripoint of North Macedonia, Albania, and Greece
Seas
Baltic Sea is the world’s largest pool of brackish water
Gulf of Bothnia is the northernmost arm of the Baltic Sea, between Finland's west coast and Sweden's east coast. The Finnish region of Aland lies in the south of the gulf
Gulf of Riga and Gulf of Finland are inlets of theBaltic Sea
Usedom is a Baltic Sea island that since 1945 has been split between Germany and Poland
Market is an uninhabited island in the Baltic Sea divided between Sweden and Finland
Skagerrak is a strait running between the southeast coast of Norway, the southwest coast of Sweden, and the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area, which leads to the Baltic Sea
Kattegat separates Sweden and Denmark, and is a continuation of the Skagerrak
Denmark Strait separates Iceland and Greenland
Barents Sea is located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia
Bering Strait is 53 miles across at the narrowest point
Chukchi Sea lies north of the Bering Strait
Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean off the coast of Siberia
Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia, between the Barents Sea and the Laptev Sea
North Sea was known as the German Sea
Graeco-Roman tradition refers to the Black Sea as the ‘Hospitable Sea’
Sea of Azov is a northern section of the Black Sea, linked to the larger body through the Strait of Kerch. It is bounded on the north by Ukraine, on the east by Russia and on the west by the Crimean Peninsula
Caspian Sea borders Russia, Iran and Azerbaijan. It is the is the world's largest inland body of water
Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Apennine peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges
Istria is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner. Istria lies in three countries: Croatia, Slovenia and Italy
Aegean Sea is a sea arm of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey respectively. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus
Ionian Sea is connected to the Tyrrhenian Sea by the Strait of Messina, and to the Adriatic Sea by the Strait of Otranto
Calypso Deep, located in the Ionian Sea south-west of Pylos, Greece, is the deepest part of the Mediterranean Sea. At the Calypso Deep, the African Plate slides under the Eurasian Plate, creating the Hellenic Trench
Strait of Otranto separates Italy from Corfu and Albania
Strait of Sicily lies between Sicily and Tunisia
Alboran Sea is the westernmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, lying between the Iberian Peninsula and the north of Africa. Alboran Island is a small islet of Spain in the Alboran Sea