Civilisation/World Geography - North America
United States
Flag of United States contains 13 stripes representing the Thirteen Colonies and 50 stars representing the 50 states. Known as the Stars and Stripes, the Star-Spangled Banner, and Old Glory
| Capital | Washington, D.C. |
| Largest cities | New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, Phoenix |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Denali (Mount McKinley) |
The United States is the world's fourth-largest country by total area and third most populous (320 million). The U.S. population almost quadrupled during the 20th century, from about 76 million in 1900
In 1507, the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller produced a world map on which he named the lands of the Western Hemisphere "America" after the Italian explorer and cartographer Amerigo Vespucci
Largest states by area – Alaska, Texas, California, Montana, New Mexico
Smallest states by area – Rhode Island, Delaware, Connecticut, New Jersey, New Hampshire
Largest states by population – California, Texas, Florida, New York, Illinois
Smallest states by population – Wyoming, Vermont, Alaska, North Dakota, South Dakota
The 49th parallel of north latitude forms part of the international boundary between Canada and the United States from Manitoba to British Columbia on the Canadian side and from Minnesota to Washington on the U.S. side. Its use as a border is a result of the Anglo-American Convention of 1818 and the Oregon Treaty of 1846
Alabama (AL)
Capital – Montgomery
Largest city – Huntsville
Nickname – Heart of Dixie, Cotton State, Yellowhammer State
Birmingham is Alabama's second-most populous city after Huntsville. The broader Birmingham metropolitan area us largest metropolitan area in Alabama
Mobile was founded in 1702 by the French as the first capital of Louisiana
Muscle Shoals Sound Studio is in Sheffield
Alaska (AK)
Capital – Juneau
Largest city – Anchorage
Nickname – The Last Frontier, Land of the Midnight Sun
Alaska time zone is UTC-09:00
Alaska is the least densely populated state
Alaska has longest coastline in USA
Alaska has boroughs, not counties
Juneau cannot be reached by car
Barrow is the northernmost settlement on the North American mainland and in the United States. Nearby Point Barrow is the northernmost point of the United States. Barrow is now known as Utqiagvik
Disenchantment Bay is in Alaska
Alexander Archipelago is in Alaska
Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve is in Alaska
Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes is a valley within Katmai National Park and Preserve in Alaska which is filled with ash flow from the eruption of Novarupta in 1912
Cape Prince of Wales is the westernmost mainland point of the Americas
Little Diomede or “Yesterday Isle” is the smaller of the two Diomede Islands located in the middle of the Bering Strait between the Alaska mainland and Siberia. Big Diomede Island is part of Russia and west of the International Date Line
Sitka is the largest city-borough by total area in the United States
Fairbanks is the second most populous metropolitan area
Tongass National Forest is the largest U.S. National Forest
Attu is the westernmost and largest island in the Near Islands group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, and the westernmost point of land relative to Alaska. The island is currently uninhabited. The island was the site of the only World War II land battle fought on an incorporated territory of the United States
Unalaska is an island in the Fox Islands group of the Aleutian Islands
Yakutat City is the largest city by area in USA
Mount Aniakchak is a volcanic caldera located in the Aleutian Range
Kodiak Island is the second largest island in USA, behind Big Island, Hawaii
Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race is an annual long-distance sled dog race run in March from Anchorage to Nome
Alaska Highway was constructed as an emergency supply route in WWII and connects the contiguous U.S. to Alaska through Canada. It runs from Dawson Creek, British Columbia to Faribanks, Alaska. Completed in 1943, it is 1,390 miles long
Dalton Highway is a 414-mile road in Alaska. It begins at the Elliott Highway, north of Fairbanks, and ends at Deadhorse near the Arctic Ocean and the Prudhoe Bay oil fields
Chilkoot Trail leads from Dyea, Alaska, to Bennett, British Columbia. It is part of Klondike Gold Rush National Historical Park in the United States. It was a major access route from the coast to Yukon goldfields in the late 1890s
Arizona (AZ)
Capital and largest city – Phoenix
Nickname – Grand Canyon State, Apache State
Phoenix is the largest city which is also a state capital
Hoover Dam, once known as Boulder Dam, is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between Arizona and Nevada. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 and designed by Frank Crowe. Produces hydroelectric power. Hoover Dam impounds Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the United States by volume
The Grand Canyon is a canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona. The Grand Canyon is 446 km long, up to 29 km wide and attains a depth of over a mile. The thick sequence of ancient rocks that are well preserved and exposed in the walls of the canyon record much of the early geologic history of the North American continent
Painted Desert is composed of stratified layers of easily erodible siltstone, mudstone, and shale. These fine-grained rock layers contain abundant iron and manganese compounds which provide the pigments for the various colours of the region
The Wave is a spectacular sandstone formation on the slopes of the Coyote Buttes in the Paria Canyon-Vermilion Cliffs Wilderness Area
Meteor crater was created about 50,000 years ago. The object that excavated the crater was a nickel-iron meteorite about 50 m across. Scientists refer to the crater as Barringer Crater in honour of Daniel Barringer who was first to suggest that it was produced by meteorite impact
Petrified Forest National Park is named for its large deposits of petrified wood
London Bridge in Lake Havasu City is the reconstruction of the 1831 London Bridge designed by John Rennie until it was dismantled in 1967. The bridge was bought by Robert P. McCulloch from the City of London
O.K. Corral (Old Kindersley) was originally from 1879 to about 1888 a livery and horse corral in the mining boomtown of Tombstone
Maricopa County is the fourth-most populous county in the United States
Canyon de Chelly National Monument preserves ruins of the indigenous tribes that lived in the area, from the Ancestral Puebloans (also known as the Anasazi) to the Navajo
Arkansas (AR)
Capital and largest city – Little Rock
Nickname – The Natural State, Bear State, Land of Opportunity
Mississippi River forms most of the eastern border of Arkansas
Hot Springs National Park is in Arkansas
California (CA)
Capital – Sacramento
Largest cities – Los Angeles, San Diego, San Jose, San Francisco
Nickname – The Golden State
Los Angeles is known as the ‘City of Angels’ and the ‘Big Orange’
The Hollywood sign originally read ‘HOLLYWOODLAND’, and its purpose was to advertise a new housing development
Sunset Strip is the name given to the 2.4 km stretch of Sunset Boulevard that passes through West Hollywood
Whisky a Go Go is a nightclub on the Sunset Strip
Los Angeles Aqueduct system comprising the Los Angeles Aqueduct (Owens Valley aqueduct) and the Second Los Angeles Aqueduct delivers water from the Owens River in the Eastern Sierra Nevada Mountains into the city of Los Angeles. Designed by William Mulholland. Completed in 1913
St. Francis Dam was a gravity dam built as a large reservoir near the city of Los Angeles. The dam was built between 1924 and 1926 under the supervision of William Mulholland, an engineer for the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. In 1928, the dam catastrophically failed
La Brea Tar Pits are a cluster of tar pits located in Hancock Park in the urban heart of Los Angeles. Over many centuries, animals that came to drink the water fell in, sank in the tar, and were preserved as bones. The George C. Page Museum is dedicated to researching the tar pits and displaying specimens from the animals that died there
John Wayne airport is in Orange County
Santa Ana is in Orange County
John Paul Getty museum is in Malibu
San Francisco cable cars are the world’s only mobile National Monument. Started operation in 1873
Fisherman's Wharf is a popular tourist attraction
The Immigration Station on Angel Island in San Francisco Bay processed approximately one million Asian immigrants and has been designated a National Historic Landmark
Alcatraz Island is 2 km offshore from San Francisco. In 1934, the island was converted into a federal prison. The strong currents around the island and cold water temperatures made escape all but impossible. The prison closed in 1963, and the island is now a major tourist attraction
Marin County is across the Golden Gate Bridge from San Francisco. Natural sites include the Muir Woods redwood forest, the Marin Headlands, Stinson Beach, the Point Reyes National Seashore, and Mount Tamalpais
Napa Valley and Sonoma Valley are part of the Wine Country in the northern San Francisco Bay Area
Farallon Islands are a group of islands off the coast of San Francisco. The islands are also sometimes referred to by mariners as the Devil's Teeth Islands, in reference to the many treacherous underwater shoals in their vicinity
San Diego has one of the world’s largest zoos
San Diego International Airport is on the site of a municipal airport named Lindbergh Field
San Jose is the county seat of Santa Clara County
John Sutter founded the city of Sacramento, first naming it New Helvetia, the ancient name of Switzerland
Neverland, formerly the Sycamore Valley Ranch, is in Santa Barbara County
Gilroy Garlic Festival is held annually in July
Lassen Volcanic National Park is in central northern California. The dominant feature of the park is Lassen Peak; the largest plug dome volcano in the world and the southern-most volcano in the Cascade Range. Lassen Volcanic National Park started as two separate national monuments designated by President Theodore Roosevelt in 1907: Cinder Cone National Monument and Lassen Peak National Monument
Yosemite National Park covers an area of 3,074 km2. It was Designated a World Heritage Site in 1984
El Capitan is a 1000 m vertical rock formation in Yosemite National Park, located on the north side of Yosemite Valley, near its western end. The granite monolith is one of the world's favourite challenges for rock climbers. The Nose is a climbing route up El Capitan
Mono Lake contains bacteria that grow in high concentrations of arsenic
Sutter Buttes in California are sometimes referred to as the world's smallest mountain range
San Bernardino County is the largest county in the contiguous United States by area
El Camino Real is a 600-mile road connecting the 21 Spanish missions in California
Zabriskie Point is in Death Valley National Park
Death Valley is the largest national park south of Alaska
Furnace Creek holds the record for the highest recorded air temperature on Earth at 134 °F (56.7 °C)
Telescope Peak is the highest point in Death Valley National Park
Joshua Tree National Park is named after the Joshua trees native to the Mojave Desert. Originally declared a national monument in 1936, Joshua Tree was redesignated as a national park in 1994
Sequoia National Park is in the southern Sierra Nevada. It contains giant sequoia trees, including the General Sherman tree, the largest tree on Earth
Salton Sea is the largest lake in California. It is a saline endorheic lake that is heavily polluted
Santa Cruz is the largest of the Californian Channel Islands
Colorado (CO)
Capital and largest city – Denver
Nickname – Centennial State
Colorado is known as the Centennial state because it was admitted to the Union in 1876
Denver International Airport has four murals, all of which have been the topic of conspiracy theorists and debate, and popularized in ‘Family Guy’
Mount Elbert is highest mountain in Rockies
Mesa Verde National Park is a U.S. National Park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado. The park features numerous ruins of homes and villages built by the ancient Pueblo people known as the Anasazi. The Anasazi made this stone village their home in the 1200s, before being killed off by drought in 13th century
Pikes Peak in the Rocky Mountains is higher than any point in the United States east of its longitude. ‘Pike's Peak or Bust’ became the slogan of the Colorado Gold Rush
Colorado River was known as the Grand River until 1921
Colorado River drains into the Gulf of California
Connecticut (CT)
Capital – Hartford
Largest city – Bridgeport
Nickname – Constitution State, Nutmeg State
Dinosaur State Park and Arboretum is in Connecticut
Delaware (DE)
Flag of Delaware has the date 7 December 1787, the day on which Delaware became the first state to ratify the United States Constitution
Capital – Dover
Largest city – Wilmington
Nickname – The First State, Diamond State
Delaware is divided into three counties, named New Castle, Kent, and Sussex
Delaware was a Dutch colony
Delaware is considered a corporate haven because of its business-friendly corporate laws. More than half of all U.S. publicly traded companies, and 63% of the Fortune 500, are incorporated in Delaware
Delaware Bay is bordered by Delaware and New Jersey
Delmarva is a large peninsula occupied by most of Delaware as well as the Eastern Shore of Maryland and the Eastern Shore of Virginia
Florida (FL)
Capital – Tallahassee
Largest city – Jacksonville
Nickname – Sunshine State, Peninsula State
Miami has the largest collection of Art Deco architecture in the world
Miami is built on a bedrock of limestone
St. Petersburg is the second largest city in the Tampa Bay Area
Orlando is nicknamed ‘The City Beautiful’ and its symbol is the fountain at Lake Eola
Orlando attracts over 75 million tourists a year
St. Augustine is the oldest continuously occupied European-established city, and the oldest port, in the continental United States
Fort Lauderdale is known as the ‘Venice of America’
Lake Okeechobee is the largest freshwater lake in Florida
Sunshine Skyway Bridge was destroyed in 1980 when hit by a ship
Three counties in the Tampa region are known as ‘sinkhole alley’
Florida's peninsula is made up of porous carbonate rocks such as limestone that store and help move groundwater. Dirt, sand and clay sit on top of the carbonate rock. Over time, these rocks can dissolve from an acid created from oxygen in water, creating a void underneath the limestone roof. When the dirt, clay or sand gets too heavy for the limestone roof, it can collapse and form a sinkhole
Mar-a-Lago is a resort in Palm Beach
The northern end of the Biscayne Bay lagoon is surrounded by Downtown Miami
Pensacola is the westernmost city of the Florida panhandle. Pensacola beach is known for its white sand beaches
Florida Keys are a coral cay archipelago forming the southernmost part of the continental United States
Key West is the westernmost island connected by U.S. Highway 1 and is 95 miles from Cuba
Key Largo calls itself the ‘Diving Capital of the World’
Straits of Florida are between Florida Keys and Cuba
Everglades is a natural region of tropical wetlands in the southern portion of Florida. The primary feature of the Everglades is the sawgrass marsh
Florida is the US state most affected by lightning
Georgia (GA)
Capital and largest city – Atlanta
Nickname – Peach State, Empire State of the South
Peachtree Street is the main north-south Street of Atlanta
Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport has been the world's busiest airport by passenger traffic since 1998
Macon is known as the ‘Heart of Georgia’
Stone Mountain is a quartz dome monadnock. Stone Mountain is well-known not only for its geology, but also for the enormous bas-relief on its north face, the largest bas-relief in the world. Three figures of the Confederate States of America are carved there: Stonewall Jackson, Robert E. Lee, and Jefferson Davis. Sculped by Gutzon Borglum
Savannah was the first state capital of Georgia
Savannah River forms most of the border between the states of South Carolina and Georgia
Okefenokee Swamp is a shallow 1770 km² peat-filled wetland straddling the Georgia–Florida border. Okefenokee is the largest "blackwater" swamp in North America
Hawaii (HI)
Capital and largest city – Honolulu
Nickname – Aloha State
Hawaii-Aleutian time zone is UTC-10:00
‘Iolani Palace was the royal residence of the rulers of the Kingdom of Hawaii ending with Queen Liliʻuokalani in 1893
Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands
Pearl Harbour and Honolulu are on the island of Oahu
Mauna Kea (‘white mountain’) is taller than Everest when measured from its base; it rises over 10,203 m when measured from its base on the mid-ocean floor, but only attains 4205 m above sea level
Mauna Kea observatory is on Hawaii
Hawaiian Volcano Observatory is a volcano observatory located at Uwekahuna Bluff on the rim of Kilauea Caldera on the Island of Hawaii
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park encompasses two active volcanoes: Kilauea, one of the world's most active volcanoes, and Mauna Loa, the world's most massive volcano
Mount Kilauea emits large quantities of sulphur dioxide
Hilo is the main town on the island of Hawaii, also called the Big Island
Kauai is the oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands
Lanai is the sixth-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is also known as the Pineapple Island
The Hawaiian Islands were (and continue to be) continuously formed from volcanic activity initiated at an undersea magma source called a hotspot. As the tectonic plate beneath much of the Pacific Ocean moves to the northwest, the hot spot remains stationary, slowly creating new volcanoes
Haleakala is a massive shield volcano that forms more than 75% of the island of Maui
Niihau is an island in Hawaii known as ‘The Forbidden Isle’ as it is privately owned
Idaho (ID)
Capital and largest city – Boise
Nickname – Gem State, Gem of the Mountains
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve is a national monument and national preserve located in the Snake River Plain in central Idaho
Illinois (IL)
Capital – Springfield
Largest city – Chicago
Nickname – Prairie State
Fort Dearborn, named in honour of Henry Dearborn, was a United States fort built on the Chicago River in 1803 by troops under Captain John Whistler. The site of the fort is now a Chicago Landmark, part of the Michigan–Wacker Historic District
Chicago is called the ‘windy city’ due to politicians being full of hot air
O’Hare airport in Chicago has the code ORD, as it was previously known as Orchard Field
LaSalle Street is a major street in Chicago named for Sieur de La Salle, an early explorer of Illinois. The portion that runs through the Chicago Loop is considered to be Chicago's financial district
Chicago Midway Airport honours the Battle of Midway
Taste of Chicago (also known locally as The Taste) is the world's largest food festival, held for five days in July
Museum of Science and Industry is housed in the former Palace of Fine Arts
Chicago "L" (short for "elevated") is the rapid transit system serving the city of Chicago
Navy Pier is a 3,300’ long pier on the Chicago shoreline of Lake Michigan
In 1900 the flow of the Chicago River was reversed using a series of canal locks, increasing the river's flow from Lake Michigan and causing it to empty into the newly completed Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal
Oak Ridge Cemetery in Springfield contains Abraham Lincoln’s tomb
Indiana (IN)
Capital and largest city – Indianapolis
Nickname – Hoosier State
Indiana received its name because the state was largely possessed by native tribes even after it was granted statehood
Fort Wayne is the second largest city in Indiana
Iowa (IA)
Capital and largest city – Des Moines
Nickname – Hawkeye State
During the 18th and early 19th centuries, Iowa was a part of French Louisiana and Spanish Louisiana; its state flag is patterned after the flag of France
Maharishi Vedic City is a city in Jefferson County, Iowa
Kansas (KS)
Capital – Topeka
Largest city – Wichita
Nickname – Sunflower State
Lebanon is the centre of the 48 contiguous states
Boot Hill Museum is in Dodge City
Kentucky (KY)
Capital – Frankfort
Largest city – Louisville
Nickname – Bluegrass State
The Bethlehem, Kentucky post office offers a special postmark during the Christmas season
Mammoth Cave National Park encompasses portions of Mammoth Cave, the longest cave system known in the world
Louisiana (LA)
Capital – Baton Rouge
Largest city – New Orleans
Nickname – Pelican State, Bayou State, Creole State
Louisiana is the only state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties
New Orleans is known as “crescent city”, alluding to the course of the Lower Mississippi River through the city, and “The Big Easy”. It is named after the Duke of Orleans, who reigned as Regent for Louis XV
Bourbon Street is a historic street in the heart of the French Quarter of New Orleans. It is famous for its many bars and strip clubs
Basin Street is a street in New Orleans with many music venues
Louis Armstrong airport serves New Orleans
Storyville was the red-light district of New Orleans from 1897 to 1917
New Orleans was catastrophically affected by Hurricane Katrina in 2005
Lake Pontchartrain Causeway is the longest continuous bridge over water
Angola Penitentiary is the State Penitentiary in Louisiana, the largest prison in the US, housing 5,000 inmates, and was set up by Isaac Franklin with profits from slave trading
Maine (ME)
Capital – Augusta
Largest city – Portland
Nickname – Pine Tree State, Vacationland
Maine is the lobster capital of the United States
Hundred-Mile Wilderness is a section of the Appalachian Trail
Mount Katahdin is the highest mountain in Maine
Portland was the former capital of Maine
Maine is the only US state that borders only one other state, having a border with New Hampshire
Maryland (MD)
Flag of Maryland consists of the heraldic banner of George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore. It is the only state flag in the United States to be based on English heraldry
Capital – Annapolis
Largest city – Baltimore
Nickname – Free State, Old Line State
Goddard Space Flight Centre was established in 1959
Mallows Bay in Maryland is regarded as the "largest shipwreck fleet in the Western Hemisphere”
Camp David received its present name from Dwight D. Eisenhower, in honour of his father and grandson, both named David. Camp David is officially known as the Naval Support Facility Thurmont
Maryland was named in honour of Henrietta Maria of France, wife of Charles I
Massachusetts (MA)
Capital and largest city – Boston
Nickname – The Bay State, Old Colony State
Boston is known as the ‘Athens of the Americas’
Boston has the oldest subway system in US, operational from 1897
Breed's Hill is a glacial drumlin located in the Charlestown section of Boston. It is best known as the location where in 1775, early in the American Revolutionary War, most of the fighting in the Battle of Bunker Hill took place
Charles River flows for 80 miles through Massachusetts before emptying into Boston Harbour
Michigan (MI)
Capital – Lansing
Largest city – Detroit
Nickname – The Great Lakes State, The Wolverine State
Detroit was founded by Antoine Cadillac in 1701
Highland Park Ford Plant in Detroit was designed by Albert Kahn in 1908 and was opened in 1910
Davison freeway in Detroit was the first US freeway
Kalamazoo is in Michigan
Grand Rapids, Michigan was first town to have fluoride added to the water supply
Ambassador Bridge connects Detroit with Windsor, Ontario. It is the busiest international border crossing in North America in terms of trade volume, carrying more than 25% of all merchandise trade between the United States and Canada
Marquette is the largest city in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan and is a major port
The State of Superior is a proposed ‘51st state’ that would be created by the secession of the Upper Peninsula from the rest of Michigan
Minnesota (MN)
In May 2024 Minnesota adopted a new flag, replacing the 1983 flag
Capital – St. Paul
Largest city – Minneapolis
Nickname – Land of 10,000 Lakes, North Star State, Gopher State
Lake Itasca is a small glacial lake in Minnesota. It is the source of the Mississippi River
Minnesota contains the most northerly point of the 48 contiguous states. Northwest Angle in Minnesota is the only part of the 48 contiguous states north of the 49th parallel. The land area of the Angle is separated from the rest of Minnesota by Lake of the Woods, but shares a land border with Canada
Mall of America is located in Bloomington, Minnesota. Opened in 1992, it is the largest shopping mall in the western hemisphere
Duluth is located on Lake Superior and is a hub for cargo shipping
Winona is a town in Minnesota
Mississippi (MS)
Flag of Mississippi was adopted on 11 January 2021. It replaces the previous flag that displayed the Confederate battle insignia in the upper left hand corner
Capital and largest city – Jackson
Nickname – Magnolia State
Mississippi has the lowest per-capita income in the United States
Tupelo is in Mississippi
Missouri (MO)
Capital – Jefferson City
Largest city – Kansas City
Nickname – Show-Me State
St. Louis is named after Louis IX of France
The Gateway Arch in St. Louis was designed by Eero Saarinen. It opened to the public in 1967
Independence in Missouri is known as the ‘Queen City of the Trails’ because it was a point of departure of the California, Oregon and Santa Fe Trails. Independence is also noted as the hometown of President Harry S. Truman
Big Spring is one of the largest springs in the United States. It rises at the base of a bluff on the west side of the Current River valley in the Missouri Ozarks
Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (c. 600–1400) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis. Monks Mound is the largest structure and central focus of the city
Montana (MT)
Capital – Helena
Largest city – Billings
Nickname – Treasure State
Glacier National Park is on the border with the Canadian provinces of Alberta and British Columbia. The park encompasses over 1 million acres (4,000 km2)
Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago
Egg Mountain is a dinosaur site in Montana. Findings demonstrated for the first time that at least some dinosaurs cared for their young
Nebraska (NE)
Capital – Lincoln
Largest city – Omaha
Nickname – Cornhusker State, Beef State, Tree Planters State
Carhenge is a replica of Stonehenge located near the city of Alliance, Nebraska on the High Plains. Carhenge is formed from vintage American automobiles, all covered with gray spray paint. Built by Jim Reinders
Nebraska is the only triply landlocked state
Nevada (NV)
Capital – Carson City
Largest city – Las Vegas
Nickname – Silver State, Sagebrush State, Battle Born State
Las Vegas (Spanish for ‘The Meadows’) lies within the Mojave Desert. It has over 2.9 million visitors a year
‘Welcome to Las Vegas’ sign was created by Betty Willis in 1959
Paradise is an unincorporated town that contains Harry Reid International Airport, most of the Las Vegas Strip, and most of the tourist attractions in the Las Vegas area (excluding downtown)
Boulder City was originally built in 1931 as housing for workers who were building Hoover Dam
Carson City was named after frontiersman Kit Carson
New Hampshire (NH)
Capital – Concord
Largest city – Manchester
Nickname – Granite State
”Live Free or Die” is the motto of New Hampshire
Bretton Woods is in New Hampshire
Dixville Notch is a village in New Hampshire. The population of the township, all of whom live in the village, was 4 at the 2020 census. The village is known for being one of the first places to declare its results during United States presidential elections
Mount Washington is the highest point in the Northeastern United States
New Jersey (NJ)
Capital – Trenton
Largest city – Newark
Nickname – Garden State
New Jersey is the fourth-smallest state, but the most densely populated. It is named after the largest of the Channel Islands
To honour the victims that died on the 9/11 attacks, in 2002 the airport's name was changed from Newark International Airport to Newark Liberty International Airport
New Mexico (NM)
Capital – Santa Fe
Largest city – Albuquerque
Nickname – Land of Enchantment
Sante Fe was formally founded and made a capital in 1610, making it the oldest capital city in what is today the United States
Santa Fe’s full name when founded was “The Royal Town of the Holy Faith of St. Francis of Assisi”
Georgia O’Keeffe Museum is in Santa Fe
Albuquerque is on the Rio Grande
White Sands Missile Range was the location of the Trinity atomic bomb test
National Museum of Nuclear Science & History (formerly named National Atomic Museum) is located in Albuquerque
Acoma Pueblo, also known as “Sky City”, is a Native American pueblo built on top of a 112 m sandstone mesa in New Mexico. It is one of the oldest continuously inhabited communities in the United States
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is in New Mexico. Evidence of archaeoastronomy at Chaco has been proposed, with the Sun Dagger petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example
Carlsbad Caverns National Park is in New Mexico. Carlsbad Cavern includes a large cave chamber, the Big Room, a natural limestone chamber
New York (NY)
Capital – Albany
Largest city – New York City
Nickname – Empire State
New York consists of five boroughs – Manhattan (1), Brooklyn (2), Queens (3), The Bronx (4), and Staten Island (5) – which were consolidated into a single city in 1898
New York is built on a bedrock of schist
New Amsterdam became New York in 1664
New York is named after the Duke of York, who became King James II of England
Gotham is a nickname of New York
Madison Avenue is associated with advertising
Wall Street extends from Broadway to the East River
Times Square was formerly known as Longacre Square. Renamed in honour of the New York Times
The Great White Way is a nickname for a section of Broadway that encompasses the Theatre District
Sixth Avenue is the Avenue of the Americas
The Bowery is in the southern portion of Manhattan. Home of many music halls in the 19th century, the Bowery later became notable for its economic depression
In 1857 a landscape design contest was held for the design of Central Park. Frederick Law Olmsted and Calvert Vaux developed what came to be known as the Greensward Plan, which was selected as the winning design. Central Park comprises 843 acres. Alice in Wonderland sculpture is in Central Park
Harlem is a district in Manhattan
Harlem River separates the island of Manhattan from the Bronx
Nolita, from ‘North of Little Italy’ is a neighbourhood in Lower Manhattan
Charging Bull sculpture on Broadway was designed by Arturo di Modica. Fearless Girl is a temporary sculpture opposite the Charging Bull
Grant's Tomb, officially the General Grant National Memorial is in Manhattan and is the largest mausoleum in America
TriBeCa is a neighborhood in downtown Manhattan. The name is a syllabic abbreviation of ‘Triangle Below Canal Street.’ It runs roughly from Canal Street south to Park Place, and from the Hudson River east to Broadway
Hell’s Kitchen is a district of New York
The Hell Gate Bridge was built over a portion of the East River known as Hell Gate
JFK Airport is on Long Island. Known as Idlewild until 1963, one month after the assassination of John F. Kennedy
The first immigrant to pass through Ellis Island was Annie Moore, a 15-year-old girl from Cork, Ireland, on 1 January 1892. The last person to pass through Ellis Island was a Norwegian merchant seaman by the name of Arne Peterssen in 1954. Since 1990, restored buildings on the island host a museum of immigration run by the National Park Service as part of the Statue of Liberty National Monument
Ellis Island was sometimes known as ‘The Island of Tears’ or ‘Heartbreak Island’ because of those 2% who were not admitted after the long transatlantic voyage
Staten Island is connected to Brooklyn by Verrazano Narrows Bridge, over the Hudson River. Opened in 1964
The west end of Long Island has the New York City boroughs of Brooklyn (Kings County) and Queens (Queens County)
High Line is a linear park built on a section of the former elevated New York Central Railroad spur called the West Side Line, which runs along the lower west side of Manhattan
New York subway opened in 1904
Grand Central Depot was financed by Cornelius Vanderbilt. It opened in 1871, and was renamed Grand Central Station in 1900. Oyster Bar is the oldest business within Grand Central
Pennsylvania Station, also known as Penn Station, is the main intercity railroad station in New York City. It is the busiest passenger transportation hub in the Western Hemisphere
Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets
Franklin D. Roosevelt Four Freedoms Park is located at the southernmost point of Roosevelt Island, in the East River between Manhattan Island and Queens
Brooklyn is the most populous borough of New York
Dumbo (Down Under the Manhattan Bridge Overpass) is a neighbourhood in Brooklyn
Coney Island is in Brooklyn
Sea Lion Park on Coney Island was the first amusement park in North America. Opened in 1895. Replaced by Luna Park in 1903
Queens is the largest borough of New York
Hunts Point Cooperative Market, a 24/7 wholesale food market located in the Bronx, is the largest food distribution centre of its kind in the world
Rikers Island is New York City's main jail complex, as well as the name of the island on which it sits, on the East River
Holland Tunnel is under the Hudson River. It connects Lower Manhattan with Jersey City
Levittown on Long Island was founded by William Levitt, who built the district as a planned community between 1947 and 1951.
Queens was named after Catherine of Braganza, the Queen consort of King Charles II of England
Staten Island was named in honor of the Dutch parliament known as the Staten-Generaal
Long Island is the most populated island in any U.S. state or territory, and the 18th-most populous island in the world. Both the longest and the largest island in the contiguous United States, Long Island extends 190 km eastward from New York Harbor to Montauk Point
Brooklyn and Queens are on Long Island
The Hamptons, also called the ‘East End’ (of Long Island), are a group of villages and hamlets in the towns of Southampton and East Hampton, which form the South Fork of Long Island
The name of Yonkers is derived from Adriaen van der Donck
Broadway runs for 33 miles from Manhattan and the Bronx through Westchester County
Bear Mountain State Park is in upstate New York
Lake Placid is in the Adirondack Mountains in upstate New York
Erie Canal is a man-made waterway in New York that runs 363 miles from Albany on the Hudson River to Buffalo at Lake Erie, completing a navigable water route from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes
North Carolina (NC)
The flag of North Carolina bears the dates of the Mecklenburg Declaration of Independence (May 20, 1775) and of the Halifax Resolves (April 12, 1776)
Capital – Raleigh
Largest city – Charlotte
Nickname – Tar Heel State, Old North State
Roanoke Island is best known for its historical significance as the site of Sir Walter Raleigh's attempt to establish a permanent English settlement with his Roanoke Colony in 1585 and 1587. The fate of the final group of colonists has never been determined, yielding persistent myths about the “Lost Colony”
Charlotte is named in honour of the German Princess Charlotte of Mecklenburg, who had become queen consort of King George III
Mount Mitchell State Park includes the peak of Mount Mitchell, the highest peak east of the Mississippi River
Fort Bragg is a large United States Army installation
Biltmore Estate is a historic house museum and tourist attraction. Built for George Washington Vanderbilt II, it is the largest privately owned house in the United States
Spruce Pine Mining District in the Blue Ridge Mountains is one of the largest suppliers of high-purity quartz, which is used in the manufacture of silicon chips
Cape Hatteras is a cape located at a pronounced bend in Hatteras Island, one of the barrier islands. The treacherous waters off the coast of the Outer Banks are known as the Graveyard of the Atlantic
Great Smoky Mountains National Park, located on the border of Tennessee and North Carolina, is the most visited US national park
North Dakota (ND)
Capital – Bismarck
Largest city – Fargo
Nickname – Peace Garden State, Sioux State
The KVLY-TV mast remained the tallest structure in the Western Hemisphere, and the tallest broadcasting mast in the world until the antenna removal in 2019
Theodore Roosevelt National Park is in North Dakota
One third of population of North Dakota are descendants of immigrants from Norway
Ohio (OH)
Capital and largest city – Columbus
Nickname – Buckeye State
Cleveland is the second largest city in Ohio
Cleveland is on the shore of Lake Erie
Cuyahoga River flows through Cleveland
Cleveland is served by Hopkins International Airport
Cincinnati is the third largest city in Ohio
Cincinnati was named after the Roman general Cincinnatus, and is on the River Ohio
Oklahoma (OK)
Capital and largest city – Oklahoma City
Nickname – Sooner State
Will Rogers World Airport serves Oklahoma City
Tallgrass Prairie Preserve is protected as the largest tract of remaining tallgrass prairie in the world
WinStar World Casino and Resort is an American tribal casino and hotel located in Thackerville. It is owned and operated by the Chickasaw Nation and is one of the largest casinos in the world
Oregon (OR)
Flag of Oregon is a two-sided flag. On the front is the escutcheon from the state seal and on the reverse is a gold figure of a beaver, the state animal. Oregon is the only state to feature different designs on either side of its flag
Capital – Salem
Largest city – Portland
Nickname – Beaver State
Fort Astoria (also named Fort George) was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, it was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast
Crater Lake is a caldera lake in Oregon. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park. The lake was formed around 7,700 years ago by the collapse of the volcano Mount Mazama. Crater Lake is the deepest lake in the United States, and the second deepest lake in North America, behind Great Slave Lake
Mount Hood is the highest point in Oregon
Oregon is slightly larger than the United Kingdom
Pennsylvania (PA)
Capital – Harrisburg
Largest city – Philadelphia
Nickname – Keystone State
Philadelphia Zoo is the oldest in the United States
Pennsylvania has the second-highest gambling revenue after Nevada
Dating back to 1829, the Eastern State Penitentiary in Philadelphia has housed some of America's most dangerous criminals, including Al Capone
Pittsburgh was named after William Pitt the Elder
The characteristic shape of Pittsburgh's central business district is a triangular tract carved by the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, which form the Ohio River
Edwin Drake was the first person to successfully drill for oil, in Titusville, Pennsylvania, in 1859
Centralia is a ghost town due to a coal mine fire in 1962
Rhode Island (RI)
Capital and largest city – Providence
Nickname – Ocean State, Little Rhody
Rhode Island is the smallest in area, the eighth least populous, but the second most densely populated of the 50 US states
In January 2021, the State of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations dropped "and Providence Plantations" from its full name
Aquidneck Island, officially known as Rhode Island, is an island in Narragansett Bay in the state of Rhode Island
South Carolina (SC)
Capital and largest city – Colombia
Nickname – Palmetto State
Charleston is the oldest and second largest city in South Carolina
North and South Carolina were named in honour of King Charles I of England
Myrtle Beach is one of the major centres of tourism
South Dakota (SD)
Capital – Pierre
Largest city – Sioux Falls
Nickname – The Mount Rushmore State, Coyote State
The Crazy Horse Memorial is a mountain monument in progress in the Black Hills of South Dakota that when complete will be the world's largest sculpture. It is named after the Lakota warrior Crazy Horse. The monument is being carved out of Thunderhead Mountain on land considered sacred by some Native Americans, between Custer and Hill City, roughly 8 miles away from Mount Rushmore. Crazy Horse Memorial was begun in 1948 by sculptor Korczak Ziolkowski
Mount Rushmore features 60’ sculptures of the heads of former United States presidents (in order from left to right) George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Theodore Roosevelt and Abraham Lincoln
Mount Rushmore is in the Black Hills in Keystone
Badlands National Park is in South Dakota
Mammoth Site is a museum and paleontological site near Hot Springs, South Dakota. It contains the remains of fauna and flora preserved by entrapment in a karst sinkhole during the Pleistocene era
Tennessee (TN)
Capital – Nashville
Largest city – Memphis
Nickname – Volunteer State
Graceland is a mansion on an estate in Memphis that was home to Elvis Presley
National Civil Rights Museum in Memphis is built around the former Lorraine Motel, which was the site of the assassination of Martin Luther King in 1968
In 1942, the United States Federal Government chose Oak Ridge, Tennessee as a site for developing materials for the Manhattan Project
Nashville is the second largest city in Tennessee, and is known as “Music City” and “Athens of the South”
Parthenon in Centennial Park, in Nashville, Tennessee, is a full-scale replica of the original Parthenon in Athens
Opryland was a theme park in Nashville known as the “Home of American Music” that closed in 1997
Dollywood is a theme park in Pigeon Forge owned by Dolly Parton
Texas (TX)
Capital – Austin
Largest city – Houston
Nickname – Lone Star State
Texas is the second most populous (after California) and the second largest state (after Alaska)
Texas has 254 counties, the most nationwide
Houston was named after former General Sam Houston, who was president of the Republic of Texas
Austin is named after Stephen F. Austin, known as the father of Texas
Austin's official slogan is ‘The Live Music Capital of the World’. The city has more music venues per capita than any other U.S. city. Austin's music revolves around the many nightclubs on 6th Street and an annual film / music / multimedia festival known as South by Southwest
Silicon Hills is a nickname for the cluster of high-tech companies in Austin
San Antonio is named after a friar and was founded as a Spanish mission and colonial outpost in 1718
The Alamo is in San Antonio, the second largest city in Texas
Bracken Cave, San Antonio is home to 40 million bats
Dallas is the third largest city in Texas
The Dallas–Fort Worth–Arlington metropolitan area is known as The Metroplex
Amarillo was once the self-proclaimed ‘Helium Capital of the World’
Padre Island (the world's longest barrier island) is located on Texas's southern coast of the Gulf of Mexico and is famous for its white sandy beaches at the south end
Barnett shale a geological formation located in the Bend Arch-Fort Worth Basin. It consists of sedimentary rocks
Hurricane Ike hit Galveston in 2008
Brownsville lies at the eastern end of USA-Mexico border, adjacent to the border with Matamoros, Mexico
Big Bend National Park is located in West Texas, bordering Mexico
Utah (UT)
In March 2024 Utah adopted a new flag. The previous flag, adopted in 1913, was re-designated as the "Historic State Flag"
New Flag
Historic State Flag
Capital and largest city – Salt Lake City
Nickname – Beehive State
Salt Lake City was founded in 1847 by the Mormon pioneers, led by Brigham Young
Bryce Canyon National Park is a national park located in southwestern Utah. Despite its name, this is not actually a canyon, but rather a giant natural amphitheatre created by erosion along the eastern side of the Paunsaugunt Plateau. Bryce is distinctive due to its geological structures, called hoodoos
Moab desert is in Utah
A prominent feature of the Zion National Park is Zion Canyon, which is 15 miles long and up to half a mile deep, cut through the reddish and tan-coloured Navajo Sandstone by the North Fork of the Virgin River
Great White Throne is a sandstone mountain in Zion National Park
Arches National Park is located on the Colorado River. It is known for containing over 2,000 natural sandstone arches, including the world-famous Delicate Arch
Monument Valley is a region of the Colorado Plateau characterized by sandstone buttes, the largest reaching 300 m above the valley floor. It is located on the Utah-Arizona state line, near the Four Corners area. The valley is a sacred area that lies within the territory of the Navajo Nation Reservation. John Ford used the location for a number of his best-known films
Rainbow Bridge National Monument is the world’s highest natural bridge
Mesa Arch is a natural arch in Utah
Great Salt Lake is the largest salt water lake in the Western Hemisphere, and the fourth-largest terminal lake in the world
Bingham Canyon Mine an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City. The mine is owned by Rio Tinto Group. It is the largest man-made excavation in the world
Pando is a colony of trembling aspen in Fishlake National Forest, Utah. World’s largest organism by mass
Vermont (VT)
Capital – Montpelier
Largest city – Burlington
Nickname – Green Mountain State
Vermont is the second least populous state. Montpelier has a population of under 8,000 making it the least populous state capital in the country
Vermont is the only state in New England not bordered by the Atlantic Ocean
Virginia (VA)
Capital – Richmond
Largest city- Virginia Beach
Nickname – The Old Dominion
Rappahannock River in Virginia was considered to have been the boundary between the North and the South in the Civil War
Hampton Roads is the name of both a body of water and the region of land areas which surround it in southeastern Virginia. Hampton Roads is notable for its year-round ice-free harbour, for U.S. Navy, Air Force, NASA, Marine, and Army facilities, shipyards, coal piers, and hundreds of miles of waterfront property and beaches
Mount Vernon, located near Alexandria, Virginia, was the plantation home of George Washington. The key to the Bastille hangs in the hall – it was sent to Washington by Lafayette in 1790. The remains of George and Martha Washington, as well as other family members, are entombed on the grounds
Monticello, located near Charlottesville, was the estate of Thomas Jefferson. Means “the little mountain”
Colonial Williamsburg is the historic district of the city of Williamsburg, Virginia. It consists of buildings that from 1699 to 1780 formed colonial Virginia's capital
The Native Americans called the James River the Powhatan River. The English colonists named it ‘James’ after King James I of England, as they also constructed their first permanent English settlement in the Americas in 1607 at Jamestown, Virginia, along the banks of the James River
Designed by the American architect George Bergstrom, and built by contractor John McShain, the Pentagon was dedicated on 15 January1943, after ground was broken for construction in1941. Located in Arlington County, Virginia, the Pentagon is the world's largest office building by floor area
Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia is a military cemetery, established during the American Civil War on the grounds of Arlington House, formerly the estate of the family of Confederate general Robert E. Lee's wife Mary Anna (Custis) Lee, a great grand-daughter of Martha Washington. The cemetery is situated directly across the Potomac River from the Lincoln Memorial in Washington
Quantico, Virginia is the site of one of the largest U.S. Marine Corps bases in the world
Virginia is the most populous state without a major sports team
Loudoun County houses over 60 massive data centres, that are estimated to carry 70 percent of global web traffic
Shenandoah National Park encompasses part of the Blue Ridge Mountains in Virginia
Washington (WA)
Capital – Olympia
Largest city – Seattle
Nickname – Evergreen State
Washington is the only US state named after a former president
Space Needle was built for 1962 World Fair in Seattle. Designed by John Graham
Seattle is known as the “Emerald City”
Pike Place Market in Seattle is one of the oldest continuously operated public farmers' markets in the United States
Fremont, Seattle was at one time a centre of the counterculture. The neighbourhood remains home to a controversial statue of Lenin salvaged from Slovakia by a local art lover
Mount Rainier is a massive stratovolcano located 54 miles southeast of Seattle. It is the most prominent mountain in the contiguous United States and the Cascade Volcanic Arc
Mount Baker is an active glaciated stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the North Cascades of Washington State
Grand Coulee Dam is a hydroelectric gravity dam on the Columbia River in Washington. It is the largest electric power producing facility and the largest concrete structure in the United States. The reservoir is called Franklin Delano Roosevelt Lake
Channeled Scablands are an erosion feature in Washington
The Hanford Site is a facility of the government of the United States established to provide plutonium necessary for the development of nuclear weapons. It was established as part of the Manhattan Project, and codenamed ‘Site W.’ No longer used to produce plutonium, it is currently the United States' most contaminated nuclear site
Olympic National Park is located on the Olympia Peninsula
West Virginia (WV)
Capital and largest city – Charleston
Nickname – Mountain State, Panhandle State
West Virginia is located entirely within the Appalachian Region, and the state is almost entirely mountainous
Harpers Ferry National Historical Park is located at the confluence of the Potomac and Shenandoah rivers
Wisconsin (WI)
Capital – Madison
Largest city – Milwaukee
Nickname – America’s Dairyland, Badger State
Wisconsin is second to Michigan in the length of its Great Lakes coastline.
Wisconsin is known as “America's Dairyland” because it is one of the nation's leading dairy producers, particularly famous for cheese
Wyoming (WY)
Capital and largest city – Cheyenne
Nickname – Equality State
Wyoming is the least populous and the second least densely populated state
Teton Range is a mountain range of the Rocky Mountains. A north-south range, it is on the Wyoming side of the state's border with Idaho, just south of Yellowstone National Park. The principal summit of the central massif is Grand Teton
President Ulysses S. Grant established Yellowstone as the first National Park in 1872
Two Ocean Pass is a mountain pass on the Continental Divide, notable for Parting of the Waters, where one stream splits into two distributaries, Pacific Creek and Atlantic Creek. These two creeks ultimately flow into their respective oceans
Devil’s Tower in the Black Hills was the first United States national monument, established in 1906 by President Theodore Roosevelt
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, is the capital of the United States. The signing of the Residence Act in 1790, approved the creation of a capital district located along the Potomac River on the country's East Coast. The states of Maryland and Virginia each donated land to form the federal district, which included the pre-existing settlements of Georgetown and Alexandria. Named in honor of George Washington, the City of Washington was founded in 1791 to serve as the new national capital
Pierre L’Enfant was a French-American military engineer who designed the basic plan for Washington, D.C
The White House address is 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue
Lafayette Park is overlooked by the White House
Dumbarton Oaks is a historic estate in the Georgetown neighbourhood
K Street is notorious for the density of its lobbying firms
Washington has no skyscrapers
Washington National Cathedral is closely modeled on the English Gothic style of the late fourteenth century
Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial is located in West Potomac Park and was carved by sculptor Lei Yixin
Miscellaneous
Mountains
Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. Includes Mount St Helens. Highest point is Mount Rainier. Formed by subduction of Juan de Fuca plate under the North American plate
Allegheny Mountain Range is part of the Appalachian Mountain Range of the eastern United States and Canada. It runs for over 500 miles from north-central Pennsylvania, through western Maryland and eastern West Virginia, to southwestern Virginia
Ozark Mountains are between Appalachians and Rockies
Cumberland Gap is a pass through the Cumberland Mountains region of the Appalachian Mountains. Famous in American history for its role as one key passageway through the lower central Appalachians, it was an important part of the Wilderness Road
Lookout Mountain is located at the northwest corner of Georgia, the northeast corner of Alabama, and along the southern border of Tennessee at Chattanooga
Blue Ridge Mountains are part of the Appalachian Mountains range. The bluish colour is caused by isoprene released from trees
Deserts
Mojave Desert is located primarily in southeastern California and southwestern Nevada
Great Basin Desert spans large portions of Nevada and Utah, and extends into eastern California
Rivers
Rising in the Rocky Mountains of western Montana, the Missouri flows east and south for 2,341 miles before entering the Mississippi River north of St. Louis. Flows through Bismarck and Pierre. Known as the ‘Big Muddy’. When combined with the lower Mississippi River, it forms the world's fourth longest river system
From its source of Lake Itasca in Minnesota, the Mississippi flows generally south for 2,340 miles to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico
Ohio River is the largest tributary, by volume, of the Mississippi River
Arkansas River is the third longest river entirely in the United States
Susquehanna River is the longest river entirely within the United States that drains into the Atlantic Ocean
Shenandoah is a tributary of the Potomac, in Virginia and West Virginia
Green River is the chief tributary of the Colorado River
Gila River is a tributary of the Colorado River
Suwannee River runs through Georgia southward into Florida
Connecticut River is the longest river in New England. Forms the boundary between Vermont and New Hampshire
Snake River is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, and the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean
Lakes
Lake Powell is a man-made reservoir on the Colorado River, straddling the border between Utah and Arizona. It is the second largest man-made reservoir in the United States behind Lake Mead
Great Salt Lake is the largest US lake
Lake Champlain is a natural freshwater lake mainly within the borders of the United States (in Vermont and New York) but partially situated across the Canada–U.S. border, in Quebec
Lake Tahoe is a freshwater lake in the Sierra Nevada, straddling the border between California and Nevada. It is the second deepest in the United States after Crater Lake in Oregon. The Truckee River is the lake's only outlet
Lake of the Woods in Minnesota and bordering Canada is the sixth largest freshwater lake located (at least partially) in the United States, after the five Great Lakes
Roads
Pan-American Highway measures 29,800 miles in total length. Except for a 54 mile rainforest break, called the Darien Gap, the road links the mainland nations of the Americas in a connected highway system. The highway extends from Prudhoe Bay in Alaska to the lower reaches of South America
National Highway System (NHS) is a network of strategic highways within the United States, including the Interstate Highway System that was championed by President Eisenhower
I-90 is the longest interstate highway in the United States at nearly 3,100 miles, and runs from Boston to Seattle
Route 66, also known as the Will Rogers Highway, is colloquially known as the Main Street of America. One of the original U.S. Highways, Route 66 was established in 1926. The highway originally ran from Chicago, Illinois, through Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, and California, before ending at Santa Monica, covering a total of 2,448 miles
Highway 101 runs through the states of California, Oregon, and Washington. It is also known as El Camino Real (The Royal Road) along the southern and central California coast
Missouri and Tennessee have borders with eight other states
Four of the constituent states of the United States officially designate themselves Commonwealths: Kentucky, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, and Virginia
Most populous counties – 1st Los Angeles County, 2nd Cook County, Illinois, 3rd Harris County, Texas
Four Corners is a region consisting of the southwestern corner of Colorado, northwestern corner of New Mexico, northeastern corner of Arizona, and southeastern corner of Utah. The Four Corners area is named after the quadripoint where the boundaries of the four states meet, where the Four Corners Monument is located Connecticut River is the longest river in New England. Forms the boundary between Vermont and New Hampshire
Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds in North America. It is noted for both its arid conditions and its Basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than 100 miles away at the summit of Mount Whitney
Chesapeake Bay is the largest inlet off the Atlantic coast and has coastlines on Virginia and Maryland. It is the largest estuary in the United States
Sea Islands are a chain of 100 tidal and barrier islands, located between the mouths of the Santee and St. Johns Rivers along the coast of South Carolina, Georgia and Florida
Intracoastal Waterway is a 4,800 km inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts, running from Point Pleasant Beach, New Jersey, southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following the Gulf Coast to Brownsville, Texas. Some sections of the waterway consist of natural inlets, saltwater rivers, bays, and sounds, while others are artificial canals
United States Minor Outlying Islands consist of eight United States insular areas in the Pacific Ocean (Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, Palmyra Atoll, and Wake Island) and one in the Caribbean Sea (Navassa Island)
Midway Atoll is the only island in the Hawaiian archipelago that is not part of the state of Hawaii
Baker Island and Howland Island are UTC-12:00 which is only uninhabited timezone. They are the last pieces of land that experience the New Year
Great Lakes
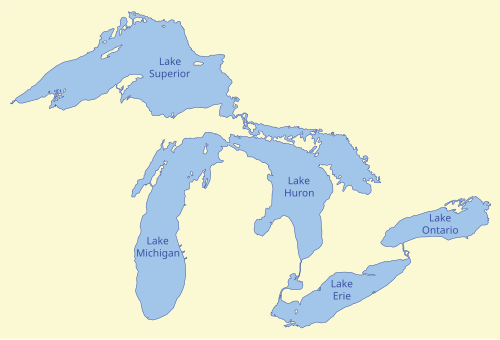
The Great Lakes are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area and are second-largest by total volume, containing 21% of the world's surface fresh water by volume. The lakes began to form at the end of the Last Glacial Period around 14,000 years ago
Lake Superior is the largest of the Great Lakes, and among freshwater lakes, it is the world's largest by surface area. It has a surface area of 82,000 km2
The largest island in Lake Superior is Isle Royale in Michigan
Thunder Bay, Ontario is the most populous city on Lake Superior
Lake Huron comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron. By surface area, Lake Huron is the second-largest of the Great Lakes
Mackinac Island is an island and resort area located in Lake Huron
Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron is the largest island in a freshwater lake in the world
Lake Manitou is the largest lake on Manitoulin Island. It is the largest lake on a freshwater island in the world
Lake Michigan is the only Great Lake entirely in the United States and is the largest lake that is entirely within one country. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume and the third-largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron
Lake Michigan is shared by the states of Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan. Ports along its shores include Milwaukee, Green Bay, Chicago, and Gary
Lake Erie is the fourth-largest of the Great Lakes by surface area, and is the shallowest of the lakes. The largest city on the lake is Cleveland. Other major cities along the lake shore are Buffalo and Toledo
Lake Ontario is the smallest and easternmost of the Great Lakes. The Canadian cities of Toronto and Kingston are located on the lake's northern and western shorelines, while the American city of Rochester in New York state is located on the south shore
Lake Ontario is the only Great Lake not to border the state of Michigan
The Chicago River and Calumet River systems connect the Great Lakes Basin to the Mississippi River System
The St. Marys River, including the Soo Locks, connects Lake Superior to Lake Huron, via the North Channel
The Straits of Mackinac connect Lake Michigan to Lake Huron
The St. Clair River connects Lake Huron to Lake St. Clair
The Detroit River connects Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie
The Niagara River, including Niagara Falls, connects Lake Erie to Lake Ontario
The Welland Canal connects Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. As a part of the St. Lawrence Seaway, this canal enables ships to ascend and descend the Niagara Escarpment and to bypass the Niagara Falls
The Saint Lawrence River and the Saint Lawrence Seaway connect Lake Ontario to the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, which connects to the Atlantic Ocean
Niagara Falls is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between Ontario in Canada and New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Falls, also known as the Canadian Falls, which straddles the international border of the two countries. The smaller American Falls and Bridal Veil Falls lie within the United States. Bridal Veil Falls is separated from Horseshoe Falls by Goat Island and from American Falls by Luna Island, with both islands situated in New York.
Formed by the Niagara River, which drains Lake Erie into Lake Ontario, the combined falls have the highest flow rate of any waterfall in North America that has a vertical drop of more than 50 m
The Rainbow Bridge is the first bridge downstream from the falls
Canada
Flag of Canada features an 11-pointed maple leaf
| Capital | Ottawa |
| Largest cities | Toronto, Montreal, Calgary, Ottawa, Edmonton |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Logan |
Canada was known as La Nouvelle France
In 1867, three provinces of British North America – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia and the Province of Canada (which, on the formation of Canada, was divided into Ontario and Quebec) – were united to form the new nation
Canada consists of ten provinces and three territories
Canadian Prairies – the provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba
Maritime Provinces of Canada – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island
Atlantic Provinces of Canada – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador
Largest provinces by area – Quebec, British Colombia, Ontario
Largest provinces by population – Ontario, Quebec, British Colombia
Alberta and Saskatchewan are the only landlocked provinces
St. Lawrence Seaway permits ocean-going vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the North American Great Lakes, as far as Lake Superior. Opened in 1959
Canada has more lakes than any other country
Canada produces 35% of the world’s uranium
Canada is divided into six time zones – Pacific, Mountain, Central, Eastern, Atlantic (UTC-04:00, covers New Brunswick, Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island), Newfoundland (UTC-03:30)
Provinces
Alberta
Capital – Edmonton
Largest city – Calgary
Alberta is named after Princess Louise Caroline Alberta, the fourth daughter of Victoria, the Queen of Canada and Albert, Prince Consort
Calgary was originally known as Fort Briseboas
West Edmonton Mall is the largest shopping mall in North America
Jasper national park is in Alberta
Banff National Park is Canada's oldest national park, established in 1885, in the Canadian Rockies. Lake Louise lies within the park
Banff is named by George Stephen, president of the Canadian Pacific Railway, recalling his birthplace in Banffshire, Scotland
Medicine Hat, known to locals as ‘The Hat’ or 'Gas City', is a city located in the province of Alberta. Its major claim to fame is Rudyard Kipling's famous line ‘all hell for a basement’ referring to the vast reserves of natural gas beneath it
Most of the oil sands (tar sands) of Canada are located in northern Alberta
British Columbia
Capital – Victoria
Largest city – Vancouver
Vancouver was originally known as Gastown, then Granville. The city is named after Royal Navy Captain George Vancouver
Vancouver is overlooked by Grouse Mountain
Whistler is a ski resort in the southern Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains
Burgess Shale Formation, located in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, is one of the world's most celebrated fossil fields. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. It is 505 million years old
The Queen Charlotte Islands or Haida Gwaii (‘Islands of the People’) are an archipelago off the northwest coast of British Columbia consisting of two main islands, Graham Island in the North, and Moresby Island in the south
Glacier National Park contains the Rogers Pass National Historic Site
Manitoba
Capital and largest city – Winnipeg
Winnipeg lies at the bottom of the Red River Valley
Churchill is a town on the shore of Hudson Bay in Manitoba. It is known as the ‘Polar Bear Capital of the World’
Nelson River drains Lake Winnipeg and runs 644 km before it ends in Hudson Bay
New Brunswick
Capital – Fredericton
Largest city – Saint John
New Brunswick is named for the city of Braunschweig in Lower Saxony. Braunschweig is the ancestral home of George I
New Brunswick is the only bilingual province
Newfoundland and Labrador
Capital and largest city – St. John’s
Gander International Airport in Newfoundland opened in 1938 and within a few years was the largest in the world
Strait of Belle Isle separates the Labrador Peninsula from the island of Newfoundland
In 1583, Newfoundland became England's first possession in North America and one of the earliest permanent English colonies in the New World
In 2001 the name of Newfoundland was changed to Newfoundland and Labrador
Nova Scotia
Capital and largest city – Halifax
Sable Island, situated off the coast of Nova Scotia, is known as the “graveyard of the Atlantic”
Joggins Fossil Cliffs is famous for its record of fossils from a rainforest ecosystem approximately 310 million years ago
Cape Breton is an island off the north coast of the Nova Scotia peninsula
Ontario
Capital and largest city – Toronto
Toronto is on Lake Ontario, and is the most populous city in Canada
Toronto was known as York until 1834
Lester B. Pearson airport serves Toronto
CN Tower (Canadian National Tower) in Toronto was completed in 1976, becoming the world's tallest free-standing structure and world's tallest tower at the time. It is 1,815 feet tall and was designed by Neil Baldwin. The antenna was flown to the top of the tower in 36 sections by as Sikorsky helicopter named "Olga"
Scarborough is one of the most diverse and multicultural areas in the Greater Toronto Area
Ottawa was founded in 1826 as Bytown
Ottawa is situated on the traditional land of the Algonquins
London is in Southwestern Ontario. It lies at the confluence of the non-navigable Thames River
Rideau Canal connects the city of Ottawa, on the Ottawa River to the city of Kingston, Ontario, on Lake Ontario. Rideau Canal Skateway in Ottawa is the world's largest skating rink at 7.8 km long
Sudbury Basin on the Canadian Shield is the third-largest impact crater on Earth
Prince Edward Island
Capital and largest city – Charlottetown
Prince Edward Island is the smallest Canadian province in both area and population
Prince Edward Island is named after the fourth son of George III and the father of Queen Victoria
Charlottetown is named after Queen Charlotte, the wife of George III
Quebec
Capital – Quebec City
Largest city – Montreal
Mirabelle airport serves Montreal
Montreal covers most of the Island of Montreal at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa Rivers. Island of Montreal is the most populous island in Canada
Jacques Cartier Bridge is a steel truss cantilever bridge crossing the Saint Lawrence River from Montreal Island to the south shore at Longueuil
Opened in 1859, Victoria Bridge was the first to span the St. Lawrence River, linking Montreal to the south shore city of Saint-Lambert
Montreal is known as the ‘City of Saints’
Montreal Biosphere’s geodesic dome was designed by Buckminster Fuller
Montreal is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill in the heart of the city
Habitat 67 is a building in Montreal
Quebec City was founded in 1608 by Samuel de Champlain
La Citadelle of Quebec contains the oldest military building in Canada, and forms part of the fortifications of Quebec City. Official residence of the governor general of Canada
Plains of Abraham is a historic area in Quebec City
Fairmont Le Chateau Frontenac in Quebec City is generally recognized as the most photographed hotel in the world
Anticosti Island is at the outlet of the Saint Lawrence River into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. Due to more than 400 shipwrecks off its coasts, Anticosti Island is sometimes called the "Cemetery of the Gulf". It has a number of lighthouses
Lake Manicouagan is an annular lake, caused by the impact of a meteorite
Saskatchewan
Capital – Regina
Largest city – Saskatoon
Saskatchewan is the only Canadian province with four straight boundaries
McArthur River Uranium Mine, in northern Saskatchewan, is the world's largest high-grade uranium deposit
Territories
Northwest Territories
Capital and largest city – Yellowknife
Yellowknife is named after the local Yellowknives Dene First Nation
Great Bear Lake is the largest lake in Canada, the fourth largest in North America, and the eighth largest in the world
Great Slave Lake is the deepest lake in North America
Mackenzie River originates in Great Slave Lake, in the Northwest Territories, and flows north into the Arctic Ocean. It is the longest river in Canada at 1,738 km. It was originally named Disappointment River
Nunavut
Capital and largest city – Iqaluit
Nunavut is the largest and newest territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories in 1999. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's map since the incorporation of the new province of Newfoundland (including Labrador) in 1949. The capital Iqaluit (formerly Frobisher Bay) on Baffin Island, in the east, was chosen in 1995
A member of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Bathurst Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in Nunavut Territory
Alert is the northernmost permanently inhabited place
Devon Island, claimed to be the largest uninhabited island on Earth, is located in Baffin Bay
Davis Strait separates Baffin Island from Greenland. The strait was named for the English explorer John Davis, who explored the area while seeking a Northwest Passage
Nettilling Lake on Baffin Island is the world’s largest lake on an island
Yukon
Capital and largest city – Whitehorse
Dawson served as the Yukon's capital from the territory's founding in 1898 until 1952, when the seat was moved to Whitehorse
Mount Logan is in Yukon. The mountain was named after Sir William Edmond Logan, a Canadian geologist and founder of the Geological Survey of Canada
Bay of Fundy is on the northeast end of the Gulf of Maine between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the state of Maine. Bay of Fundy has the highest tides in the world
Lake Athabasca is located in the northwest corner of Saskatchewan and the northeast corner of Alberta. Athabasca means ‘lake of the hills’
Lake Winnipeg and Lake Manitoba are remnants of prehistoric Glacial Lake Agassiz
Labrador Peninsula includes the region of Labrador, which is part of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, and parts of Quebec
Victoria Island in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories. It is Canada's second largest island, after Baffin Island
Queen Elizabeth Islands are the northernmost cluster of islands in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, split between Nunavut and Northwest Territories. Ellesmere Island is the largest of the Queen Elizabeth Islands
Nares Strait separates Greenland from Ellesmere Island
Hudson Strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik (the northern third of Quebec)
The source of the Yukon River is located in British Columbia. The next portion lies in, and gives its name to, Yukon. The lower half of the river lies in Alaska. It is the second-longest river in Canada
Aspen parkland refers to a transitional biome between prairie and boreal forest stretching from northeastern British Columbia through central and northwestern Alberta, central Saskatchewan to central and southern Manitoba. Aspen parkland consists of groves of aspen poplars and spruce interspersed with areas of prairie grasslands
Trans-Canada Highway travels through all ten provinces of Canada, The main route spans 7,476 km across the country
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France and is the remaining vestige of the territory of New France. Its residents are French citizens. The islands are in the Gulf of St. Lawrence near the entrance of Fortune Bay, which extends into the southwestern coast of Newfoundland
Saint-Pierre is the capital and largest city
Mexico
Coat of arms on the flag of Mexico depicts a golden eagle perched on a prickly pear cactus eating a rattlesnake
| Capital | Mexico City |
| Largest cities | Mexico City, Tijuana, Leon |
| Currency | Peso |
| Highest point | Pico de Orizaba |
With an estimated population of 128 million, Mexico is the tenth most populous and the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world and the second most populous country in Latin America. It is the tenth largest oil producer in the world, and the largest silver producer in the world
The United Mexican States are a federation of 31 free and sovereign states
The Greater Mexico City population is 21 million people, making it the second-largest metropolitan area in the western hemisphere behind Sao Paulo
Paseo de la Reforma is a wide avenue that runs diagonally across the heart of Mexico City. It is now home to many of Mexico's tallest buildings
Soumaya Museum in Mexico City contains a large collection of casts of sculptures by Auguste Rodin. It is owned by the Carlos Slim Foundation
Frida Kahlo Museum, also known as the Blue House (La Casa Azul) for the structure's cobalt-blue walls, is in Mexico City
Palacio de Bellas Artes (Palace of Fine Arts) is one of the most prominent cultural centres in Mexico City
Angel of Independence was built in 1910 during the presidency of Porfirio Díaz by architect Antonio Rivas Mercado, to commemorate the centennial of the beginning of Mexico's War of Independence
Aztec sun stone is a Mexica sculpture housed in the National Anthropology Museum in Mexico City
Tenochtitlan was an Aztec altepetl (city-state) located on an island in Lake Texcoco, in the Valley of Mexico. Founded in 1325, it became the capital of the expanding Mexican Empire in the 15th century, until captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak it was the largest city in the Pre-Columbian Americas. Today the ruins of Tenochtitlan are located in Mexico City's downtown
Teotihuacan was an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub valley of the Valley of Mexico, 48 km northeast of modern-day Mexico City, known today as the site of many of the most architecturally significant Mesoamerican pyramids built in the pre-Columbian Americas. At its zenith, perhaps in the first half of the 1st millennium AD, Teotihuacan was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas, with a population estimated at 125,000. Teotihuacan has the Pyramid of the Moon, Pyramid of the Sun, and Avenue of the Dead. The name Teotihuacan was given by the Nahuatl-speaking Aztecs centuries after the fall of the city around 550. The term has been glossed as "birthplace of the gods"
Chicxulub Crater is an ancient impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula, with its center located near the town of Chicxulub. The crater is over 180 kilometers in diameter, making the feature one of the largest confirmed impact structures in the world; the asteroid or comet whose impact formed the crater was at least 10 km in diameter. The impact associated with the crater is implicated in causing the extinction of the dinosaurs as suggested by the K–T boundary, 65 million years ago
Chichen Itza is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site built by the Maya civilization, located in the northern centre of the Yucatan Peninsula. Dominating the centre of Chichen is the Temple of Kukulcan (the Maya name for Quetzalcoatl), often referred to as “El Castillo” (the castle). This step pyramid with a ground plan of square terraces has stairways up each of the four sides to the temple on top
Monte Alban is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site in the southern Mexican state of Oaxaca. Monte Alban's importance stems also from its role as the pre-eminent Zapotec socio-political and economic centre for 1,000 years
The city of Veracruz is a major port city and municipality on the Gulf of Mexico in the Mexican state of Veracruz
Naica Mine of the Mexican state of Chihuahua is a working mine that is known for its extraordinary selenite (a variety of gypsum) crystals in the Cave of the Crystals
Guadalajara Metropolitan Area is the second largest in the country after Greater Mexico City. Guadalajara is the capital of the state of Jalisco
Torres Obispado is a skyscraper complex in Monterrey, Upon completion in 2020, T.Op Torre 1 became the tallest skyscraper in Latin America and the first to reach a height of 1,000 feet
Palanque is a Maya city state in Southern Mexico that flourished in the 7th century
Tula, in the state of Hidalgo, was the ancient capital of the Toltecs. The city was destroyed in the 12th century
Great Pyramid of Cholula is an adobe brick pyramid in the state of Puebla. It is the largest pyramid in the world, with a base four times larger than the Great Pyramid at Giza and nearly twice the volume. The pyramid is a temple that traditionally has been viewed as having been dedicated to the god Quetzalcoatl
El Tajin is a pre-Columbian archeological site in southern Mexico and is one of the largest and most important cities of the Classic era of Mesoamerica. A part of the Classic Veracruz culture, El Tajin flourished from 600 to 1200 AD
Chihuahua is the largest state of Mexico
Ciudad Juarez is the largest city in Chihuahua. It lies on the Rio Grande south of El Paso, Texas
Cancun is located on the northeast coast of the Yucatan Peninsula in the state of Quintana Roo. It is an important tourist destination
Acapulco is a major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific coast. Due to a massive upsurge in gang violence and homicide numbers since 2014, Acapulco no longer attracts many foreign tourists
Tijuana is the largest city in Baja California, and is part of the international San Diego–Tijuana metropolitan area
Villahermosa is the capital and largest city of the state of Tabasco
Manzanillo is the largest port in Mexico
Cozumel is an island in the Caribbean Sea off the eastern coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, opposite Playa del Carmen. The economy of Cozumel is based on tourism
Gulf of California (also known as the Sea of Cortez) is a body of water that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland
Popocatepetl is the second highest peak in Mexico, after the Pico de Orizaba. The name Popocatepetl comes from the Nahuatl words for ‘Smoking Mountain’
Paricutin is a dormant volcano in Mexico. It is thought to be the youngest volcano in the world
Lake Chapala is the largest freshwater lake in Mexico
Central America
Belize
The coat of arms on the flag of Belize features woodcutters and a mahogany tree. The flag of Belize is the only country to have humans depicted as a major design element on its national flag, although the flag of Malta contains an image of Saint George on the badge of the George Cross
| Capital | Belmopan |
| Largest cities | Belize City, San Ignacio, Belmopan |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Doyle’s Delight |
Belize is is the only commonwealth country in Central America and the only country in Central America whose official language is English
Belize is the only Central American country connected only to the Atlantic
Belize City is the largest city in Belize. It was the capital of British Honduras (as Belize was then named) until it was devastated by Hurricane Hattie and the government was moved to the new capital of Belmopan in 1970
Chalillo Dam is a gravity dam in Belize
Lamanai and Caracol are Mayan ruins in Belize
Great Blue Hole is a large submarine sinkhole off the coast of Belize
Belize Barrier Reef is Belize's top tourist destination
Rio Hondo forms most of the border between Belize and Mexico
Costa Rica
| Capital | San Jose |
| Largest cities | San Jose |
| Currency | Colon |
| Highest point | Mount Chirripo |
Costa Rica permanently abolished its army in 1949
San Jose means ‘Saint Joseph’
Cocos Island is an island located off the shore of Costa Rica and is known as ‘Shark Island’
Stone spheres of Costa Rica are commonly attributed to the extinct Diquis culture
El Salvador
| Capital | San Salvador |
| Largest cities | San Salvador |
| Currency | US dollar |
| Highest point | Cerro El Pital |
El Salvador is the only Central American country that does not have a Caribbean coastline
El Salvador is the smallest country in Central America and the most densely populated country in the Americas
Izalco is a stratovolcano on the side of the Santa Ana Volcano
Bitcoin is legal tender in El Salvador
Guatemala
The coat of arms of the flag of Guatemala includes the resplendent quetzal
| Capital | Guatemala City |
| Largest cities | Guatemala City |
| Currency | Quetzal |
| Highest point | Volcan Tajumulco |
Guatemala is the most populous state in Central America
Guatemala City is the most populous in Central America
El Mirador is a large pre-Columbian Mayan settlement, located in the north of the modern department of El Peten, Guatemala. Discovered in 1926
Tikal is one of the largest archaeological sites and urban centres of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization. It is located in the archaeological region of the Peten Basin in northern Guatemala. Situated in the department of El Petén, the site is part of Guatemala's Tikal National Park and in 1979 it was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Tikal reached its apogee during the Classic Period, c. 200 to 850. Discovered by Alfred Maudslay
Antigua is a World Heritage site that served as the capital of the Kingdom of Guatemala
Volcan Tajumulco is a large stratovolcano in Guatemala. It is the highest mountain in Central America
Honduras
| Capital | Tegucigalpa |
| Largest cities | Tegucigalpa, San Pedro Sula |
| Currency | Lempira |
| Highest point | Cerro Las Minas |
Honduras was at times referred to as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became Belize. Honduras was home to several important Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya, prior to being conquered by Spain in the 16th century
La Ciudad Blanca (Spanish for "The White City") is a legendary settlement said to be located in the Mosquitia region of Honduras
Copan was a Mayan city in Honduras
Nicaragua
| Capital | Managua |
| Largest cities | Managua |
| Currency | Cordoba |
| Highest point | Mogoton |
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American isthmus. The Spanish Empire conquered the region in the 16th century. Nicaragua achieved its independence from Spain in 1821
Nicaragua is the most triangular-shaped country
On the Pacific side of the country are the two largest freshwater lakes in Central America – Lake Nicaragua and Lake Managua
Ometepe is the largest island in Lake Nicaragua
Bosawas Biosphere Reserve is the second largest rainforest in the Western Hemisphere, after the Amazon Rainforest
Panama
| Capital | Panama City |
| Largest cities | Panama City |
| Currency | Balboa and US dollar |
| Highest point | Volcan Baru |
Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903, allowing the Panama Canal to be built by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
Panama Canal was designed by Ferdinand de Lesseps in 1880, but the project failed. Work began again in 1904, and the canal was completed in 1914
There are three sets of locks in the Panama Canal. A two-step flight at Miraflores, and a single flight at Pedro Miguel, lift ships from the Pacific up to Lake Gatun; then a triple flight at Gatun lowers them to the Atlantic side
Gatun Lake was created between 1907 and 1913 by the building of the Gatun Dam across the Chagres River. At the time it was created, Gatun Lake was the largest man-made lake in the world
Bridge of the Americas spans the Pacific entrance to the Panama Canal. Built in 1962
Chagres River is a major source of water for Panama Canal
Coiba is the largest island in Central America, off the Pacific coast of Panama
JW Marriott Panama is the tallest building in Central America
Caribbean
The West Indies consist of the Antilles, divided into the larger Greater Antilles which bound the Caribbean Sea on the north and the Lesser Antilles on the south and east (including the Leeward Antilles), and the Bahamas. Bermuda lies much further to the north in the Atlantic Ocean (570 miles east of North Carolina) and is in the West Indies
Lucayan Archipelago, also known as the Bahama Archipelago, is an island group comprising the Commonwealth of the Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands
Greater Antilles – Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, and Cayman Islands
Lesser Antilles – Leeward Islands and Windward Islands
Leeward Islands – Northern group of the Lesser Antilles. Virgin Islands, Guadeloupe, St Kitts and Nevis, Antigua and Barbuda, Anguilla and Montserrat
Windward Islands – Southern group of the Lesser Antilles. Martinique, Dominica, Grenada, St Lucia, St Vincent and Grenadines
Caribbean Sea is known as “Sea of the Antilles”
Windward Passage is a strait in the Caribbean Sea, between the islands of Cuba and Hispaniola
Caribbean is the deepest sea. Deepest point is the Cayman Trough
ABC islands are the three western-most islands of the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. From west to east they are, in order Aruba, Curacao, and Bonaire. All three islands are part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Netherlands Antilles was an autonomous country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean. It was also informally known as the Dutch Antilles. The country was dissolved in 2010. Historically the Netherlands Antilles included the colony of Curacao and its dependencies
Antigua and Barbuda
| Capital | Saint John’s |
| Largest cities | Saint John’s |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar |
| Highest point | Boggy Peak |
Antigua and Barbuda became an independent state within the Commonwealth of Nations in 1981
Most of the population of Barbuda lives in the town of Codrington
Redonda is an uninhabited island that is part of Antigua and Barbuda
In 2009, Boggy peak was renamed Mount Obama after United States president Barack Obama. The original name was restored in 2016
Bahamas
| Capital | Nassau |
| Largest cities | Nassau |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Alvernia |
Bahamas consists of 29 islands, 661 cays, and 2387 islets
Nassau was formerly known as Charles Town; it was burned to the ground by the Spanish in 1684. Rebuilt, it was renamed Nassau in 1695 in honour of William III from the Dutch House of Orange-Nassau. Nassau is on the island of New Providence
Nassau is served by Lyndon Pindling International Airport
New Providence is the most populous island in the Bahamas, containing more than 70% of the total population
Andros Island is an archipelago within the archipelago-nation of the Bahamas. It is the largest of the 26 inhabited Bahamian Islands
Bimini comprises a chain of islands known for sport fishing
Barbados
Flag of Barbados is known as The Broken Trident
| Capital | Bridgetown |
| Largest cities | Bridgetown |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Hillaby |
Barbados is the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands
Barbados is served by Grantley Adams airport
Bridgetown was formerly ‘The Town of Saint Michael’
In 1813, a statue was erected in Bridgetown, in what was known as Trafalgar Square, (now renamed National Heroes’ Square) in recognition of Nelson's bravery and as a tribute to his honour within the British Empire. This statue was sculpted from bronze by Richard Westmacott
Cuba
| Capital | Havana |
| Largest cities | Havana, Santiago de Cuba |
| Currency | Peso |
| Highest point | Pico Turquino |
Cuba comprises the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud and several archipelagos
Cuba is the largest island in the Caribbean
Isla de la Juventud is the second largest Cuban island
Havana is the country's main port and leading commercial centre and has a population of 2.1 million. Havana was founded by the Spanish in the 16th century
In 1982, Old Havana was made a World Heritage Site, because of its unique Baroque and neoclassical architecture, and its fortifications
The Malecon is a promenade that stretches for 8 km along the coast in Havana
Necropolis Cristobal Colon is a cemetery and open-air museum in Havana named for Christopher Columbus
The United States assumed territorial control over the southern portion of Guantanamo Bay under the 1903 Lease. The United States exercises jurisdiction and control over this territory, while recognizing that Cuba retains ultimate sovereignty
Alejandro de Humboldt National Park is a World Heritage site
Pico Turquino is located in the Sierra Maestra mountain range
Dominica
Flag of Dominica features the sisserou parrot
| Capital | Roseau |
| Largest cities | Roseau |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Diablotins |
Dominica has been nicknamed the "Nature Isle of the Caribbean" for its unspoiled natural beauty. Christopher Columbus named the island after the day of the week on which he spotted it, a Sunday, 3 November 1493
Dominica was the last Caribbean island to be colonized
Boiling Lake is a flooded fumarole located in Morne Trois Pitons National Park. The lake is filled with bubbling water that is usually enveloped in a cloud of vapour
Dominican Republic
Coat of arms on the Dominican Republic flag features a bible
| Capital | Santo Domingo |
| Largest cities | Santo Domingo, Santiago de los Caballeros |
| Currency | Peso |
| Highest point | Pico Duarte |
Dominican Republic occupies the eastern half of the island of Hispaniola
Santo Domingo, known officially as Santo Domingo de Guzman, is the largest city in the Caribbean by population. Santo Domingo de Guzman was founded in 1501. Oldest continuously inhabited European settlement in the Americas, and was the first seat of Spanish colonial rule in the New World
Santo Domingo was called Ciudad Trujillo from 1936 to 1961, after the Dominican Republic's dictator, Rafael Trujillo, named the capital after himself
The first cathedral in the Americas was in Santo Domingo
Pico Duarte is the highest peak in all the Caribbean islands. It lies in the Cordillera Central range, the greatest of the Dominican Republic's mountain chains
Saona Island lies off the coast of the Dominican Republic
Grenada
Flag of Grenada is charged with a nutmeg at the hoist triangle
| Capital | St. George’s |
| Largest cities | St. George’s |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Saint Catherine |
Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Petite Martinique, and several small islands which lie to the north of the main island and are a part of the Grenadines
Grenada is known as the ‘Island of Spice’ due to its production of nutmeg and mace crops
St. George’s was named after the patron saint of England when the island was ceded to Great Britain by the Treaty of Paris in 1763
Haiti
| Capital | Port-au-Prince |
| Largest cities | Port-au-Prince, Cap-Haitien |
| Currency | Gourde |
| Highest point | Pic la Selle |
Haiti occupies the western half of the island of Hispaniola
Haiti was known as Saint-Domingue before independence in 1804
Haiti is the only French speaking independent republic in the Americas
Sans-Souci Palace was the royal residence of King Henri I (better known as Henri Christophe) of Haiti, Queen Marie-Louise and their twin daughters. Construction of the palace started in 1810 and was completed in 1813. It is located in the town of Milot, Nord Department. Its name translated from French means “without worry”. Close to the Palace is the renowned mountaintop fortress; the Citadelle Laferriere, built under decree by Henri Christophe to repel a feared French invasion
Navassa Island is a small uninhabited island in the Caribbean Sea. It is subject to an ongoing territorial dispute between Haiti and the United States
Jamaica
Flag of Jamaica is the only national flag that does not contain a shade of the colours red, white, or blue
| Capital | Kingston |
| Largest cities | Kingston, Portmore, Spanish Town, Montego Bay |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | Blue Mountain Peak |
Jamaica is a Commonwealth realm. Once a Spanish possession known as Santiago, in 1655 it came under the rule of England, and was called Jamaica. It achieved full independence from the United Kingdom in 1962
Black River is one of the longest rivers in Jamaica
Spanish Town was the former capital of Jamaica
Jamaica is divided into 14 parishes, which are grouped into the three historic counties of Cornwall, Middlesex and Surrey
Kingston is in the county of Surrey
Montego Bay is the second largest anglophone city in the Caribbean, after Kingston
Port Royal was a city located at the mouth of the Kingston Harbour. Founded in 1588, it was the centre of shipping commerce in the Caribbean Sea during the latter half of the 17th century. It was destroyed by an earthquake in 1692 and subsequent fires, hurricanes, flooding, epidemics and a final earthquake in 1907
Blue Mountain Peak is the home of Blue Mountain coffee
Saint Kitts and Nevis
| Capital | Basseterre |
| Largest cities | Basseterre |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Liamuiga |
Saint Kitts and Nevis specifically became the first ever British colony in the West Indies in 1624, and then became the first ever French colony in the Caribbean in 1625, when both nations decided to partition the island
St Kitts was named by Christopher Columbus after St Christopher. Kit was a common nickname for Christopher
The Narrows separates St Kitts from Nevis
Charlestown is the capital of Nevis
St Kitts and Nevis is the smallest sovereign state in the Western Hemisphere, in both area and population
Saint Lucia
| Capital | Castries |
| Largest cities | Castries, Soufriere |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar |
| Highest point | Mount Gimie |
Saint Lucia was named after Saint Lucy of Syracuse by the French, and is the only country named after an actual female historical figure
The Pitons, Gros Piton and Petit Piton, are two giant volcanic plugs located south of Soufriere and are a World Heritage Site
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
The current flag of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was adopted in 1985. A breadfruit leaf was replaced by three diamonds forming the letter “V”
| Capital | Kingstown |
| Largest cities | Kingstown |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar |
| Highest point | La Soufriere |
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines consists of the main island of Saint Vincent and the northern two-thirds of the Grenadines
Bequia is the second-largest island of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Christopher Columbus, the first European to discover the island, named it after St. Vincent of Saragossa
La Soufriere is an active volcano on the island of Saint Vincent. Many volcanoes in the Caribbean are named Soufriere (French: ‘sulphur outlet’). These include Soufriere Hills on Montserrat and La Grande Soufriere on Guadeloupe. The latest eruptive activity began in December 2020, with a series of explosive events beginning in April 2021
Mustique is a small private island in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Trinidad and Tobago
| Capital | Port of Spain |
| Largest cities | Chaguanas, San Fernando, Port of Spain |
| Currency | Dollar |
| Highest point | El Cerro del Aripo |
Trinidad and Tobago is the southernmost island in the Caribbean and lies just 11 km off the northeastern coast of Venezuela
Pitch Lake is a lake of natural asphalt located at La Brea in Trinidad. It was discovered by Sir Walter Raleigh in 1595
Scarborough is the chief town of Tobago
Overseas territories
Anguilla
Anguilla is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean, one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands. The territory's capital is The Valley
Aruba
Aruba is one of the four constituent countries that form the Kingdom of the Netherlands, along with the Netherlands, Curacao and Sint Maarten. Aruba’s capital is Oranjestad
Bonaire
Bonaire is one of the ABC islands, along with Aruba and Curacao. Bonaire's capital is Kralendijk
British Virgin Islands
British Virgin Islands is a British overseas territory located to the east of Puerto Rico. Consists of the main islands of Tortola, Virgin Gorda, Anegada, and Jost Van Dyke, along with over fifty other smaller islands and cays. About 15 of the islands are inhabited. The capital, Road Town, is situated on Tortola, the largest island
Necker Island is in the British Virgin Islands, and is owned by Richard Branson
Cayman Islands
Cayman Islands comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Little Cayman and Cayman Brac
Cayman Islands are named after a reptile
George Town is the capital of the Cayman Islands, and was named after George III
One of Grand Cayman's main attractions is Seven Mile Beach
Curacao
Curacao is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Willemstad is the capital of Curacao
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an overseas department and region of France
Basse-Terre and Grande-Terre are the two main islands, and are separated by a narrow sea channel called Salt River
Pointe-a-pitre is the largest city in Guadeloupe
The capital city is Basse-Terre
Martinique
Martinique is a single territorial collectivity of the French Republic. It is also part of the European Union as an Outermost Region
In Martinique there is a statue of the Empress Josephine, who was born in Martinique, holding a locket with a portrait of Napoleon
In 1902, Mont Pelee erupted and completely destroyed St. Pierre, killing 30,000 people
The capital city is Fort-de-France
Montserrat
Montserrat is a British Overseas Territory
Christopher Columbus gave Montserrat its name on his second voyage to the New World in 1493, after Montserrat mountain located in Catalonia. Montserrat is nicknamed the ‘Emerald Isle of the Caribbean’
In 1995, the previously dormant Soufriere Hills volcano became active. Eruptions destroyed Montserrat's Georgian era capital city of Plymouth and two-thirds of the island's population was forced to flee. Interim government buildings have since been built at Brades, becoming the political capital in 1998
Little Bay is a port town under construction which is intended to be the future capital
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico is located in the northeastern Caribbean Sea, east of the Dominican Republic and west of the Virgin Islands
Puerto Rico is an incorporated territory of the United States
San Juan is the capital and largest city
In a referendum in 2020, 52% voted that Puerto Rico should be admitted immediately into the Union as a State
Saba
Saba is the smallest special municipality of the Netherlands
The capital of Saba is The Bottom
Mount Scenery on the island of Saba, now considered an integral part of the Netherlands following the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, is the highest point of the entire Kingdom of the Netherlands at 887 m
Saint Barthelemy
Saint Barthelemy is a French overseas collectivity. Until 2003 Saint Barthelemy was a French commune forming part of Guadeloupe
Gustavia is the main town and capital. Named in honour of King Gustav III of Sweden
Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius is a special municipality of the Netherlands in the northern Leeward Islands. The capital is Oranjestad
Caribbean Netherlands consists of the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba, known as the BES islands
Turks and Caicos Islands
Turks and Caicos Islands is a British Overseas Territory consisting of two groups of islands southeast of the Bahamas. The capital is Cockburn Town
United States Virgin Islands
United States Virgin Islands are an unincorporated and organized territory of the United States
Named by Christopher Columbus on his second voyage in 1493 for Saint Ursula and her virgin followers. The main islands are Saint Croix, Saint John, and Saint Thomas. Formerly the Danish West Indies, they were sold to the United States by Denmark in 1916
Charlotte Amalie, located on Saint Thomas, is the capital and largest city
Bermuda
Bermuda is Britain's second oldest remaining British Overseas Territory. It lies 1,000 km southeast of North Carolina, 1,700 km northeast of Cuba and 1,500 kn north of the British Virgin Islands
Capital – Hamilton
Largest city – St Georges
Bermuda is an archipelago consisting of 181 islands
Bermuda is divided into nine parishes
Somers Isles was Britain’s oldest colony. Named after Admiral George Somers
St George’s was the first capital of Bermuda
St. George's Island is one of the main islands of the territory of Bermuda
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark. It is the world's largest island, located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans
Capital and largest city – Nuuk
Highest point – Gunnbjorn Fjeld, which is also the highest mountain north of the Arctic circle
Greenland ice sheet is a vast body of ice covering 1,710,000 square kilometres (660,235 sq mi), roughly 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is the second largest ice body in the world, after the Antarctic Ice Sheet
Cape Farewell is the southernmost point of Greenland
Ilulissat Icefjord is a fjord in western Greenland. At its eastern end is the Jakobshavn Isbrae glacier, the most productive glacier in the Northern Hemisphere. Larger icebergs typically do not melt until they reach 40 – 45 degrees north
Petermann glacier connects the Greenland ice sheet to the Arctic Ocean
Scoresby Sound is a large fjord system of the Greenland Sea on the eastern coast of Greenland
Northeast Greenland National Park is the world's largest national park
Kaffeklubben Island is an uninhabited island off the northern tip of Greenland. It contains the most northerly point of land on Earth
King Christian IX Land and King Frederick VIII Land are geographical areas of Greenland
Hispaniola
Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the region's second largest in area, after the island of Cuba
The island is divided into Dominican Republic to the east and Haiti to the west
Saint Martin
Saint Martin is shared between France (Saint Martin) and the Netherlands (Sint Maarten). it is the smallest inhabited sea island divided between two nations
Princess Juliana International Airport is the main airport on Sint Maarten. The airport has very low-altitude flyover landing approaches, owing to one end of its runway being extremely close to the shore and Maho Beach
Physical Geography
Regions
The Canadian Shield, also called the Precambrian Shield, Laurentian Shield, or Laurentian Plateau, is a large thin-soiled area over a part of the North American craton (a deep, common, joined bedrock region) in eastern and central Canada and adjacent portions of the US, composed of base rock dating to the Precambrian Era
Continental Divide (or Great Divide) of the Americas is the name given to the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas that separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from, 1) those river systems which drain into the Atlantic Ocean and 2) those river systems which drain into the Arctic Ocean
Mountains
Highest mountains in North America – McKinley, Logan, Pico de Orizaba
Rocky Mountains stretch more than 3,000 miles from the northernmost part of British Columbia to New Mexico. Within the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the Pacific Coast Ranges and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada which all lie further to the west. The highest point is Mount Elbert in Colorado
Appalachian Mountains extend over 2,000 miles from Newfoundland and Labrador to Alabama. The highest point is Mount Mitchell, in North Carolina
Appalachian Trail extends between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine. It is approximately 2,181 miles long
Mount Saint Elias is the second highest mountain in both Canada and the United States, being situated on the Yukon and Alaska border
Maya Mountains are located in Belize and eastern Guatemala
American Cordillera is a chain of mountain ranges (cordilleras) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western ‘backbone’ of the Americas. Aconcagua is the highest peak of the chain. It is also the backbone of the volcanic arc that forms the eastern half of the Pacific Ring of Fire
Deserts
Sonoran Desert covers large parts of the southwestern United States (in Arizona and California), as well as the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur
Chihuahuan Desert covers parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States
Rivers
Longest rivers of the United States – Missouri, Mississippi, Yukon, Rio Grande
St. Lawrence River flows from Lake Ontario into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean and forming the primary drainage outflow of the Great Lakes Basin. The river traverses the provinces of Ontario and Quebec as well as the U.S. state of New York, and is part of the international boundary between Canada and the United States. It also provides the basis for the commercial St. Lawrence Seaway
Thousand Islands constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario
Thousand Island dressing is named after the Thousand Islands region
Just Room Enough Island is located in the Thousand Islands chain, belonging to New York. The island is known for being the smallest inhabited island
Seas
Beaufort Sea is in Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska
Lincoln Sea is a body of water in the Arctic Ocean, stretching from Cape Columbia, Canada, in the west to Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland
Greenland Sea borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean. Molloy Deep, within the Greenland Sea, is the deepest point of the Arctic Ocean
Lomonosov Ridge is an underwater ridge of continental crust in the Arctic Ocean. It spans 1800 km from the New Siberian Islands over the central part of the ocean to Ellesmere Island of the Canadian Arctic islands. Named in honour of Russian scientist and polymath Mikhail Lomonosov
Salish Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington. It includes the Strait of Georgia, Strait of Juan de Fuca, and Puget Sound
Strait of Juan de Fuca forms the principal outlet for the Georgia Strait and Puget Sound, connecting both to the Pacific Ocean. It provides part of the international boundary between the United States and Canada
San Juan Islands are an archipelago between the state of Washington and Vancouver Island
Sargasso Sea is an elongated region in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by ocean currents. On the west it is bounded by the Gulf Stream; on the north, by the North Atlantic Current; on the east, by the Canary Current; and on the south, by the North Atlantic Equatorial Current
Gulf of Paria is an inland sea located between Trinidad and Venezuela. In the north, the Gulf is connected to the Caribbean Sea through the Dragons' Mouths. In the south, the Gulf is connected to the Atlantic through the Columbus Channel, also known as the Serpent's Mouth
Gulf of Fonseca is in the Pacific Ocean and borders El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua
Mona Passage separates the islands of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico
Yucatan Channel separates Mexico from Cuba
Puerto Rico trench has a maximum depth of 8648 metres at Milwaukee Deep, which is the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean and the deepest point not in the Pacific Ocean
Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, also known as the Great Mayan Reef, is a marine region that stretches over 1000 km from the tip of the Yucatan Peninsula down to Belize, Guatemala and Honduras